Embed presentation
Downloaded 128 times







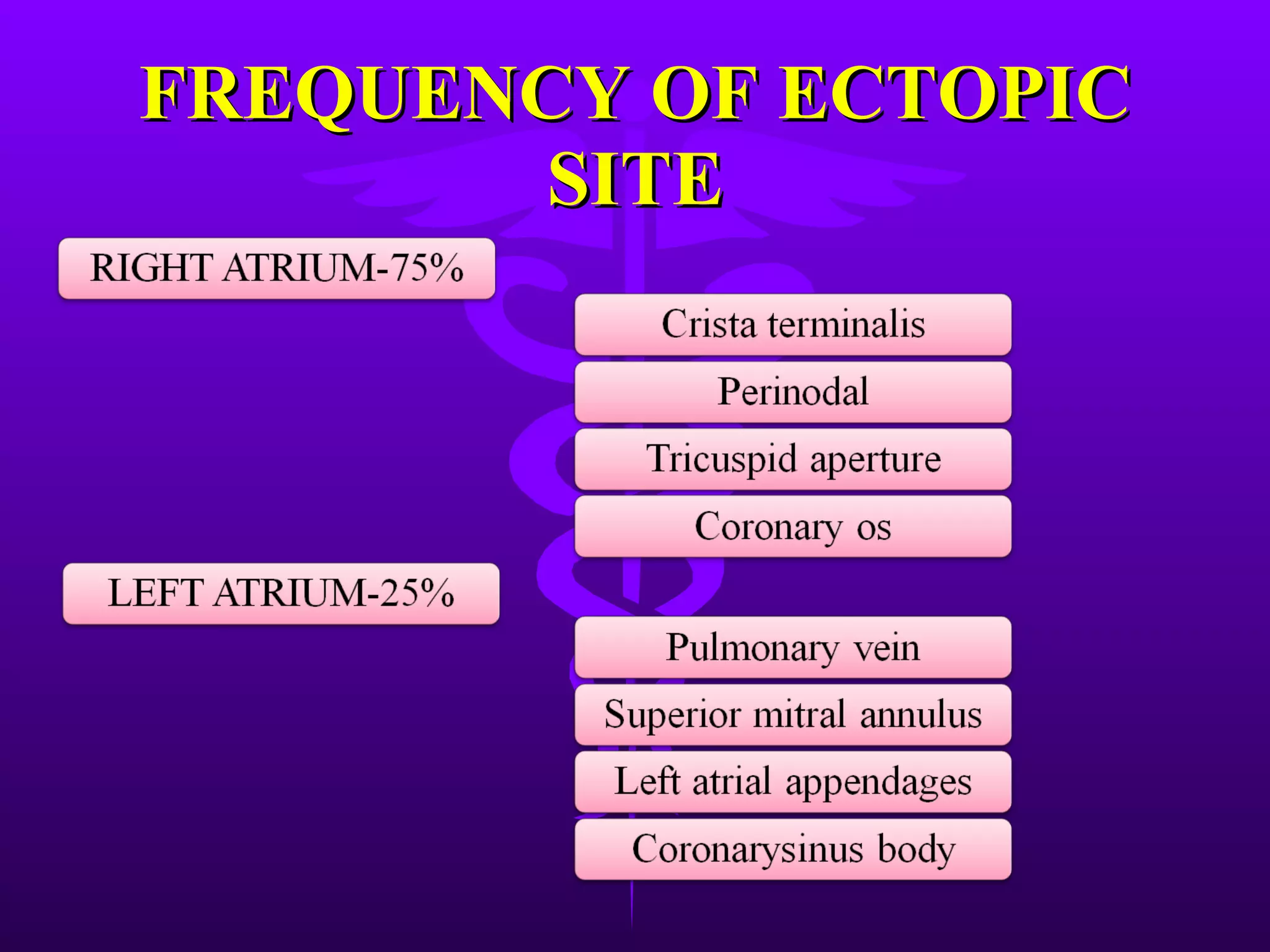

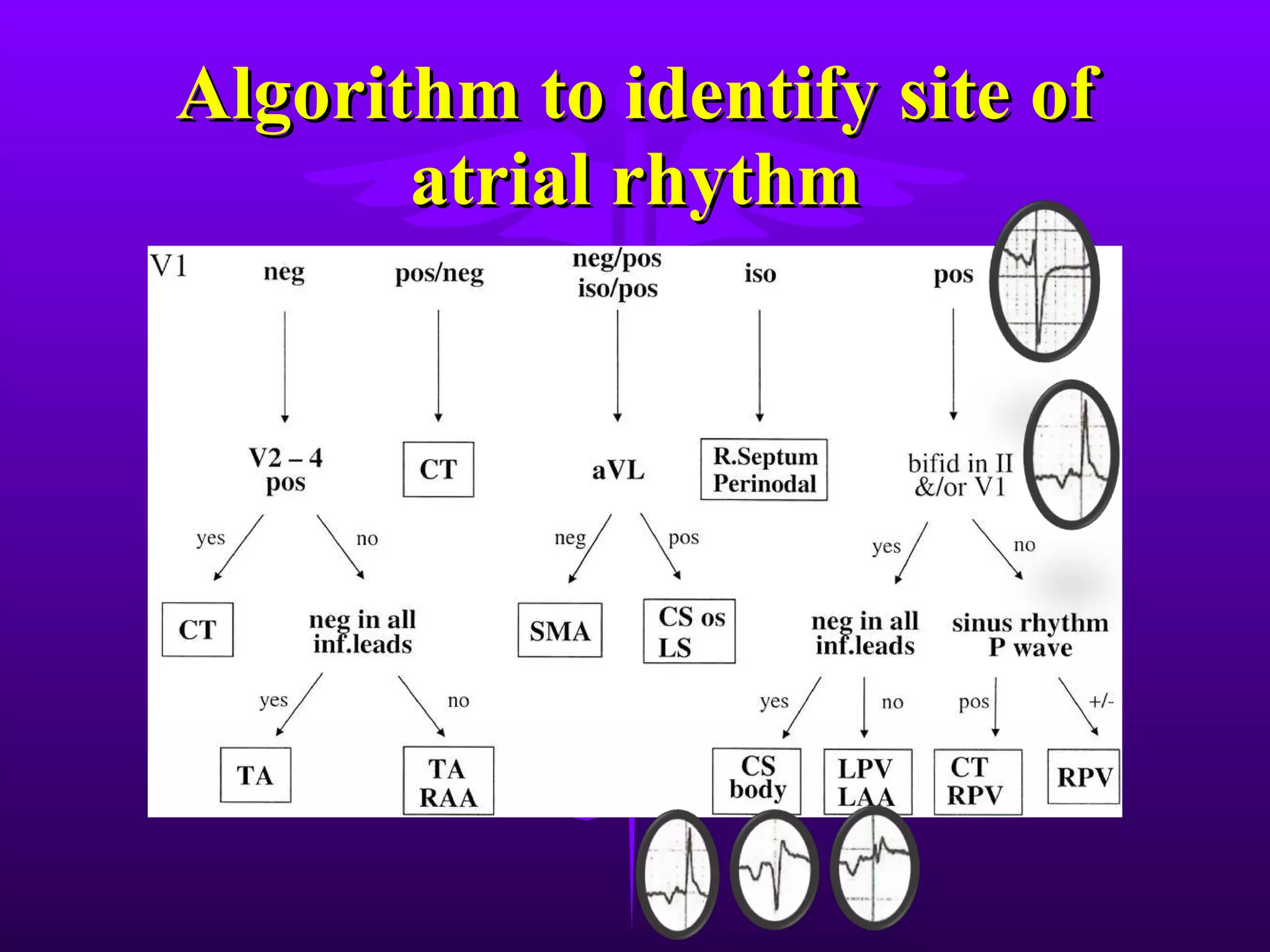

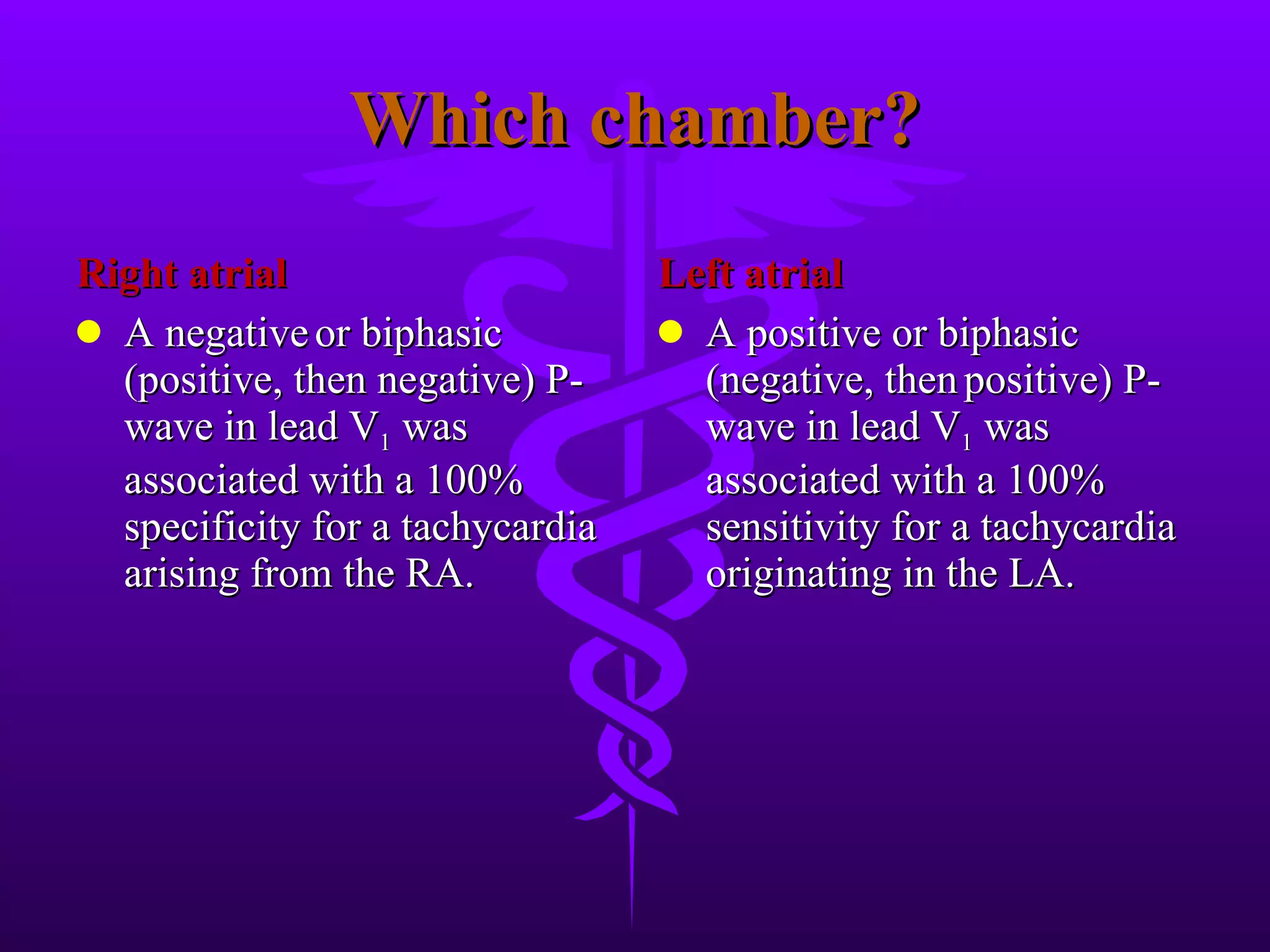


The patient presented with chest pain for 3 hours and a history of hypertension. An ECG showed an atrial rhythm originating from the coronary sinus with a heart rate of 100 bpm and inverted P waves in leads II, III, and aVF. The diagnosis was a coronary sinus rhythm with an inferior-posterior wall myocardial infarction based on ST elevations in leads II, III, and aVF with T wave inversions and ST depressions in leads V2-V4.













