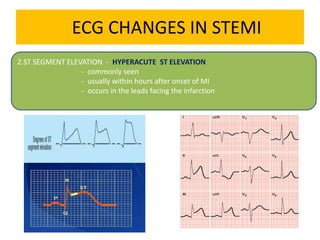
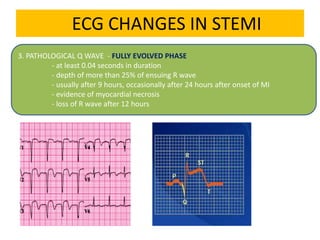
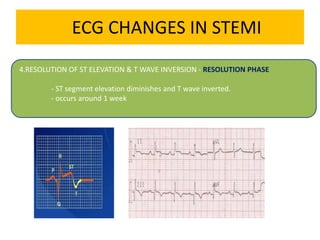
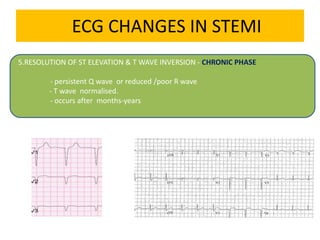
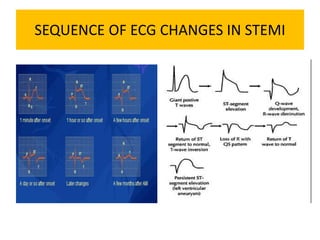
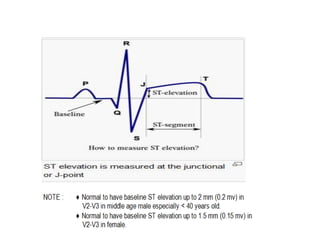
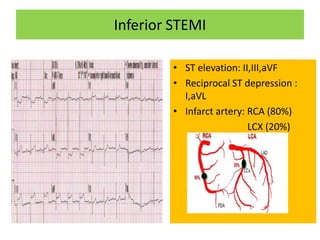
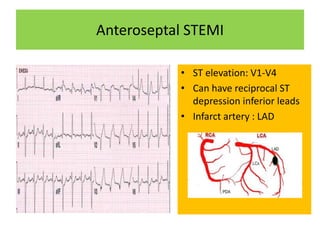
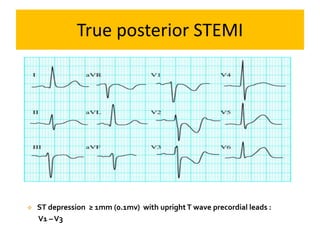
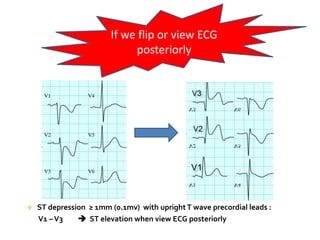
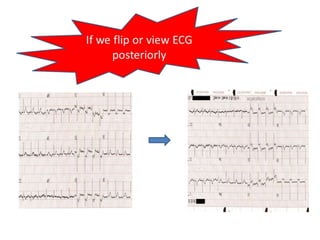
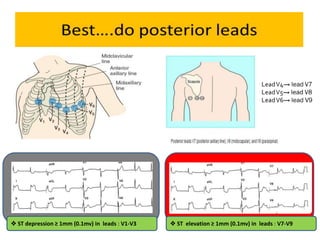
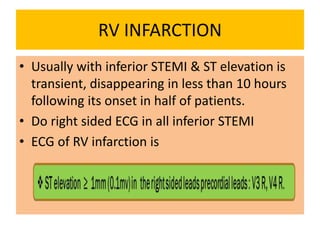
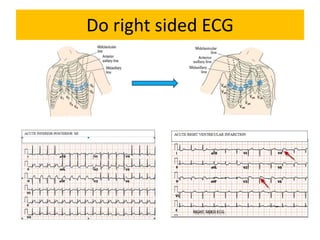
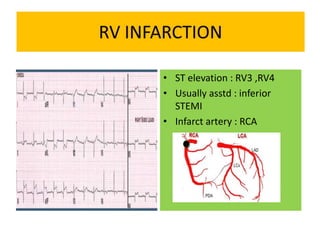
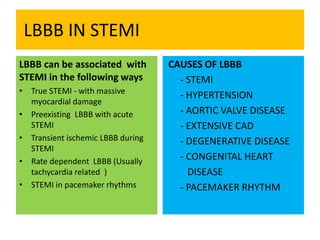
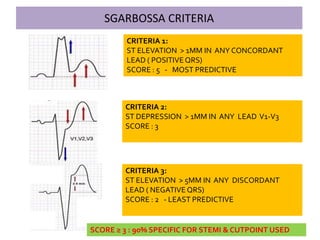
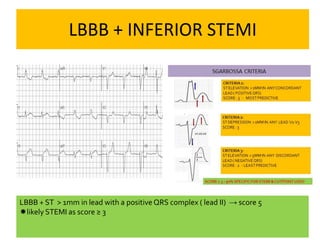
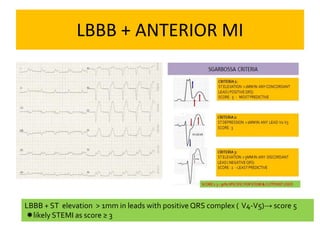
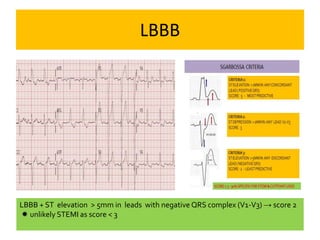
This document discusses the role of electrocardiograms (ECGs) in diagnosing ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It describes how ECGs can be used to:
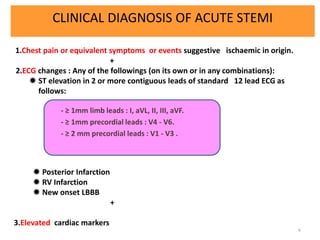
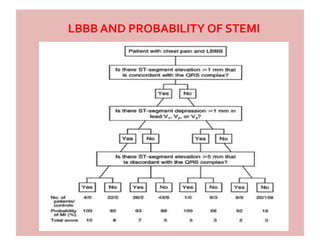
1) Diagnose acute STEMI based on specific ST elevation patterns and cardiac marker changes.
2) Determine candidates for reperfusion therapy.
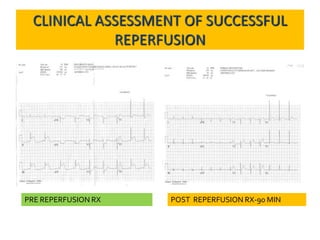
3) Assess the success of reperfusion therapy by observing the resolution of ST elevation.
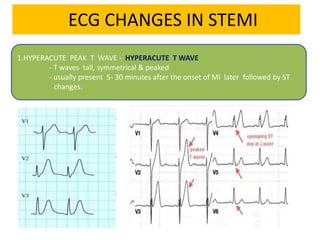
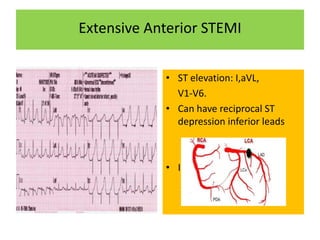
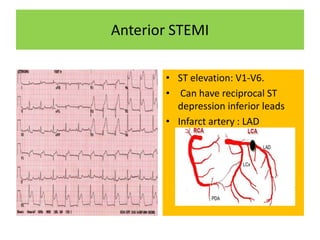
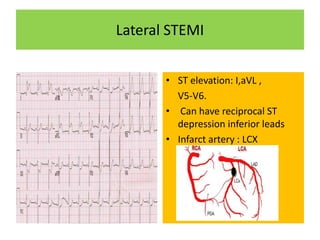
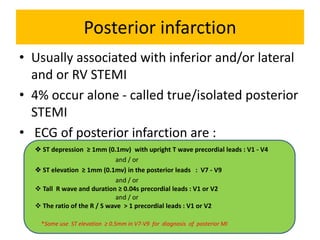
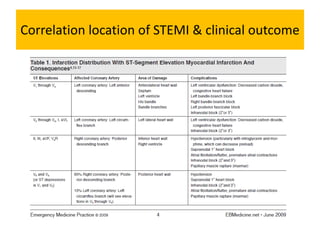
It then outlines the typical ECG patterns seen in different types of STEMI based on the affected coronary artery.