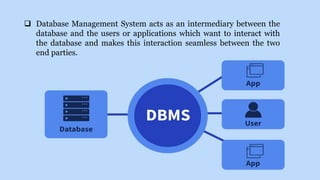
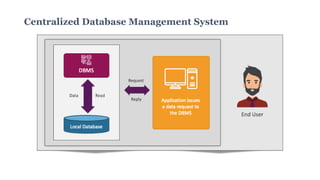
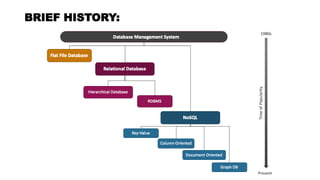
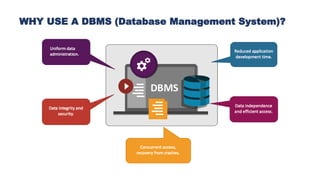
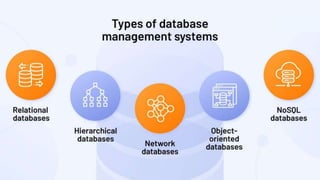
A database management system (DBMS) is middleware that allows users to store, organize, access, and manipulate data in a database. A DBMS consists of a collection of interrelated data and a set of application programs to manage that data. It acts as an intermediary between the database and users or applications. Common DBMS types include hierarchical, relational, graph, and object-oriented relational. Features of DBMS include reducing data redundancy, allowing multi-user access, efficient data storage and retrieval, and high data security. Components include hardware, software, data, procedures, and database access languages like DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL.