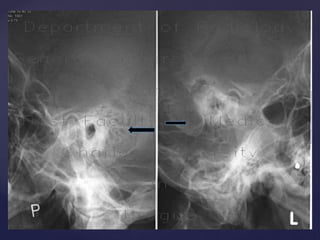
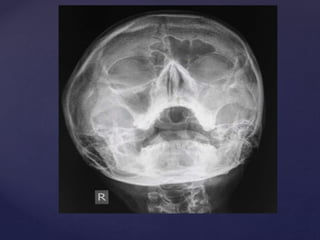
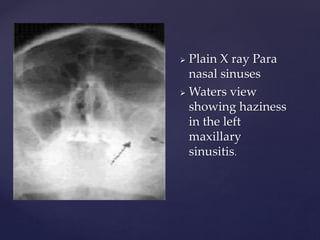
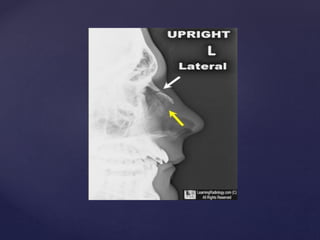
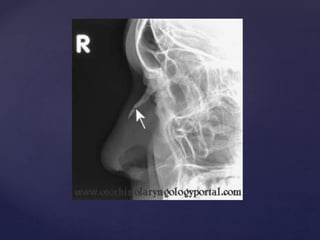
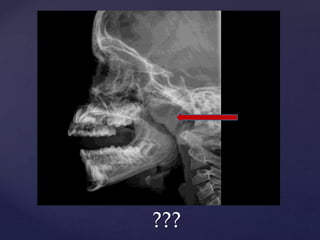
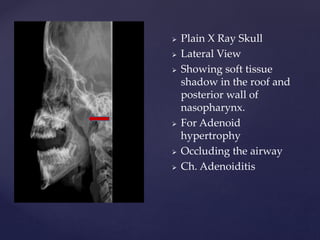
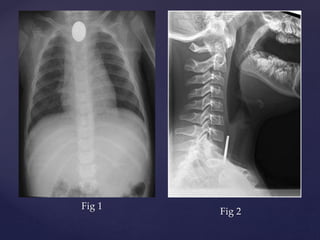
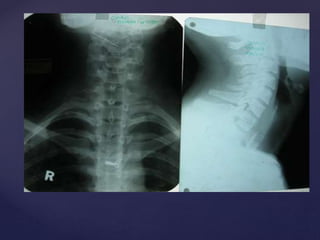
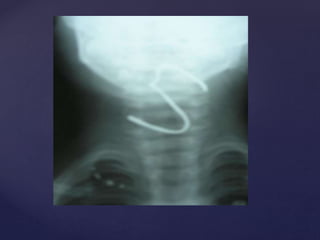
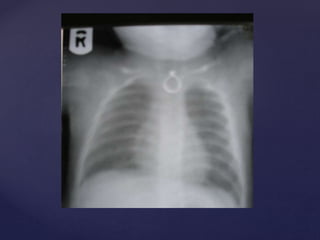
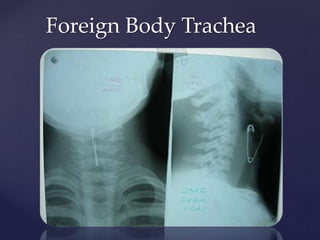
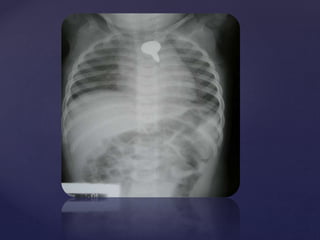
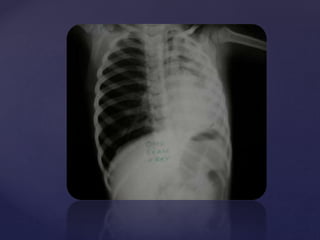
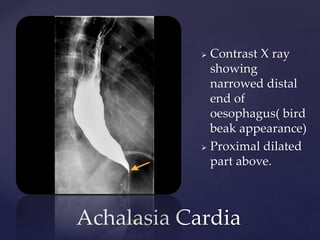
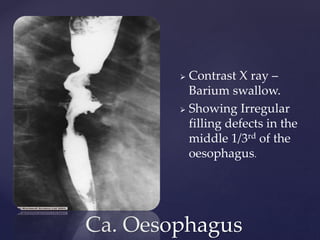
This document provides guidance on reading and interpreting various types of x-rays. It addresses x-rays of the mastoids, paranasal sinuses, nasal bones, nasopharynx, esophagus, trachea, and other areas. Key questions are provided for each type of x-ray to help understand what is shown, how to identify common findings and diagnoses, and how conditions should be managed. The goal is to equip radiologists and other medical professionals with the knowledge to properly analyze x-rays and utilize the images to facilitate patient care.