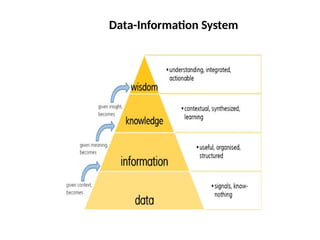
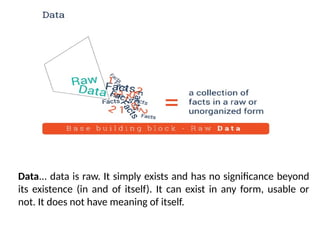
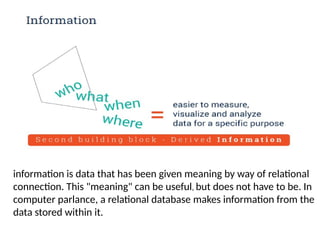
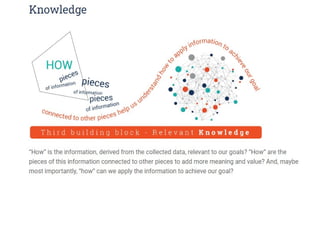
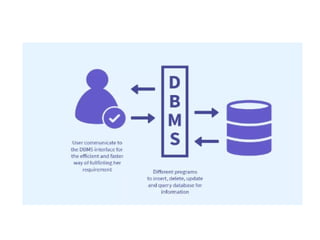
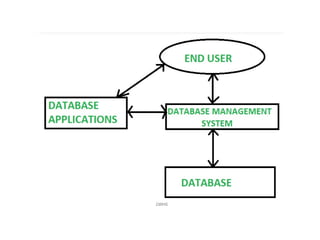
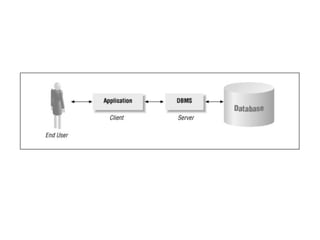
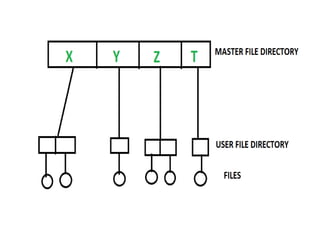
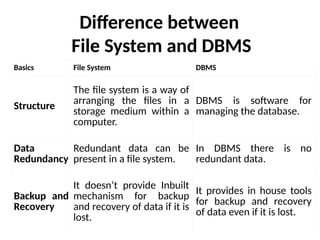
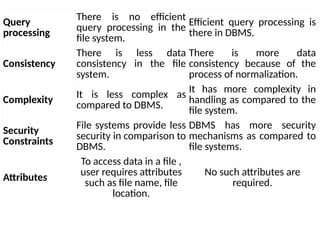
The document outlines fundamental concepts of data and databases, distinguishing between raw data, which lacks significance, and information, which is data with meaning. It covers different types of databases, including relational, NoSQL, cloud, object-oriented, and key-value databases, each serving unique organizational needs. The text also discusses database management systems (DBMS), their functionalities, and compares file systems with DBMS in terms of data handling, redundancy, security, and efficiency.