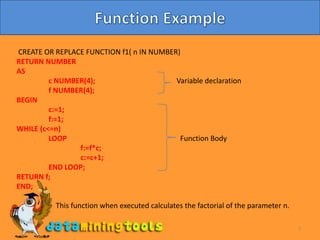
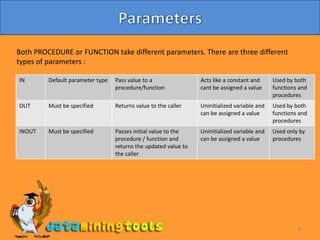
This document discusses procedures and functions in Oracle. Procedures are reusable blocks of SQL and PL/SQL code that perform a specific task and are stored in the database. There are two types of procedures - anonymous and stored. Stored procedures have a unique name and can accept parameters. Functions are similar to procedures but return a single value. Both procedures and functions can take input parameters of different types. The document provides examples of creating and calling a procedure and function.



![4Procedure SyntaxSYNTAX:CREATE [/REPLACE] PROCEDURE procedure_name [(parameter datatype),…...][LANGUAGE { ADA|C|….|SQL}ASStatement 1;…..…… Procedure body. SQL/PLSQL statements….….END;To execute the procedure:EXEC procedure_name;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oracleppt9proceduresdone-100408081207-phpapp01/85/Oracle-Procedures-4-320.jpg)