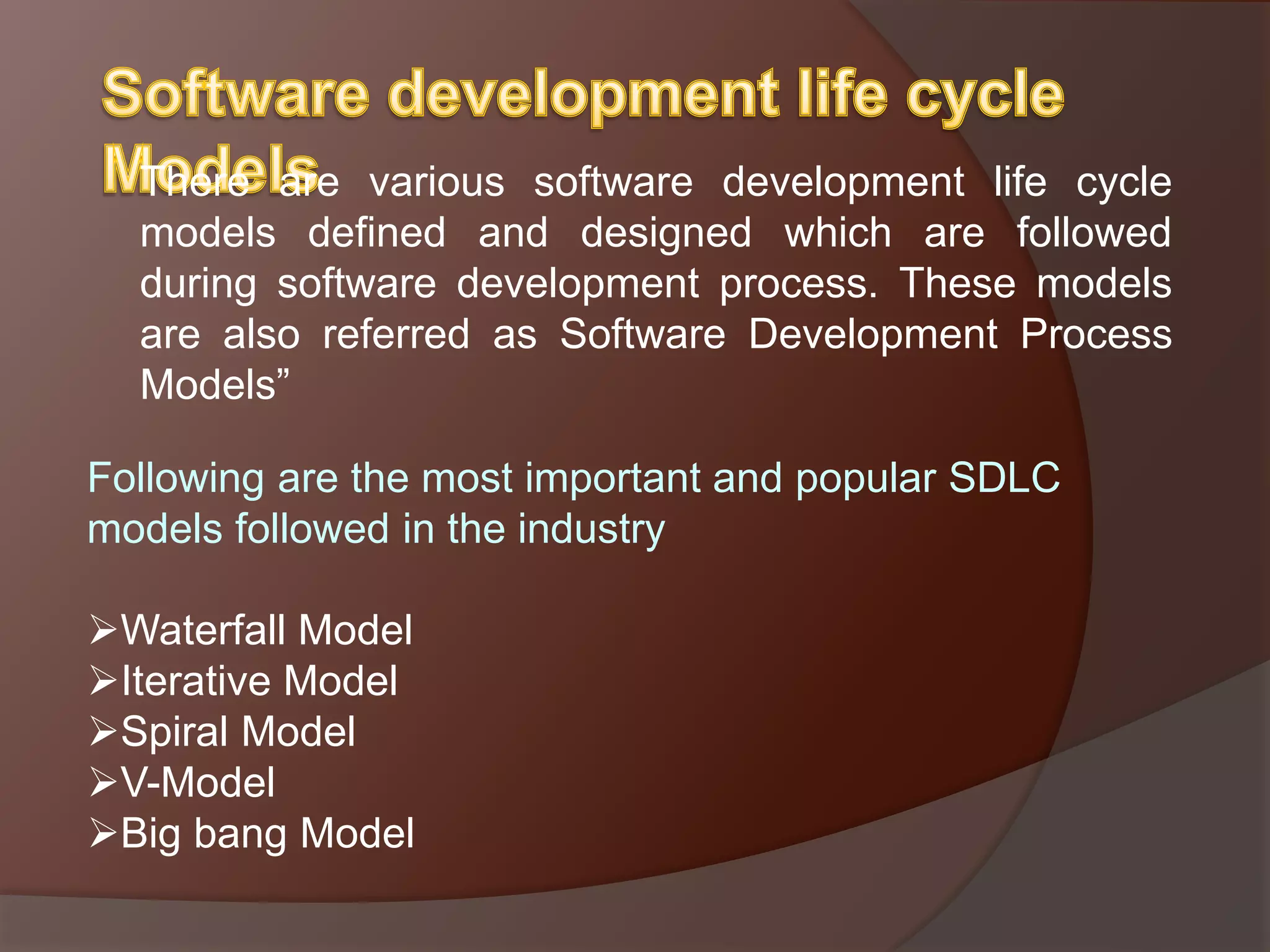
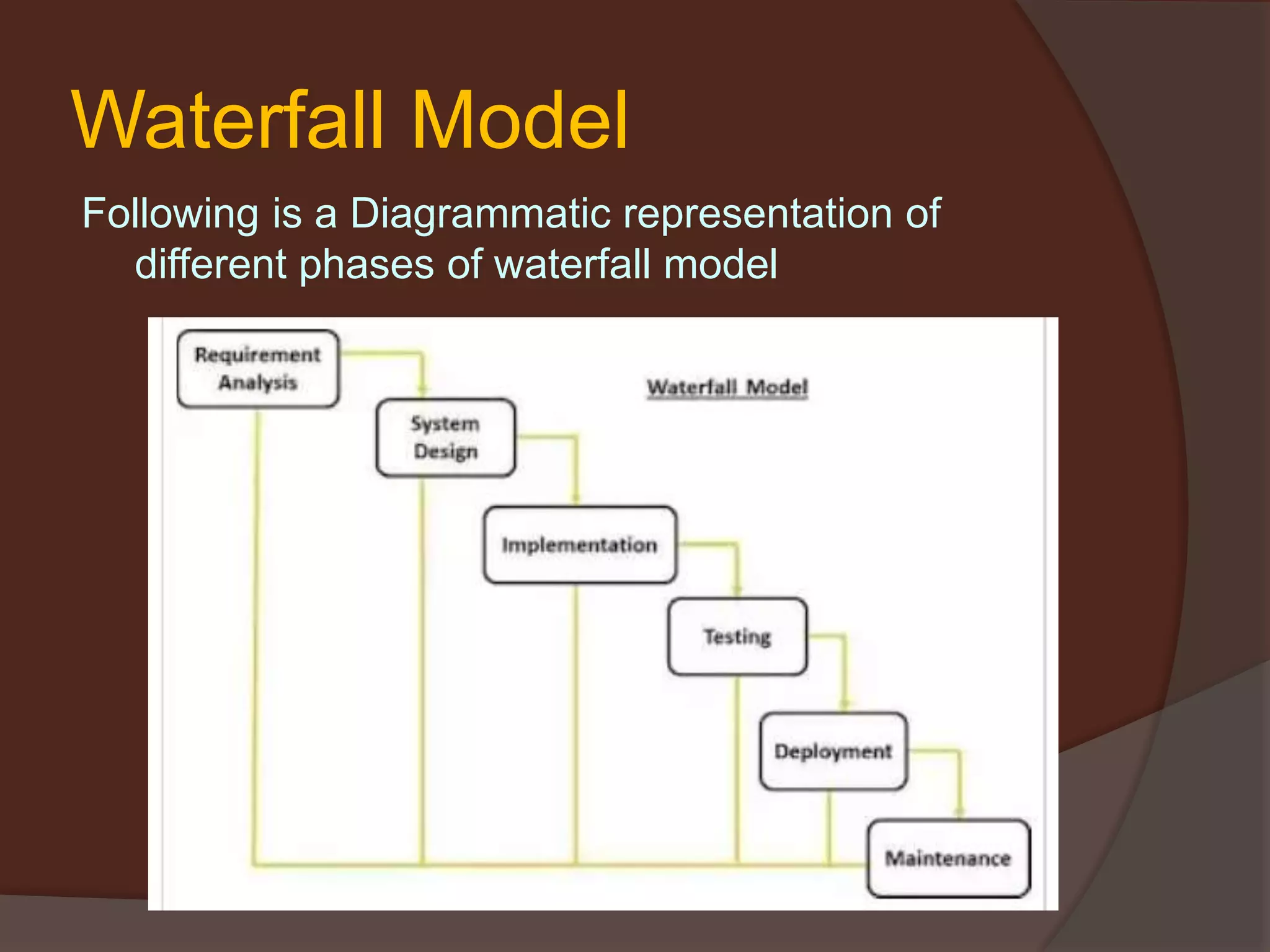
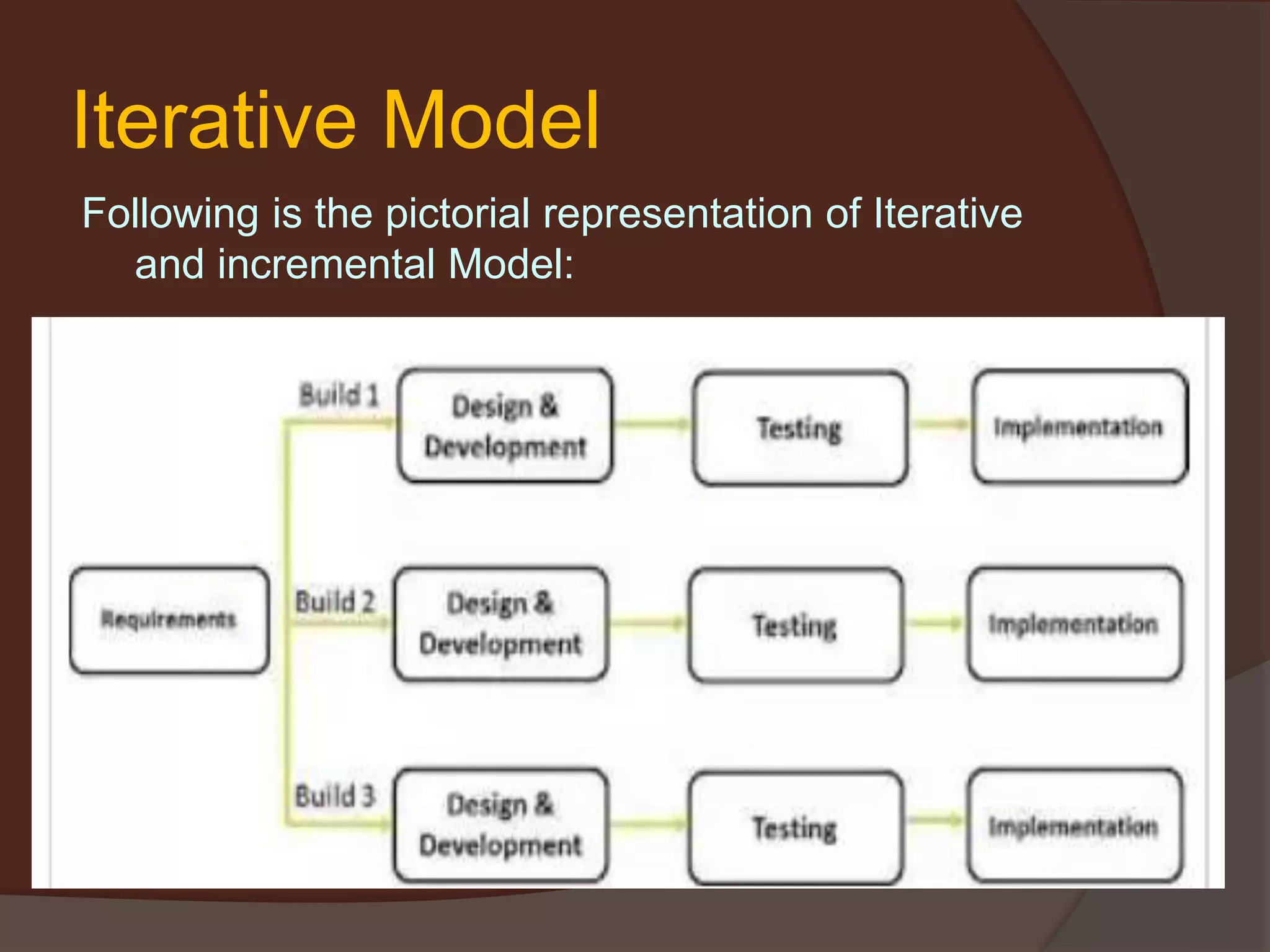
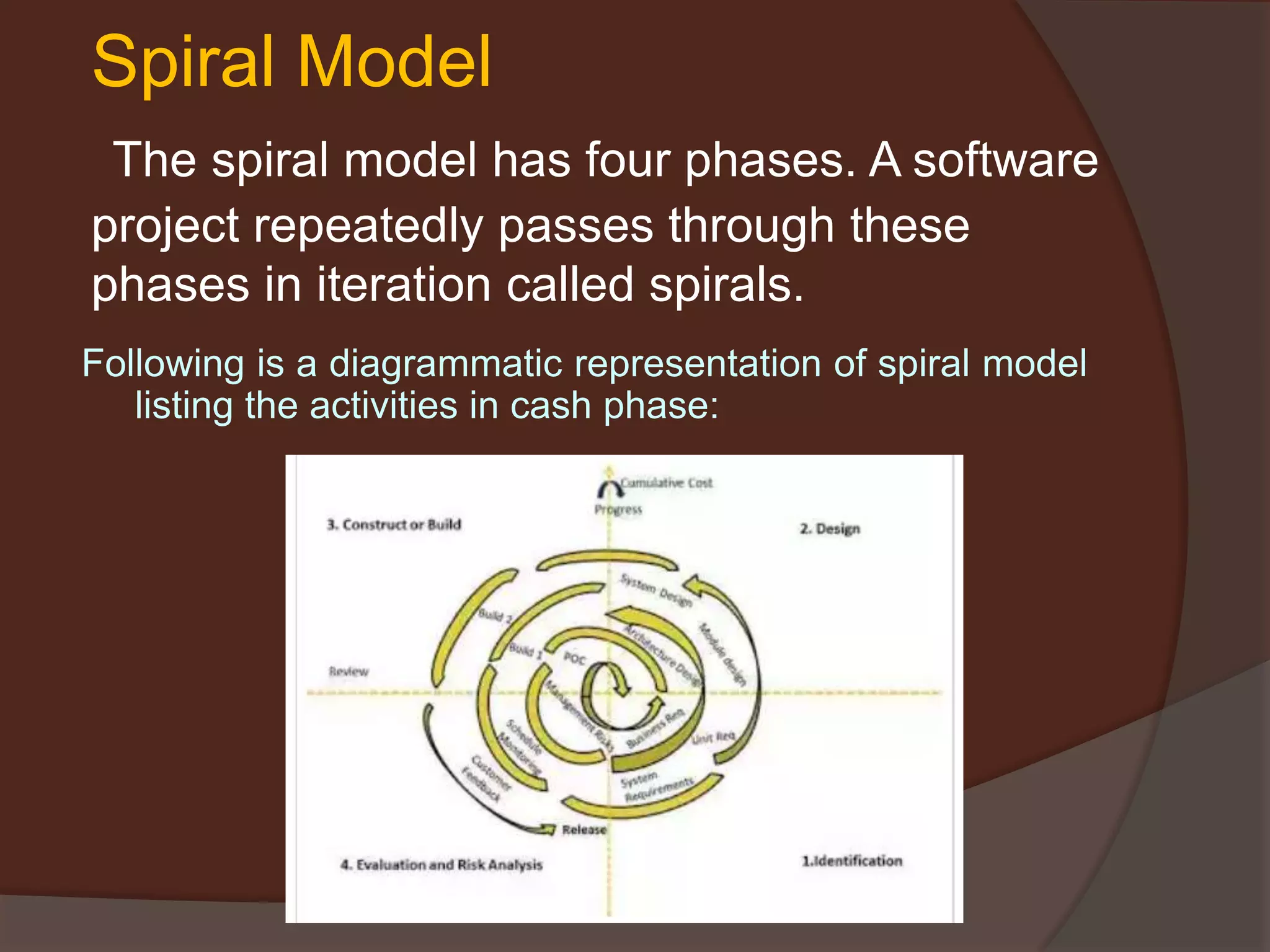
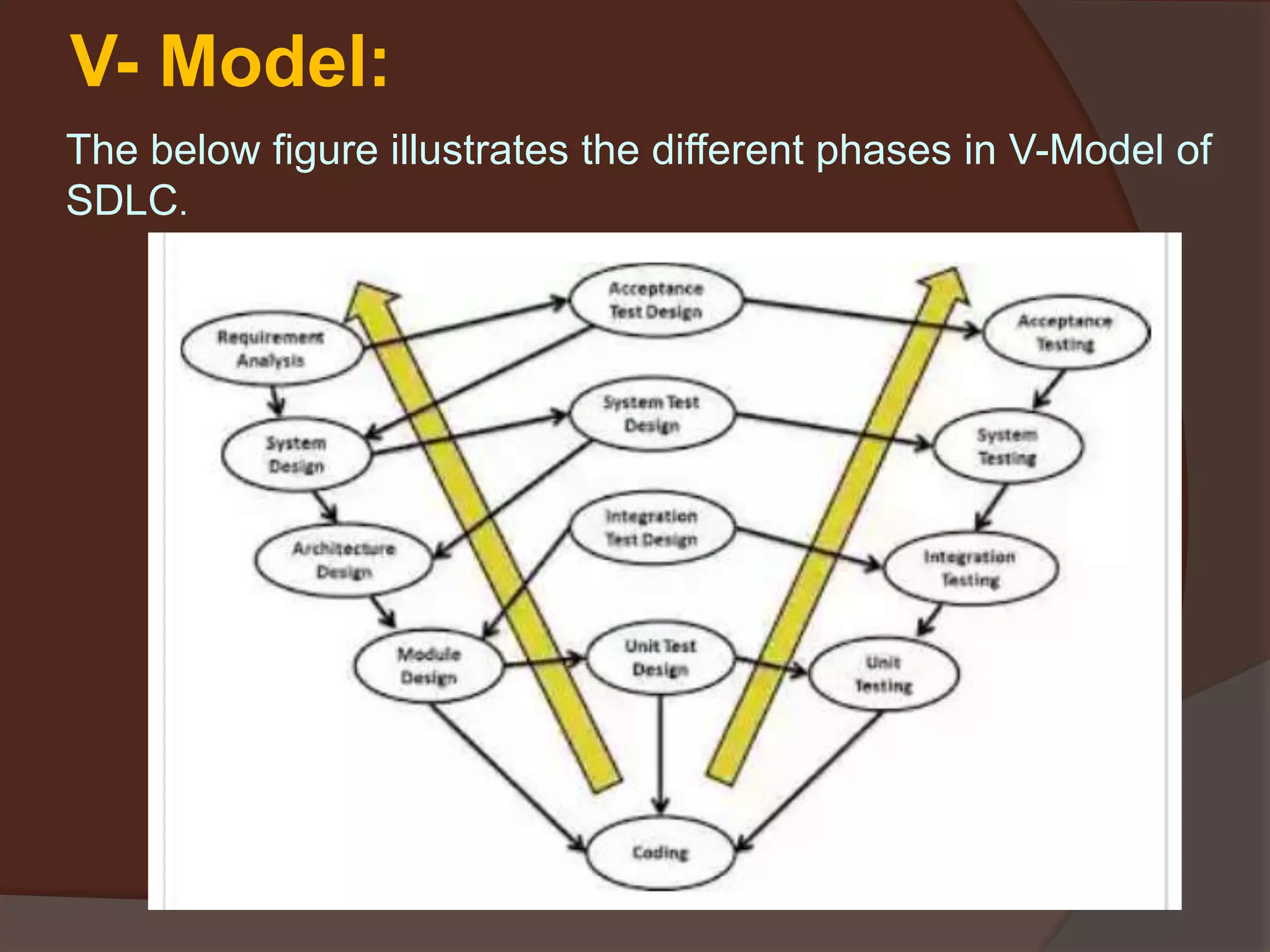
The document discusses the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) which is a process used by the software industry to design, develop, and test high-quality software. It describes several SDLC models including waterfall, iterative, spiral, V-model, and big bang. The different models are used depending on factors like requirements clarity, time and budget constraints, and technology maturity.