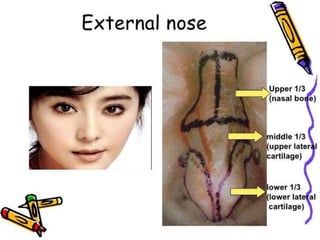
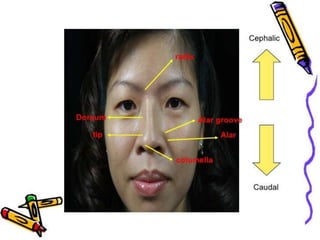
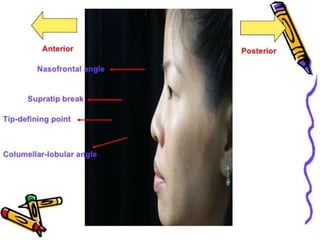
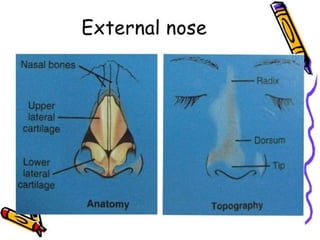
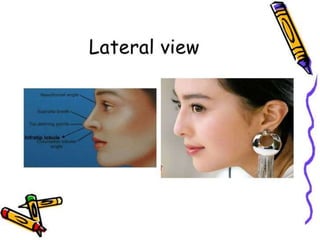
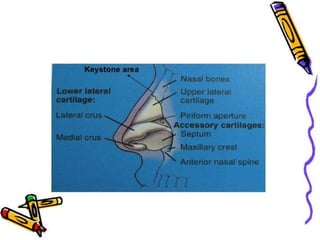
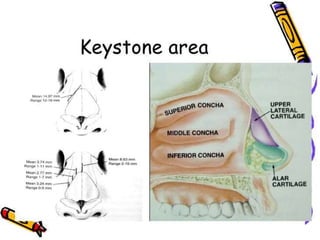
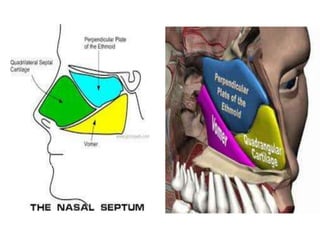
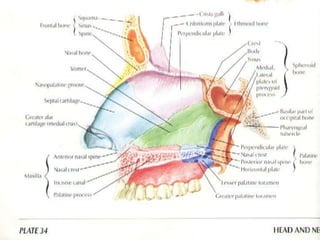
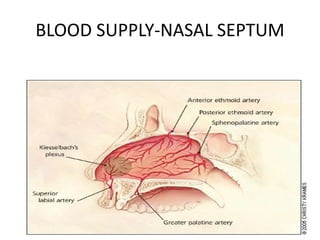
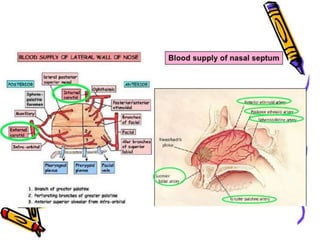
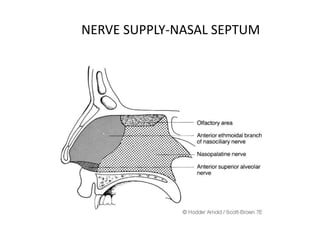
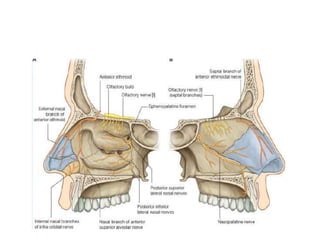
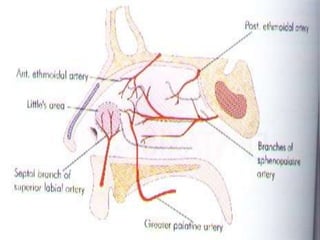
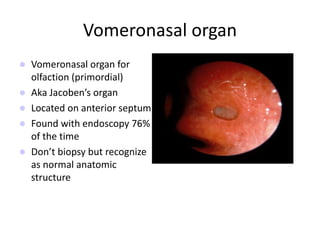
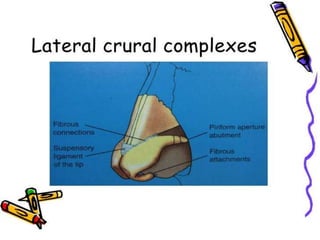
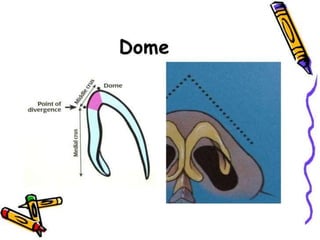
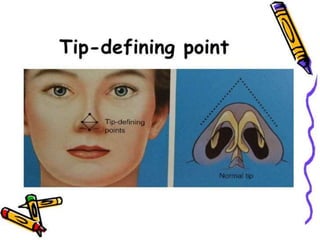
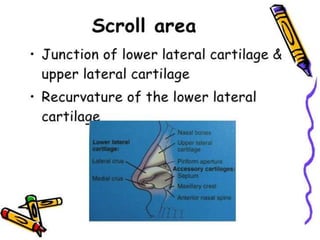
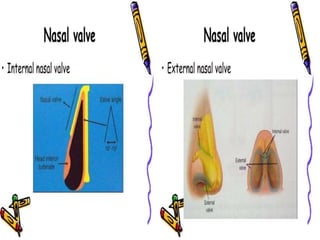
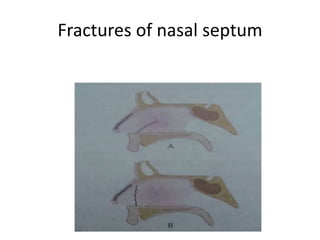
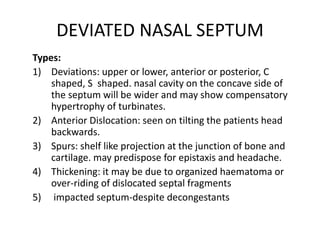
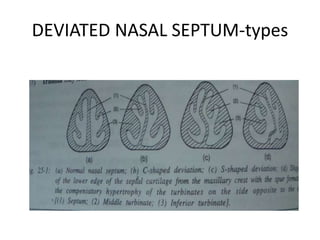
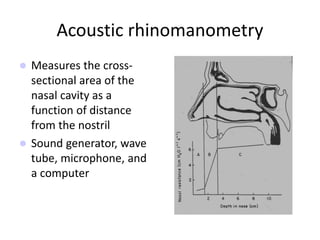
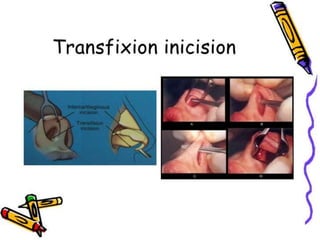
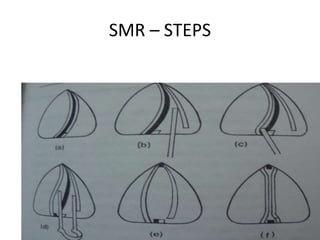
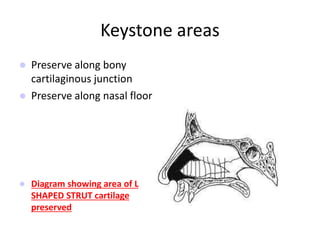
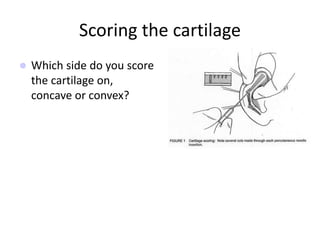
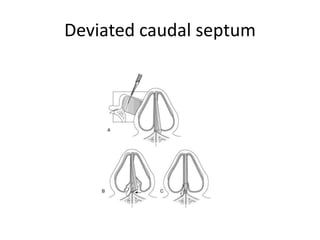
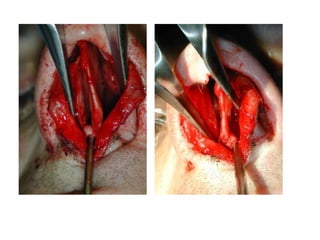
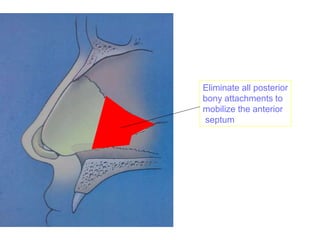
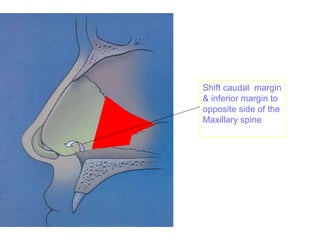
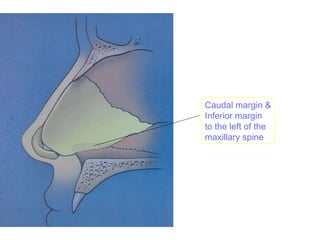
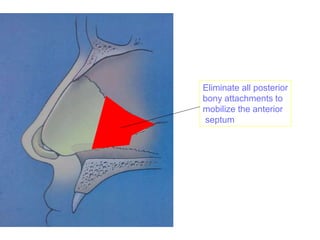
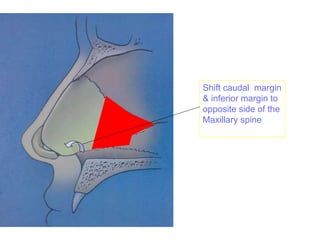
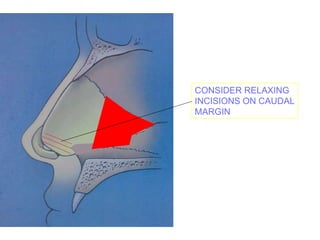
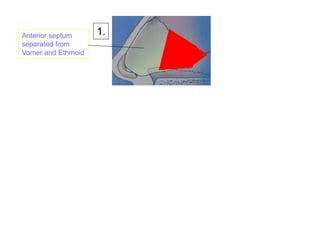
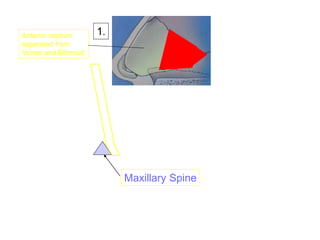
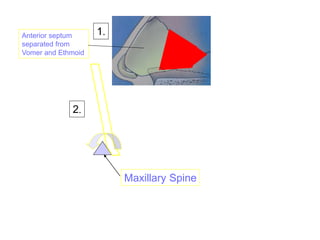
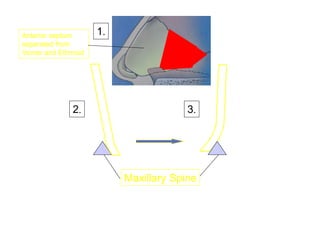
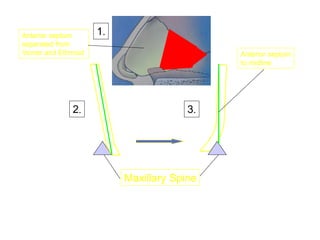
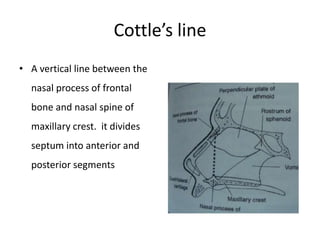
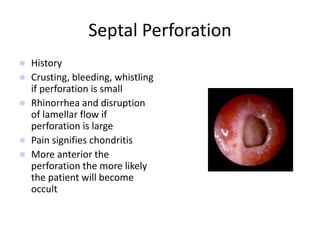
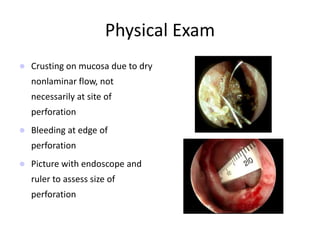
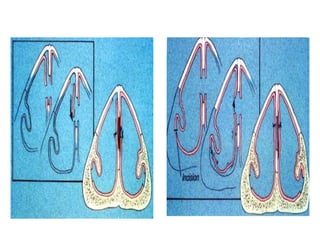
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomy, development, and clinical significance of the nasal septum, detailing its structure, blood supply, and innervation. It discusses various conditions related to the nasal septum, including deviations and fractures, their etiologies, clinical features, diagnostic tests, and treatment options such as submucous resection (SMR) and septoplasty. Additionally, it outlines the preoperative assessments and complications associated with surgical interventions on the nasal septum.