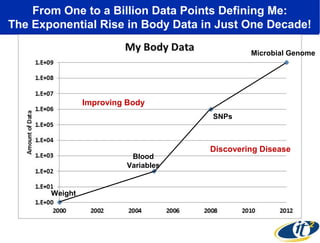
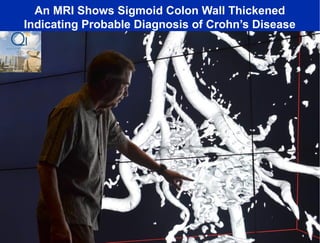
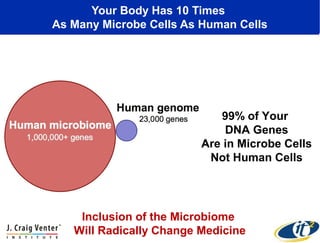
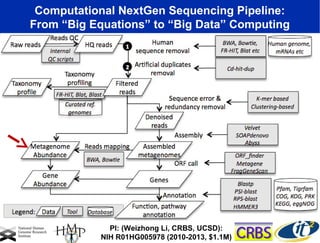
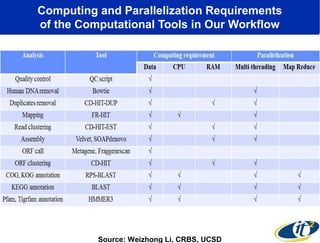
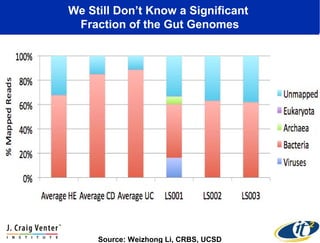
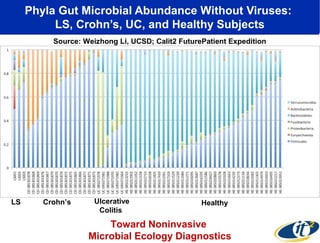
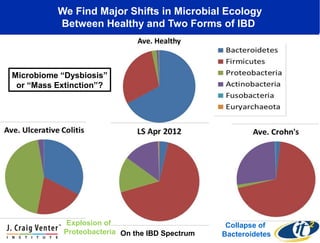
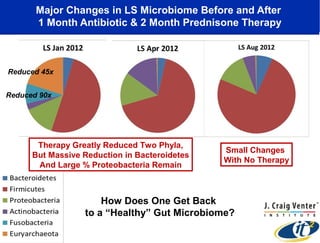
This document summarizes a talk about research analyzing gut microbiome data from patients with autoimmune diseases and healthy subjects. The research used large memory high performance computing on the Gordon supercomputer to analyze over 1.2 trillion DNA bases of metagenomic sequencing data from the gut microbiomes. Analysis found major shifts in microbial ecology between healthy subjects and those with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Therapies for one subject's Crohn's disease reduced certain phyla but others remained at high levels. The research aims to develop noninvasive microbial diagnostics and new therapeutic tools for managing the microbiome.