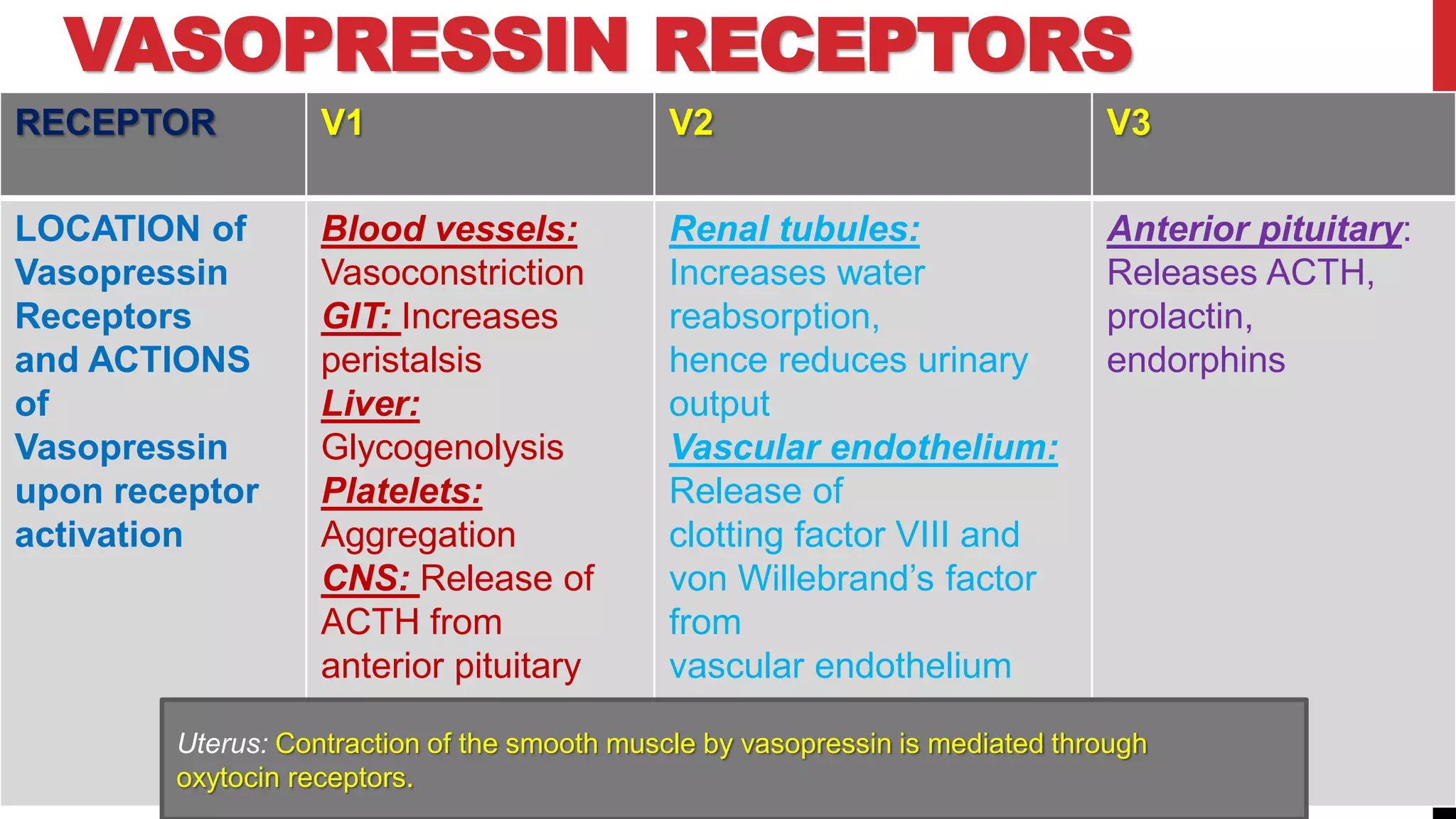
Vasopressin, also known as the antidiuretic hormone, is synthesized in the hypothalamus and plays significant roles in regulating water reabsorption and various physiological functions through its receptors. Analogues like desmopressin serve specific medical purposes, including managing hemophilia and nocturnal enuresis, while others like terlipressin are used for emergency bleeding control. Potential adverse effects of vasopressin and its analogues include gastrointestinal disturbances, fluid retention, and irritation from nasal administration.