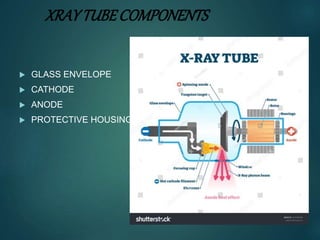
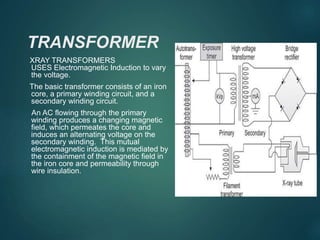
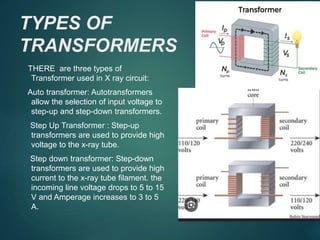
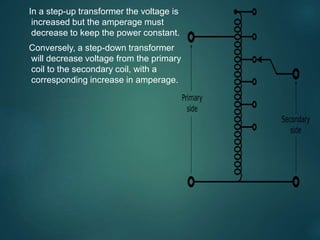
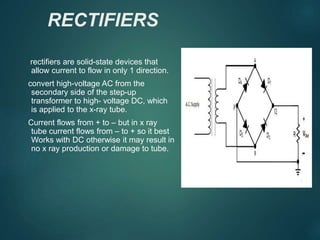
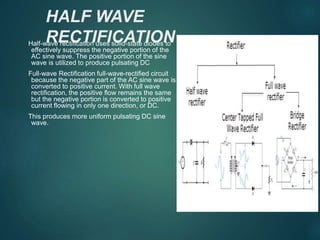
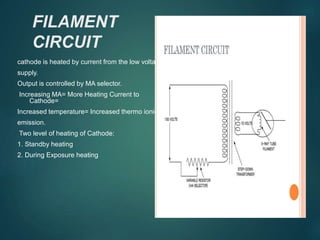
This document discusses the key components of an X-ray circuit, including the X-ray tube, transformer, rectifier circuit, filament circuit, and exposure controls. The X-ray tube generates X-rays by accelerating electrons which are then decelerated upon impact with the anode. Transformers are used to step up or down voltages to power the tube filament and provide high voltage. Rectifiers convert the transformer's AC output to DC to power the X-ray tube. Exposure is controlled through manual timers, electronic timers, or automatic exposure control based on a photodetector.