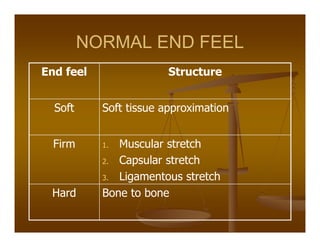
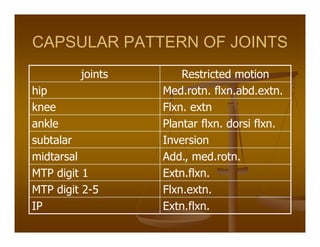
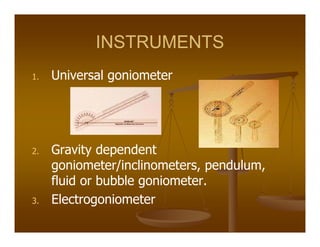
Goniometry refers to the precise measurement of joint angles using instruments such as a universal goniometer. Goniometric data is used to determine impairment, establish diagnoses, develop treatment plans, and evaluate progress. Joint motion includes arthrokinematics (gliding and spinning of joint surfaces) and osteokinematics (bone movements). Range of motion is measured in three planes (sagittal, frontal, transverse) using instruments properly aligned with bony landmarks. Both active and passive range of motion are measured to evaluate joint integrity and flexibility. Restricted or increased range of motion can indicate conditions like capsular patterns of hypomobility or generalized hypermobility.