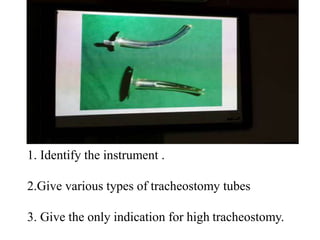
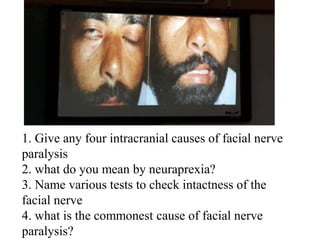
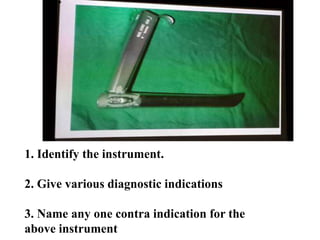
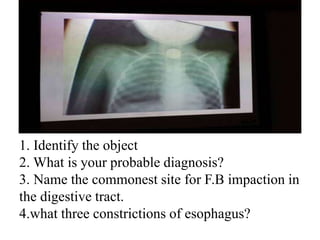
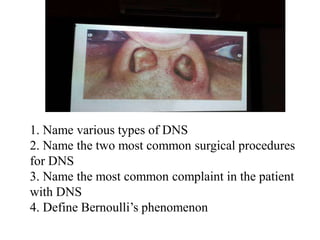
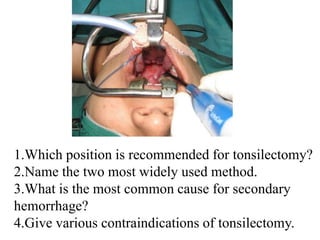
This document contains questions and answers related to ENT OSPE (Objective Structured Practical Examination). It includes questions on various ENT instruments, procedures, diseases and their management. Some key topics covered include types of tracheostomy tubes, causes of facial nerve paralysis, indications and complications of direct laryngoscopy, diagnostic workup for a foreign body in the esophagus, types of deviated nasal septum, surgical treatments for nasal polyps, and differences between ethmoidal and antroconal nasal polyps.