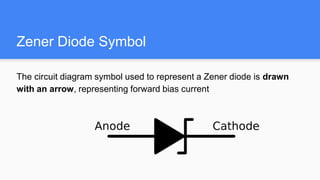
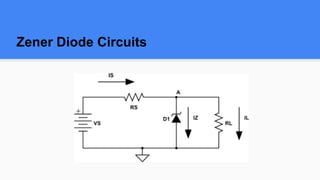
A Zener diode is a semiconductor device designed to operate in reverse bias by taking advantage of the Zener effect. It can regulate voltage in a circuit by maintaining a constant voltage drop when the reverse bias voltage exceeds the Zener voltage. The Zener diode symbol is drawn with an arrow representing forward bias current. It has applications in voltage regulation, signal clamping, voltage references, and overvoltage protection.