Embed presentation
Downloaded 228 times
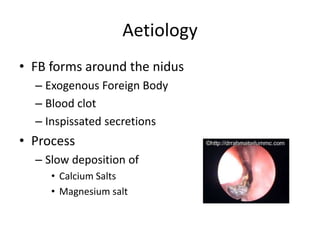
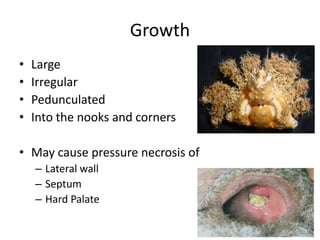

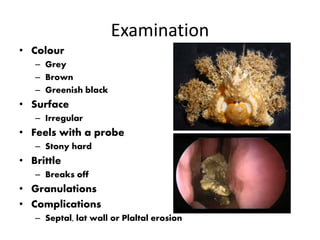
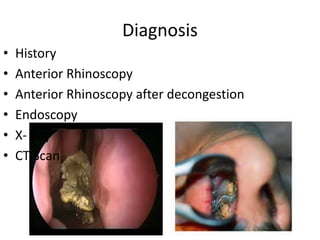
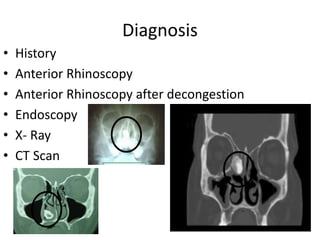
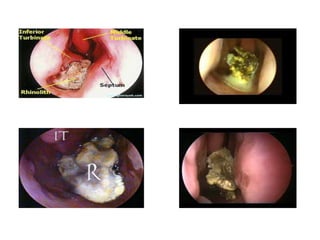



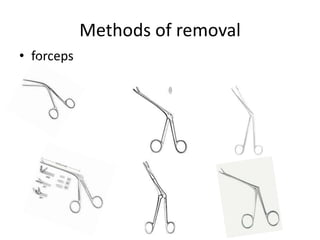




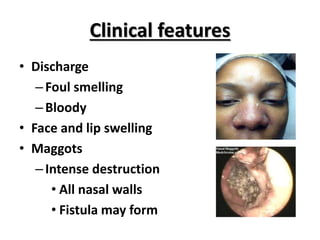



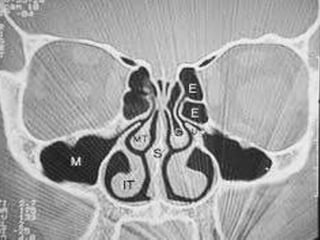
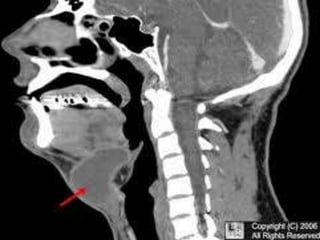
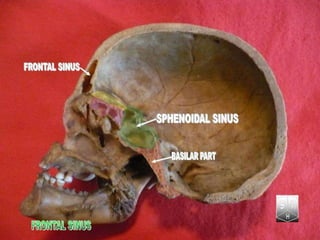
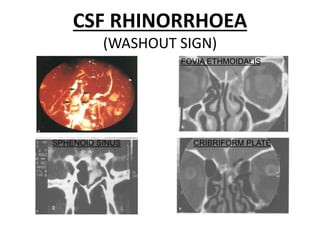
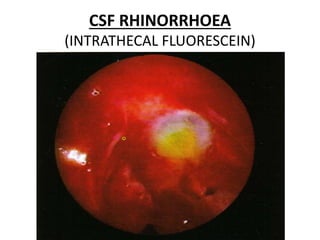
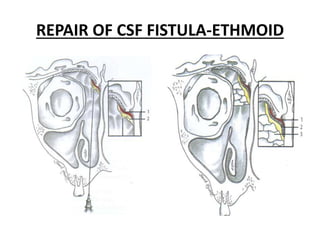
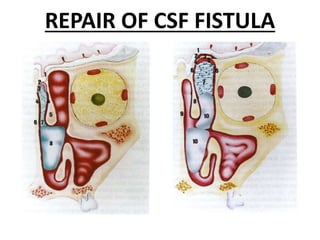

This document discusses various conditions that can result in stones or foreign bodies in the nasal cavity. It describes rhinoliths, which are stones that form around a nidus like a blood clot or inspissated secretions. Rhinoliths can grow large and irregularly, causing nasal obstruction, discharge, pain and other symptoms. Examination finds hard, irregular masses that break into pieces. CT scans are used for diagnosis. Rhinoliths are removed using various tools under local or general anesthesia. Myiasis and cerebral spinal fluid leaks into the nasal cavity from skull base fractures are also discussed.



























