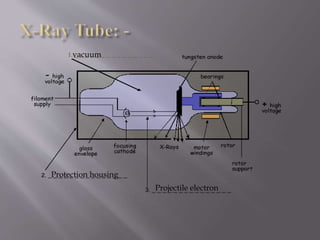
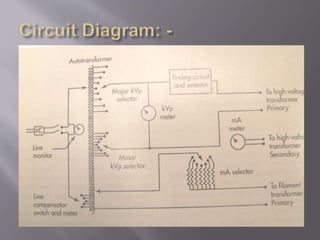
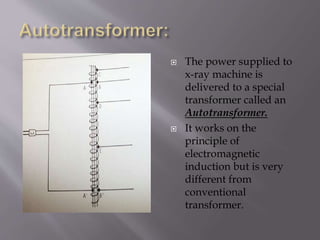
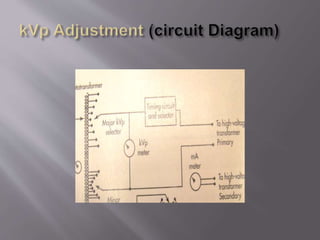
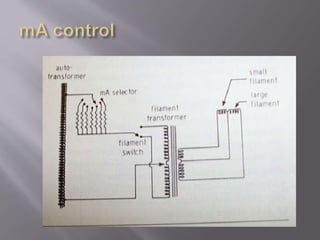
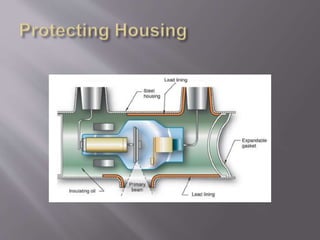
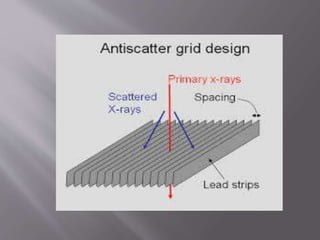
The document describes the key components of an X-ray machine, including the X-ray tube, operating console, transformer, tube housing, collimator, patient table, grid, Bucky, and radiographic film. It provides details on what each component is, what it does, and how it works within the overall system to produce X-ray images.