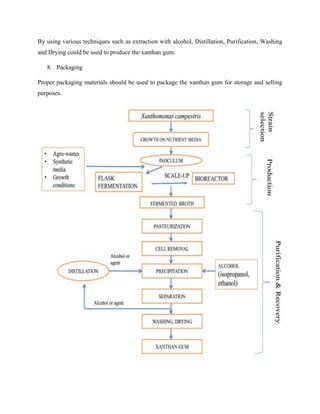
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide produced through the fermentation of the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris. It is commonly used as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer in foods. The production process involves isolating the bacteria from an infected plant, purifying it, growing it in culture media, and then producing xanthan gum at an industrial scale using a bioreactor. The bacteria are then separated and the xanthan gum is recovered through extraction and purification processes before final packaging. Xanthan gum helps prevent ingredients from separating and is found in many products like salad dressings, sauces, ice cream, toothpaste, and gluten-free baked goods.