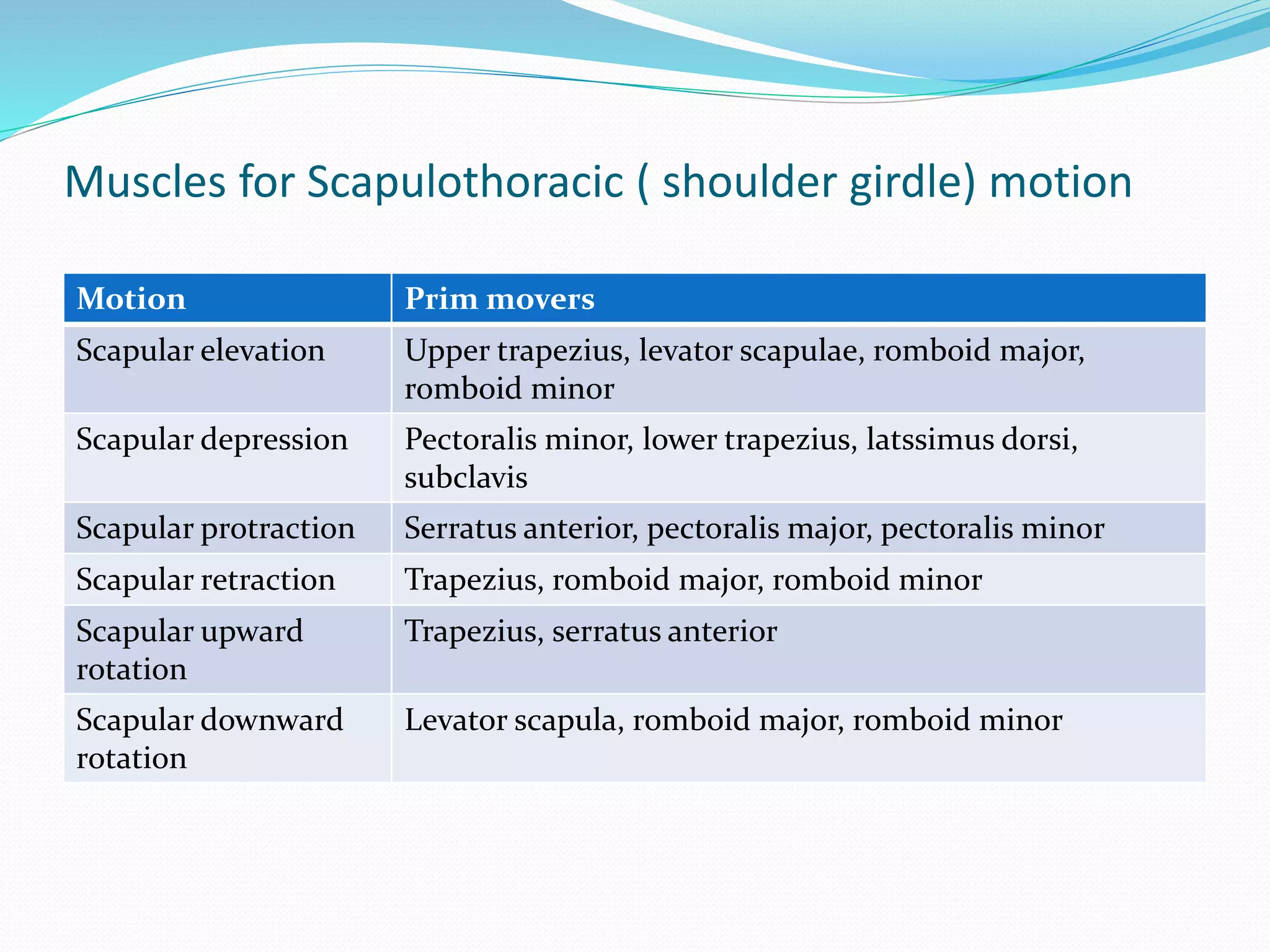
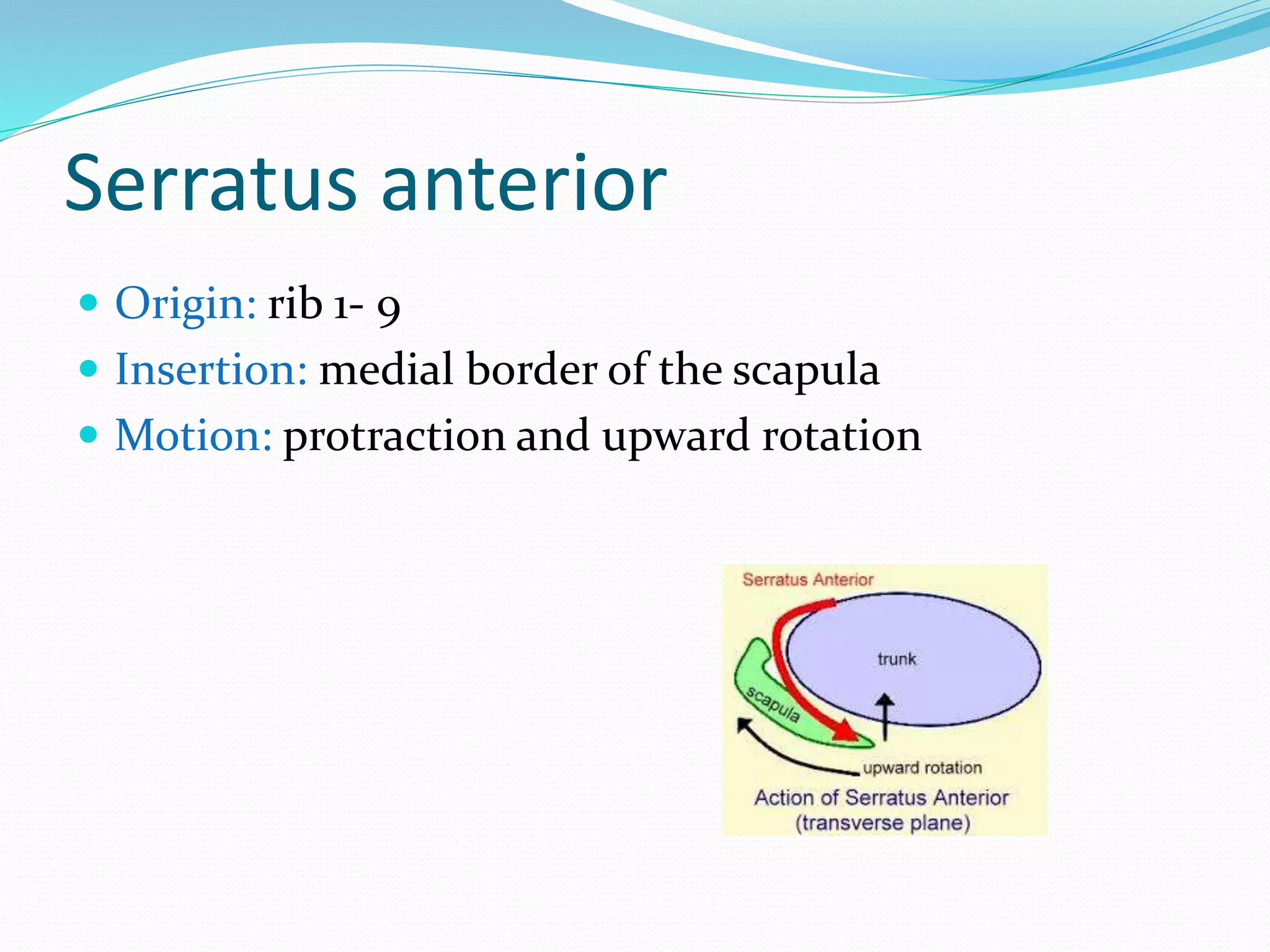
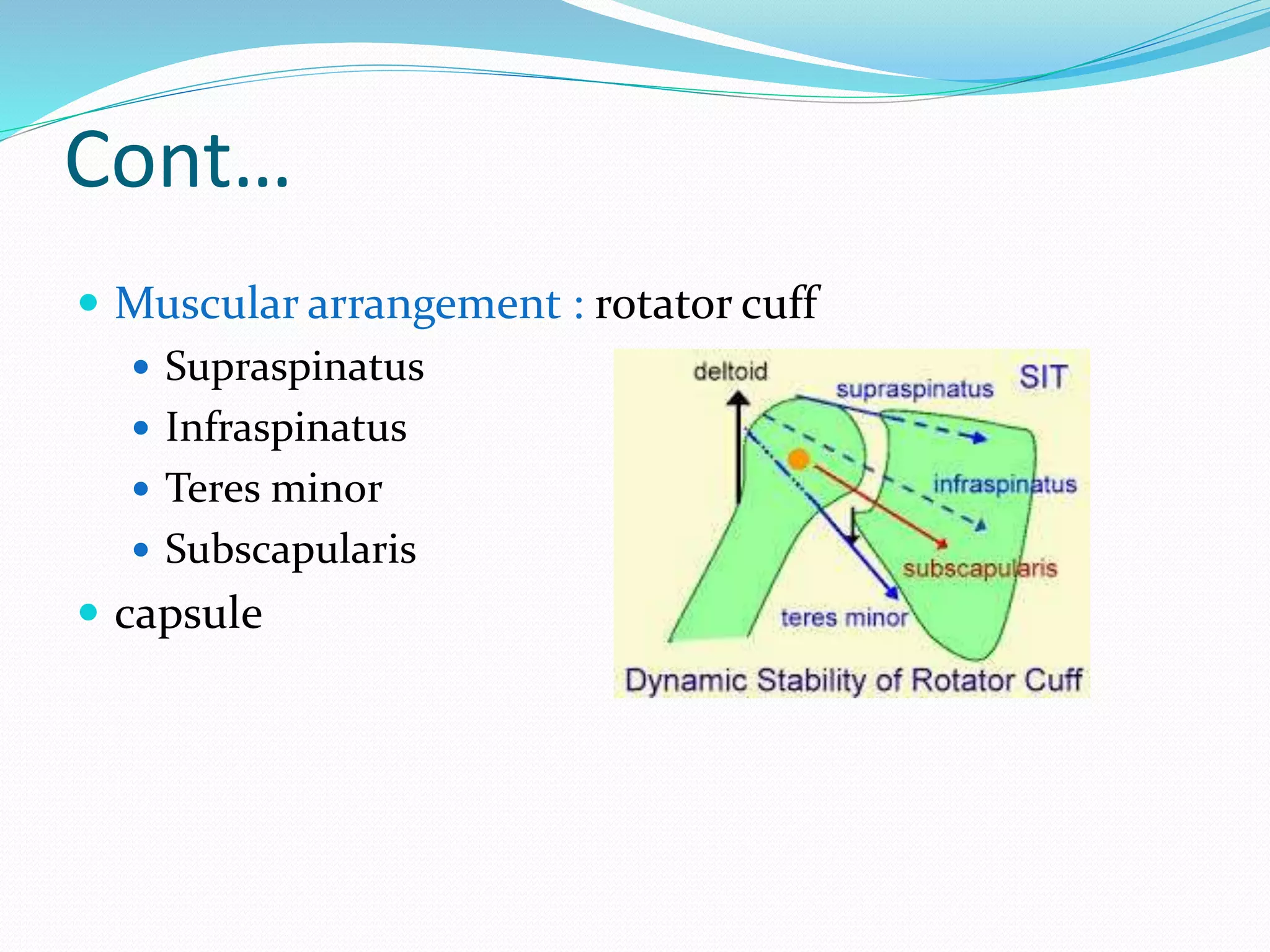
The document provides an overview of the biomechanics of the shoulder complex. It describes the structure including the glenohumeral joint, sternoclavicular joint, acromioclavicular joint, and scapulothoracic articulation. It details the kinematics of the shoulder including motions like flexion, abduction, and rotation. The stability mechanisms are discussed as well as the muscles involved in shoulder motions. Injuries are addressed relating to impingement and ligament laxity.