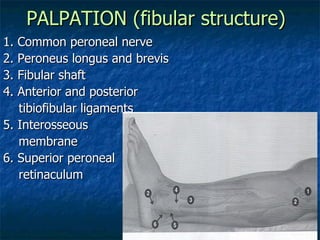
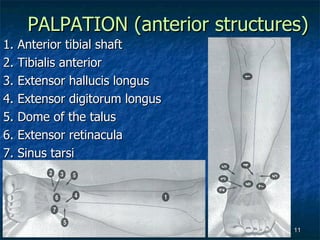
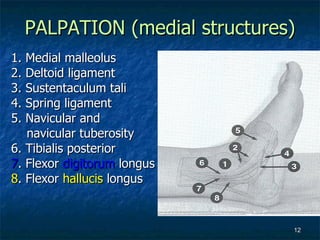
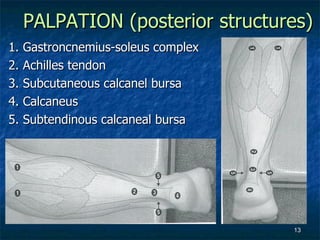
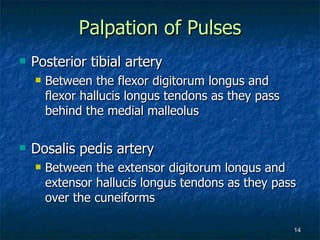
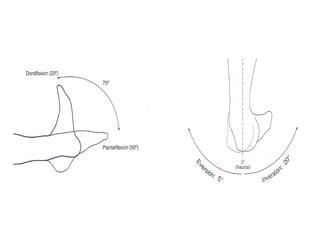
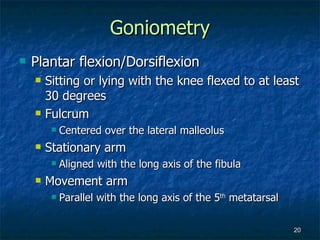
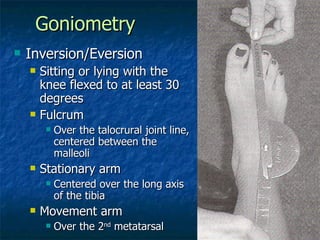
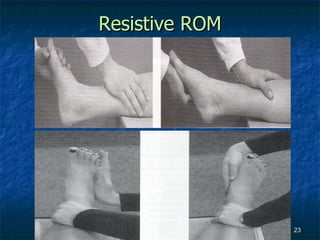
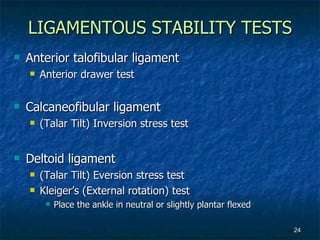
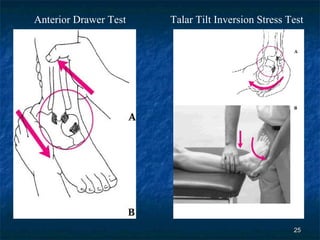
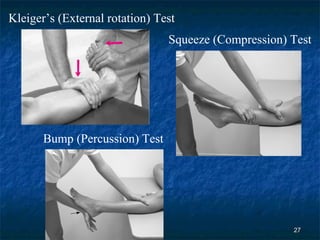
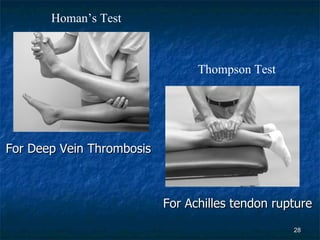
The document provides an overview of procedures for evaluating lower extremity injuries of the ankle and lower leg. It details assessing history, inspecting for signs of injury, performing palpation of anatomical structures, range of motion and ligament stability testing, and evaluating neurologic and vascular function. The evaluation covers the anterior, lateral, medial, and posterior structures of the ankle and lower leg.