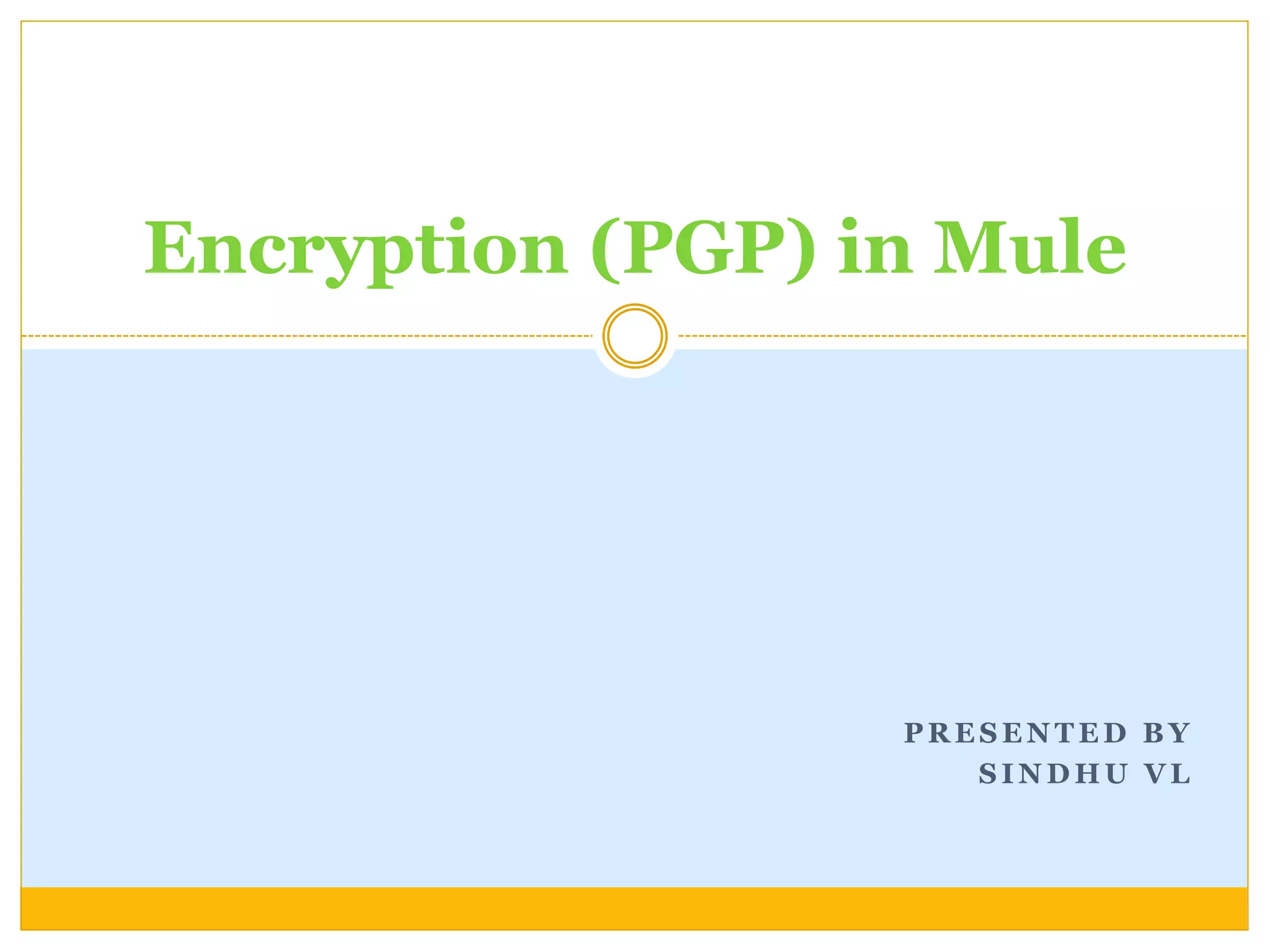
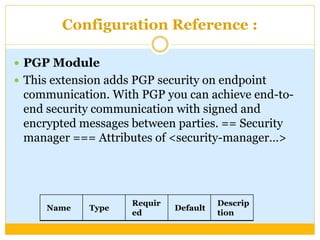
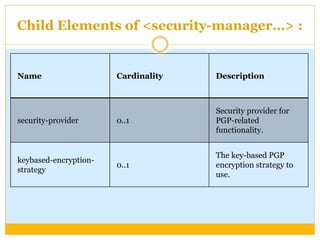
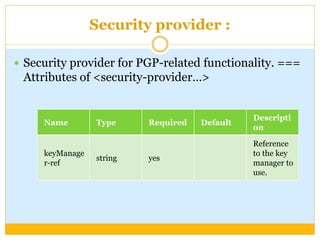
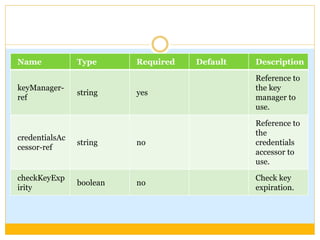
This document discusses how to configure Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) encryption in Mule. PGP provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication. Configuring PGP in Mule involves setting up a security manager, key manager, and credential accessor. The security manager holds the encryption strategy and key rings. The key manager reads the key rings and requires configuration of the public/secret rings, alias ID, and passphrase. The credential accessor determines which key ID to use and can return different IDs for different messages. Examples show configuring these components and using encrypt and decrypt transformers.