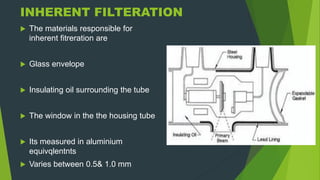
Filters are used in x-ray imaging to shape the beam and increase the ratio of useful photons for imaging to those that increase patient dose or decrease image contrast. Filters are typically made of metal like aluminum or copper and are placed between the x-ray tube and patient. They absorb the low energy photons that do not penetrate tissue deeply but deposit much radiation in superficial tissues. This provides better tissue penetration by the beam while reducing the skin dose and improving contrast. Different types of filters include inherent, added, compound, and wedge filters which vary in materials and thickness used.