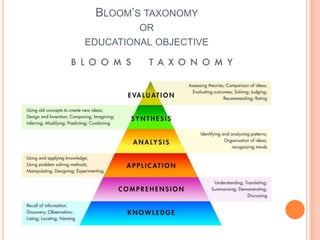
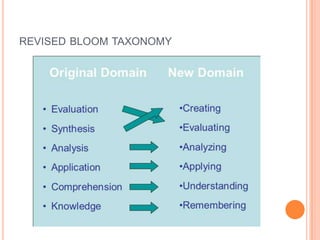
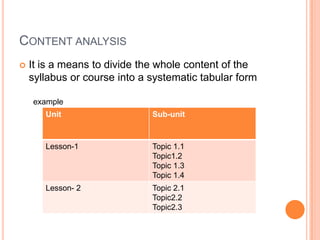
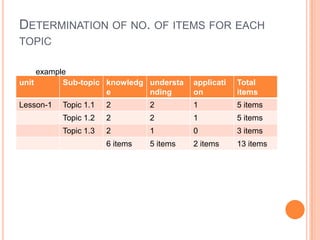
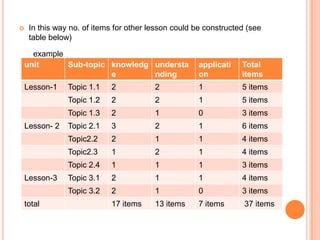
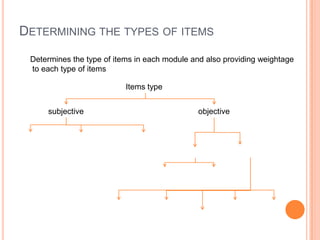
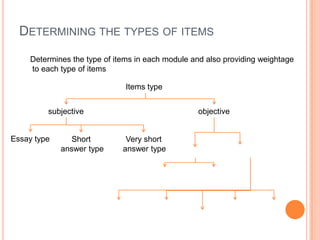
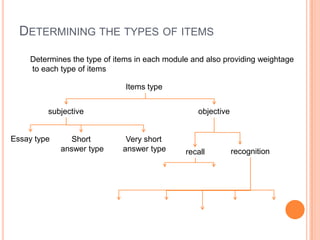
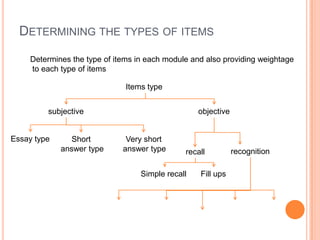
A blueprint provides a detailed guide for developing an assessment. It outlines the key topics to be covered, learning objectives to be assessed, and the number and type of questions to include. The document presented discusses how to create a blueprint by analyzing content, determining learning objectives based on Bloom's taxonomy, allocating questions to each topic based on objectives, and specifying question types and their weightings. Blueprints benefit students, teachers and administrators by ensuring assessments comprehensively and validly measure the intended curriculum.