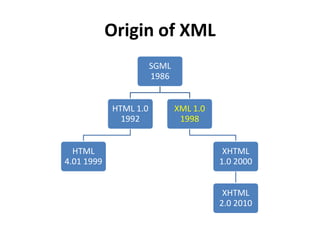
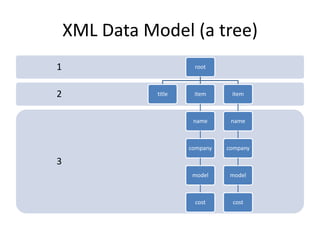
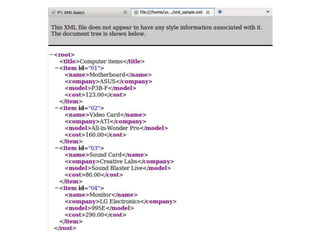
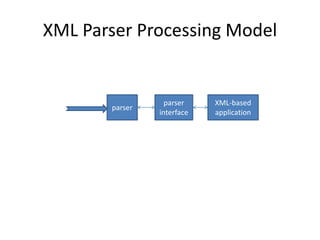
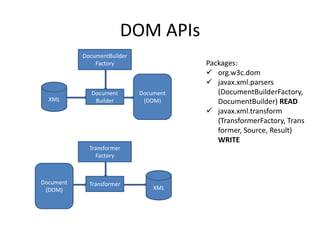
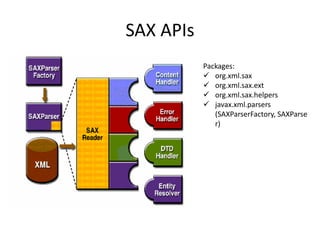
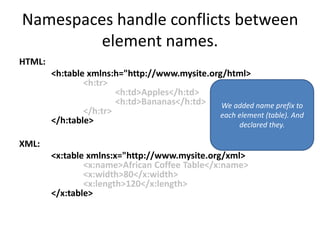
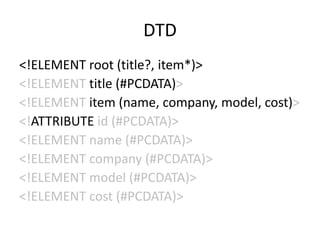
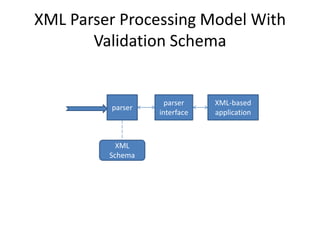
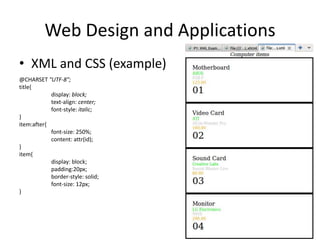
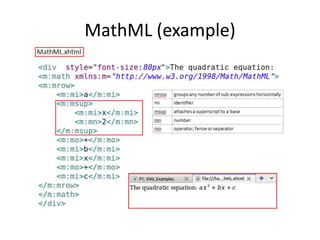
This document provides an overview and introduction to XML (eXtensible Markup Language). It discusses the basic rules of XML, parsing XML, XML namespaces, XML schemas, XSLT transformations, and examples of where XML is applied such as web design, web services, mobile web, and content authoring.