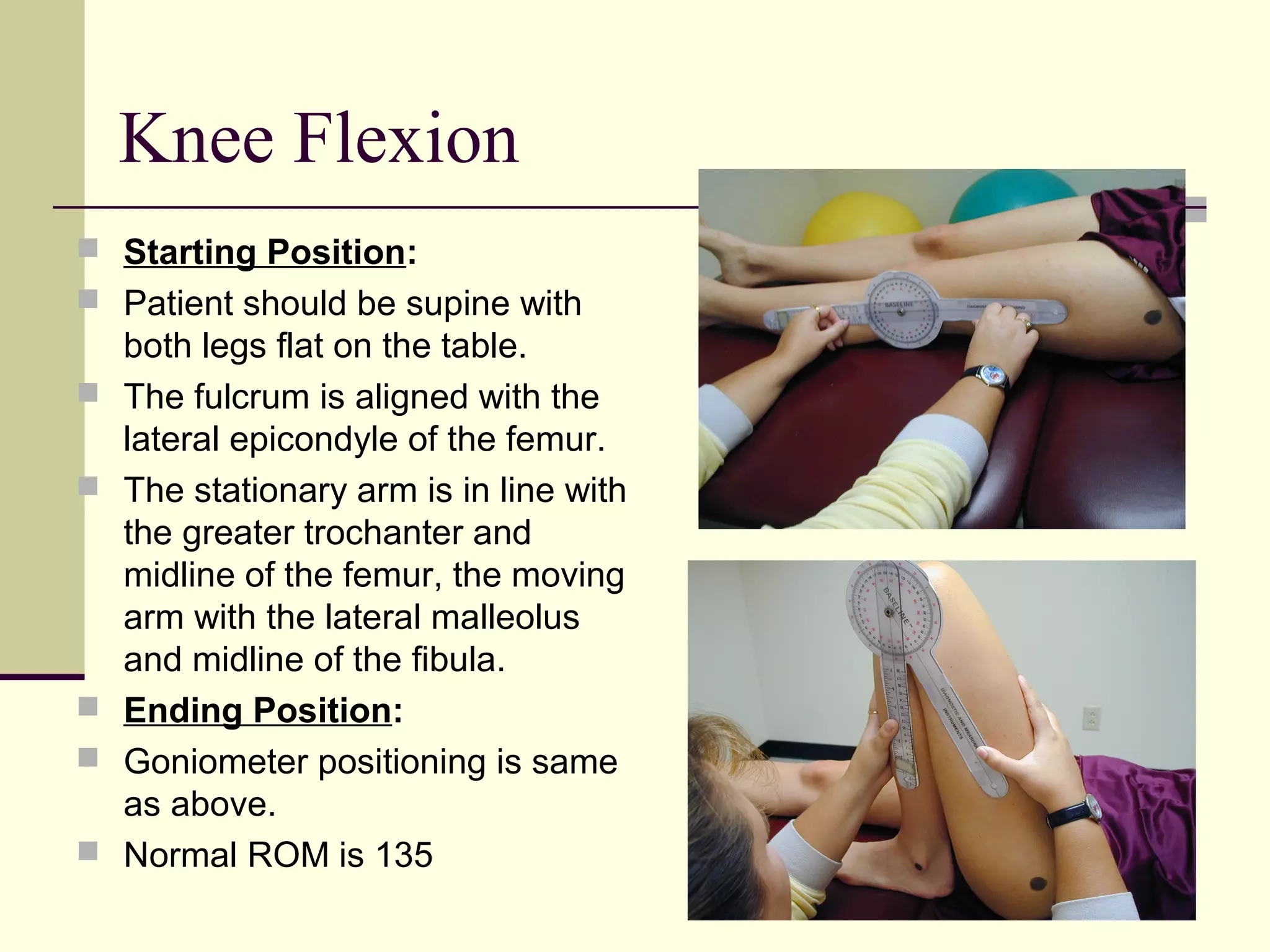
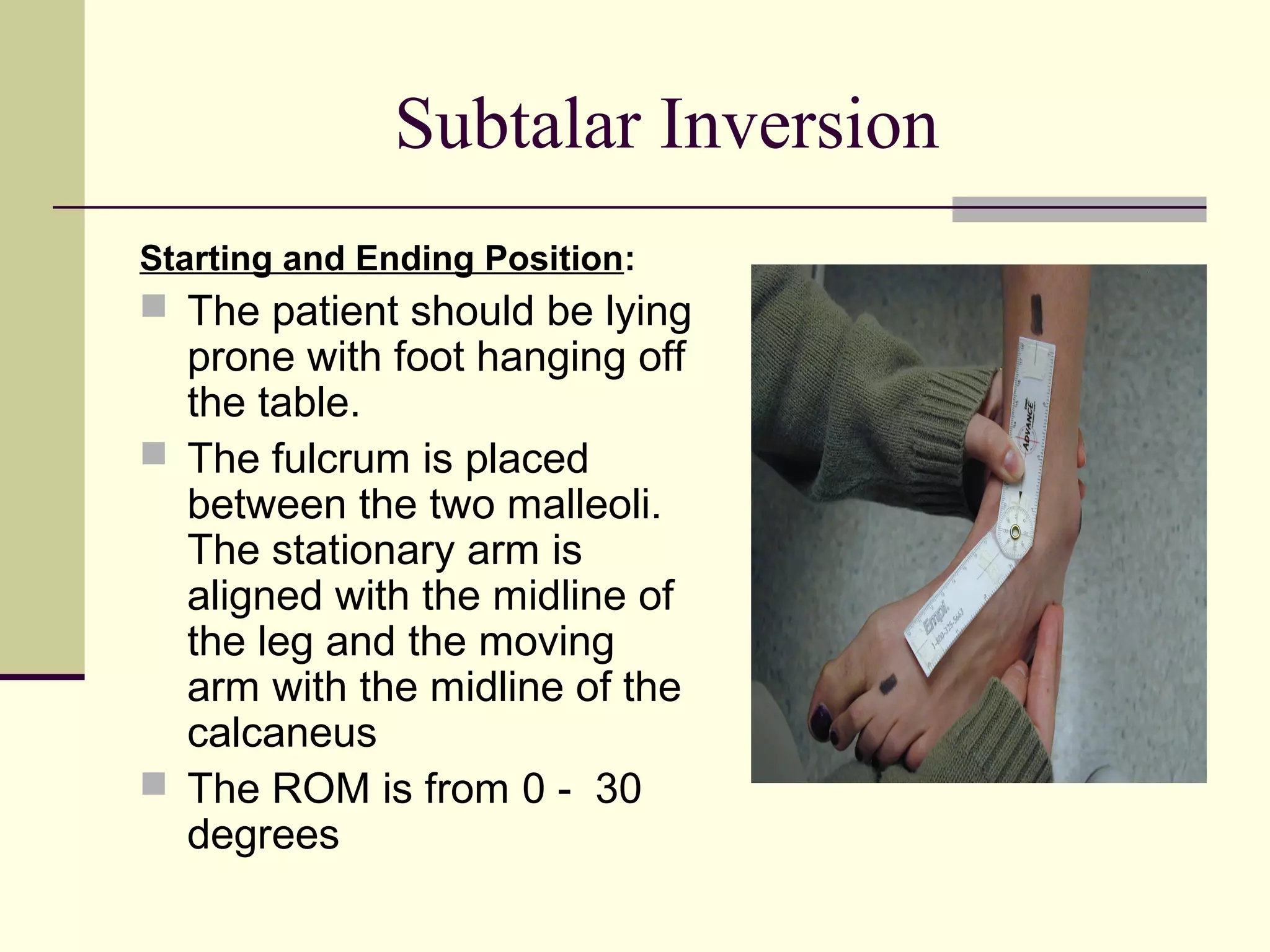
The document describes the procedures for measuring range of motion of the knee, ankle, and subtalar joint using a goniometer, including starting position, ending position, normal range of motion, precautions, and factors that can limit motion. Precautions include preventing unwanted movement at adjacent joints, while factors limiting motion include tension in relevant muscles and ligaments or bone contact. Standard range of motion values are provided for flexion, extension, plantarflexion, dorsiflexion, and inversion/eversion.