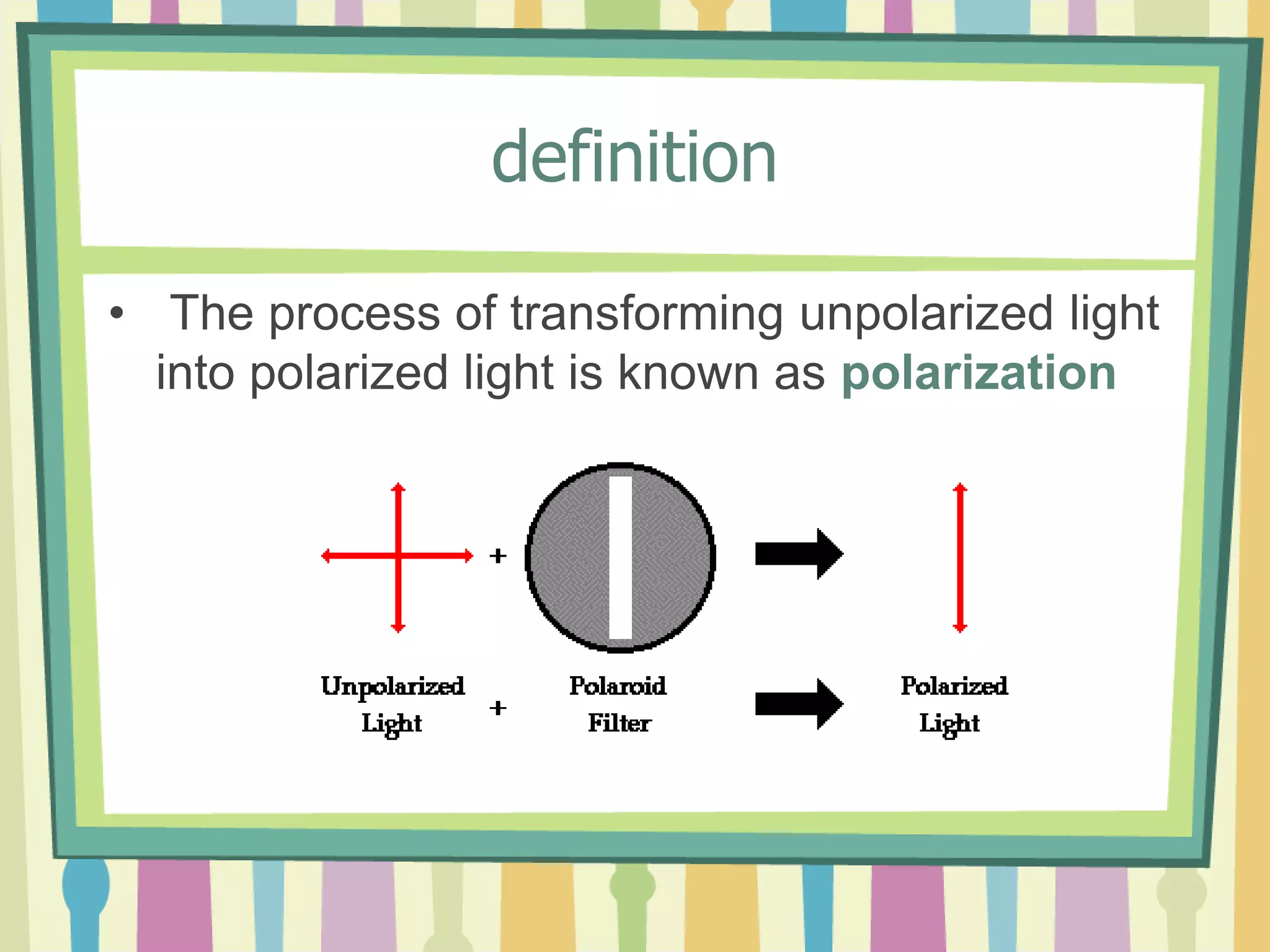
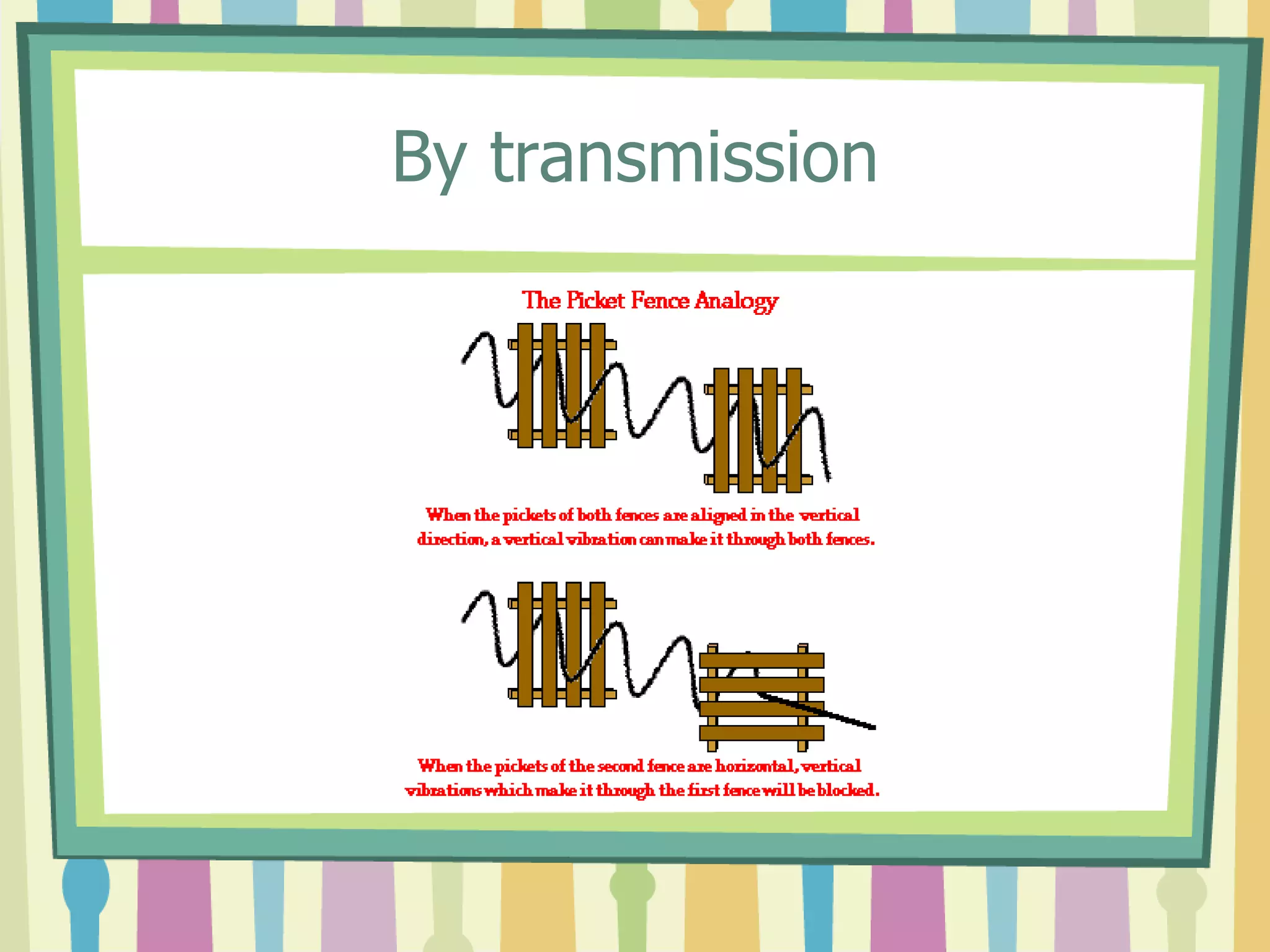
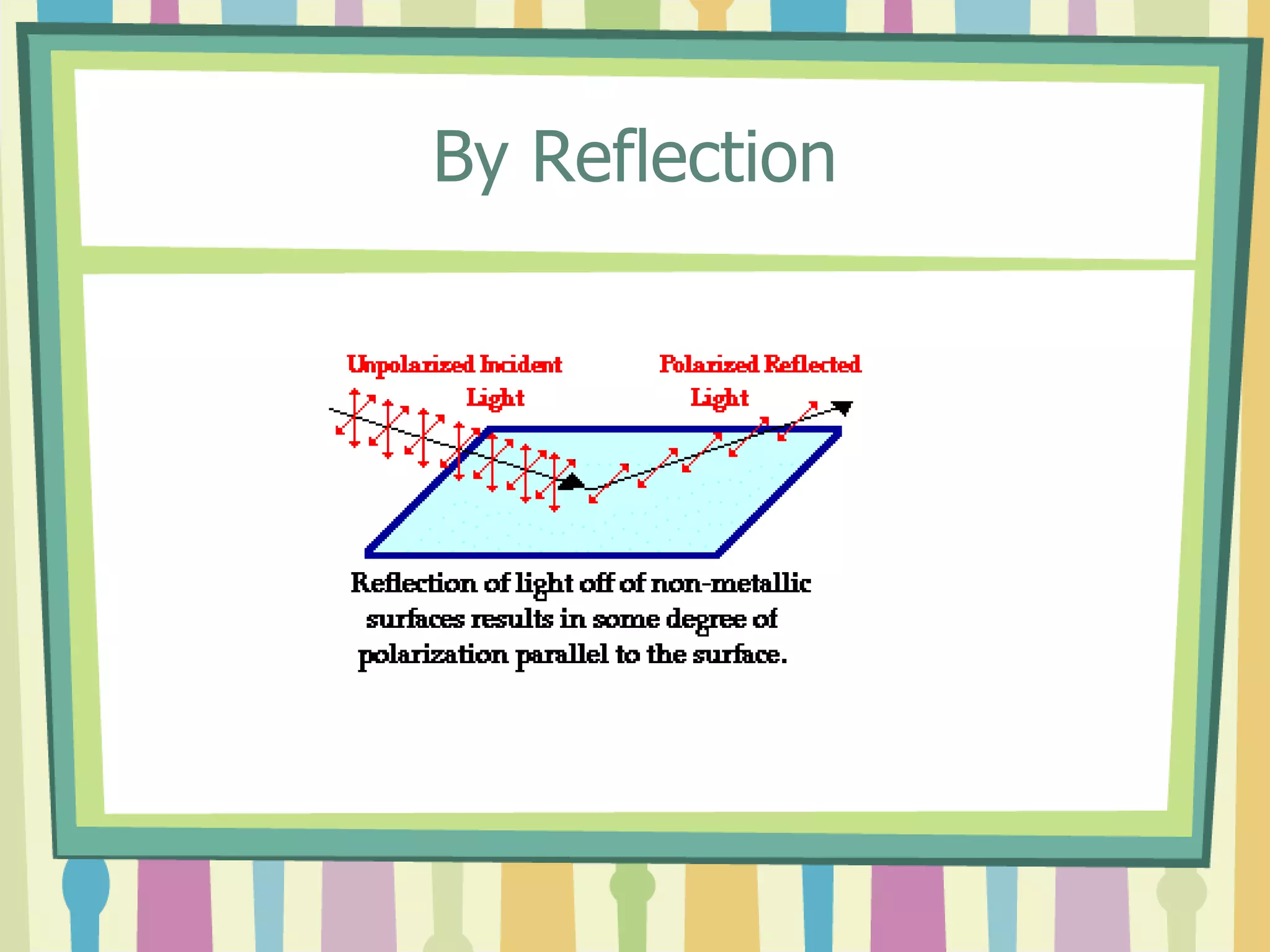
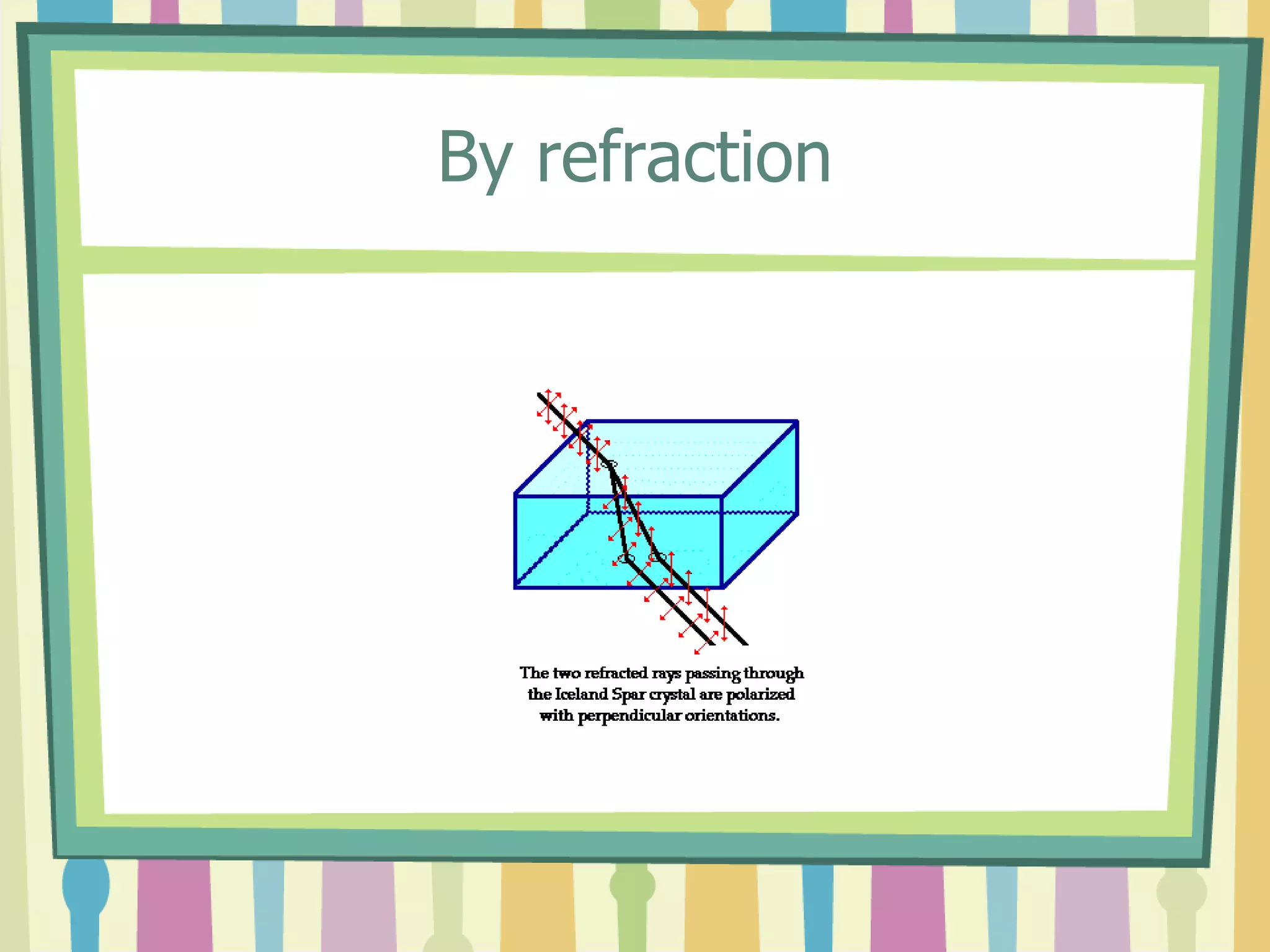
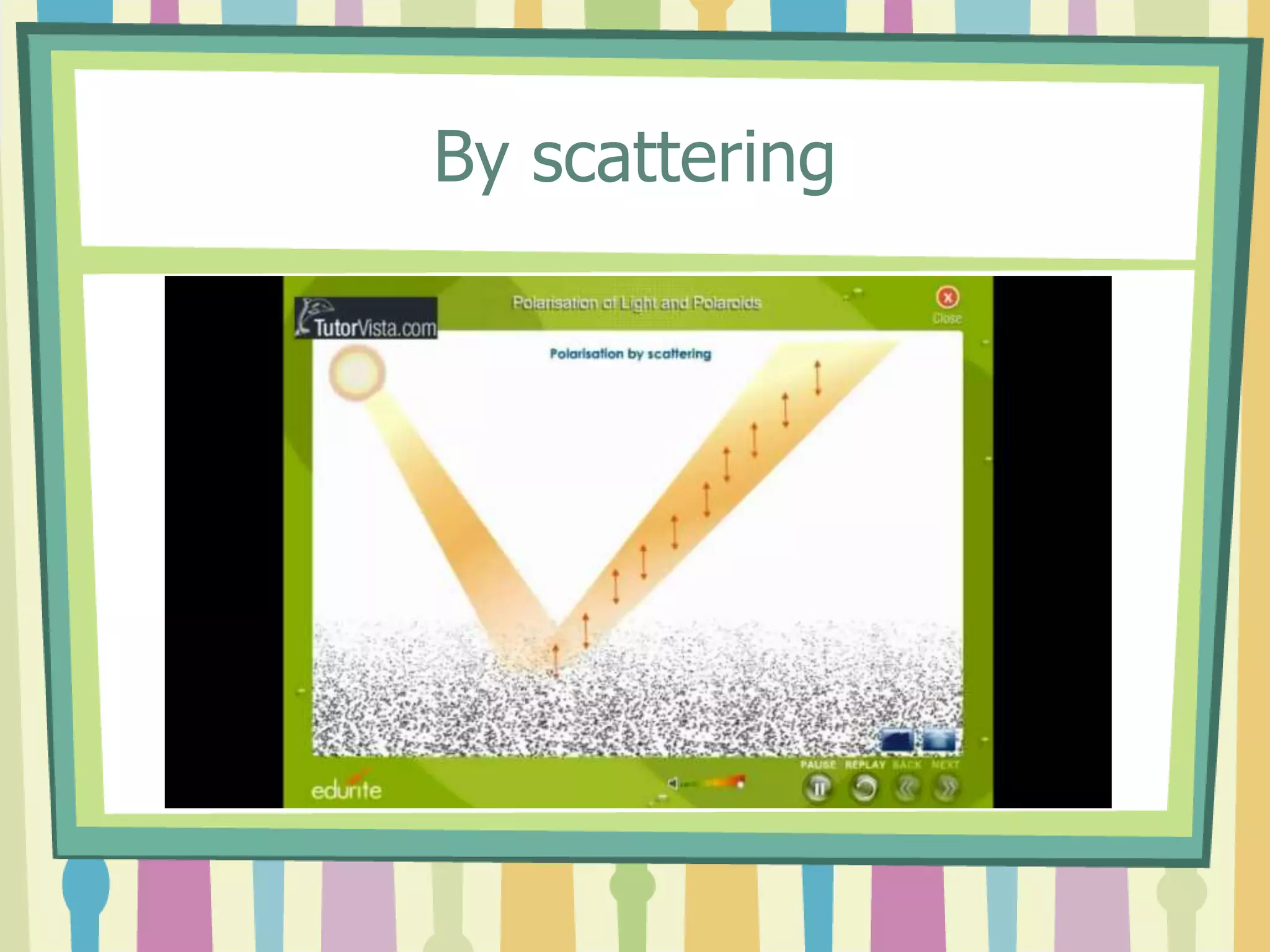
Polarization is the process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light. Light can be polarized through transmission, reflection, refraction, or scattering. Polarized light has many applications including reducing glare in sunglasses, performing stress analysis in engineering, and enabling 3D viewing through special glasses. Polarizers are also used to determine properties like the size and shape of viruses and in various industrial applications.