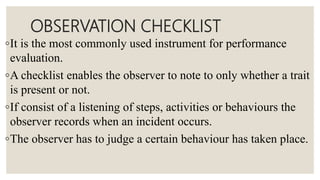
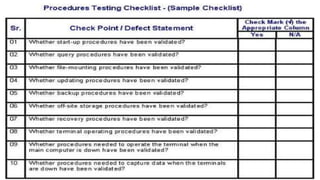
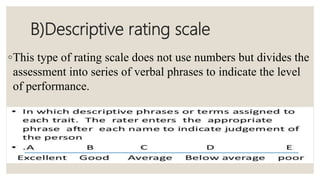
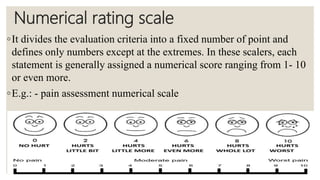
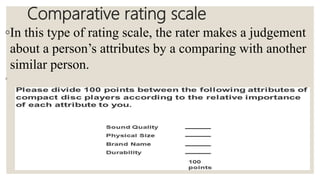
The document discusses checklists and rating scales used for performance evaluation. It defines checklists as lists that check for the presence or absence of traits, and rating scales as tools that assess levels of performance. Checklists are useful for objective evaluations but only assess limited aspects, while rating scales provide flexibility in judging performance qualitatively through descriptive or numerical scales. Both tools have advantages like structure and adaptability, but also limitations such as subjectivity.















![◦ GUIFORD [1954] CHARACTERISTICS.
◦ Clarity: it must be constructed using short, concise statements in simple and
unambiguous language.
◦ Relevance: the statement should be relevant to the phenomenon and should be
exactly in accordance with the variables understudy.
◦ Variety: monotony of the statements must be avoided and variety and difference
statements must be ensured.
◦ Objectivity: it must be objective in a nature so that it is convenient for the rater to
judge the attributes or performances of the subjects under study.
◦ Uniqueness: each statement constructed must be unique in itself so that the
attributers can be judged appropriately.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/checklistandratingscale-181211175119/85/Checklist-and-rating-scale-21-320.jpg)



