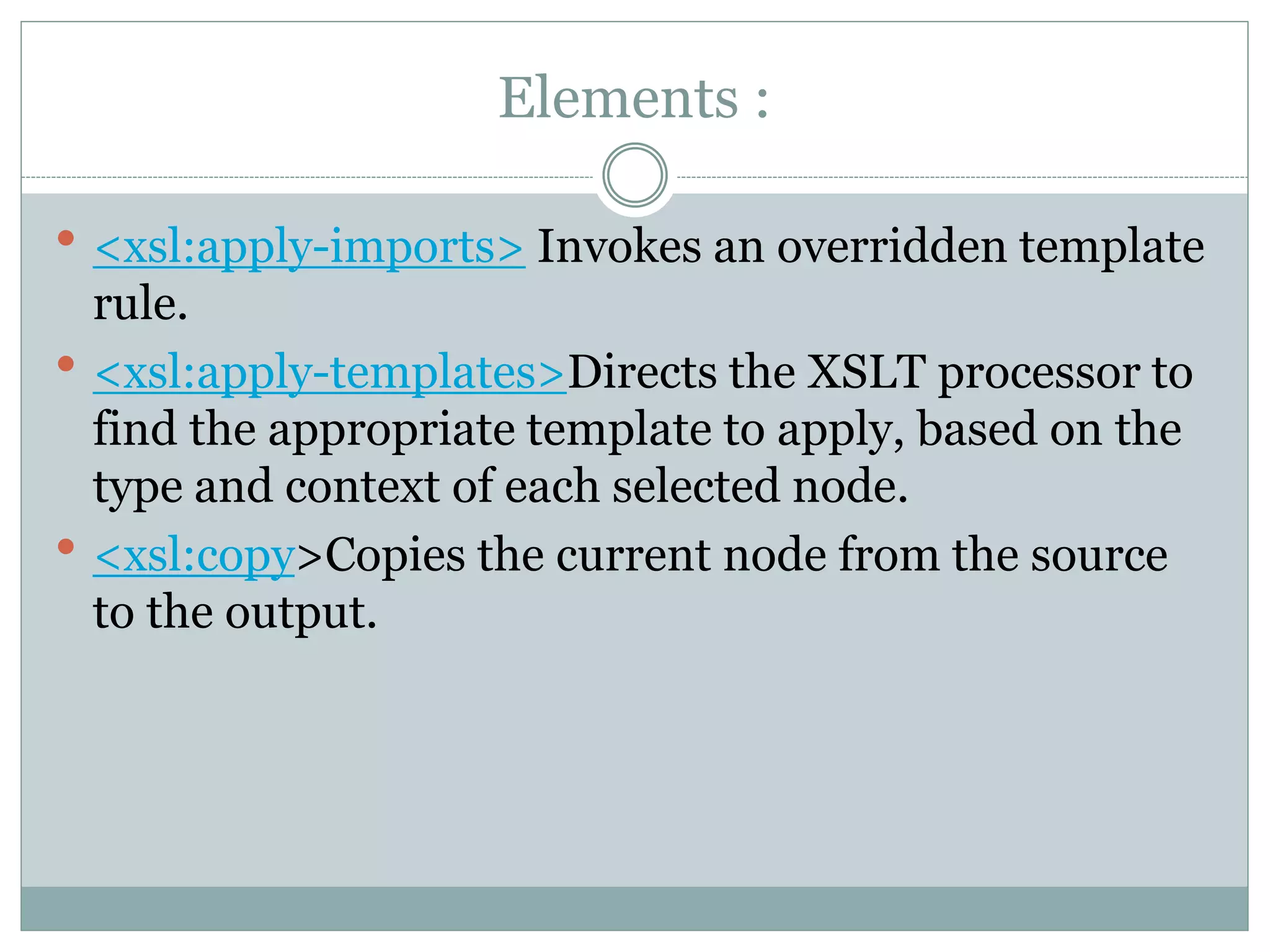
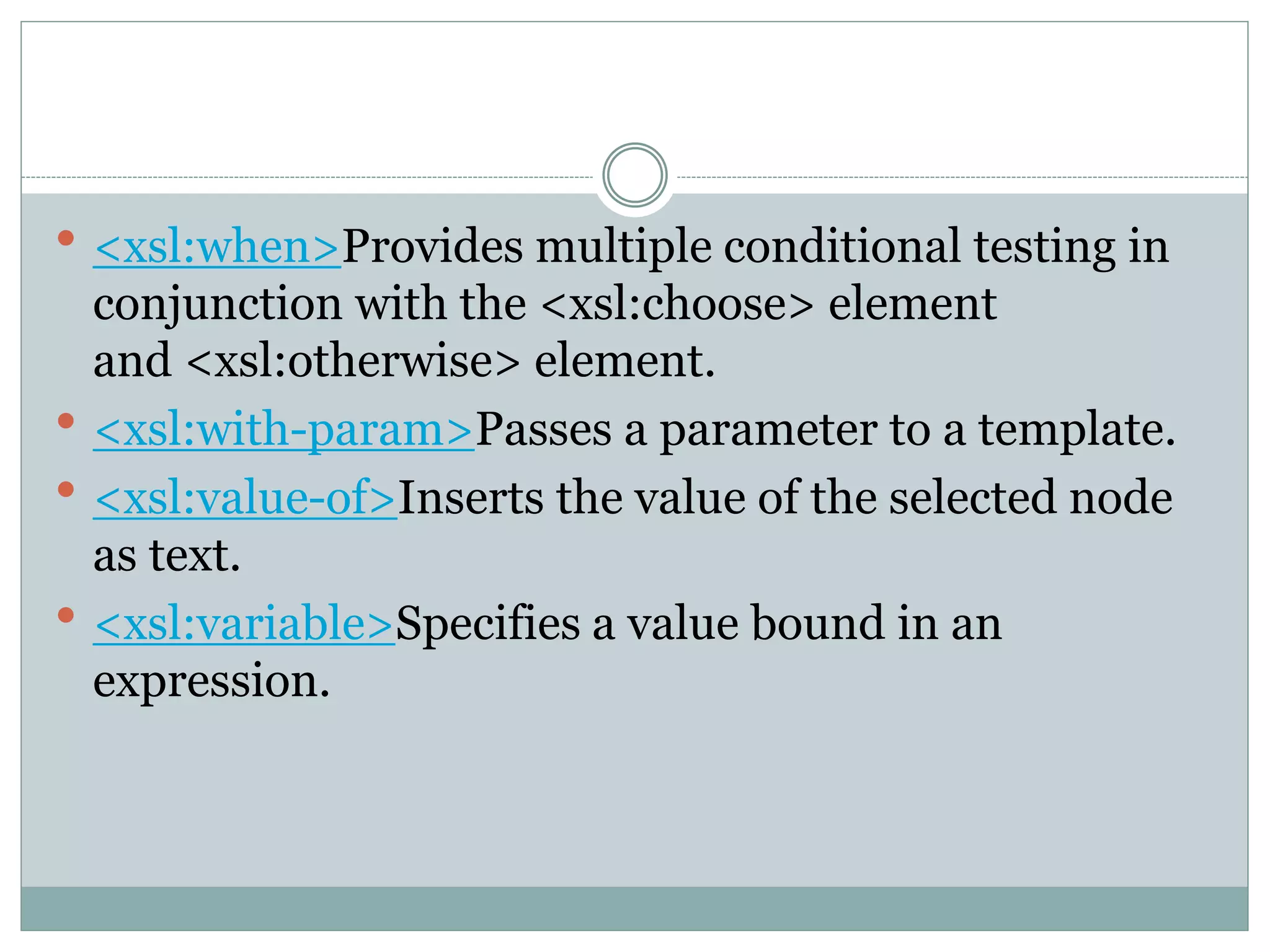
XSLT is a language for transforming XML documents into other formats like HTML, text, PDF. The document lists various XSLT elements used to transform XML, including elements to apply templates, copy nodes, create attributes, comments, choose conditional paths, import/include other XSLT files, define keys, sort nodes, and more. It provides a high-level overview of the functionality of key XSLT elements used in transforming XML documents.