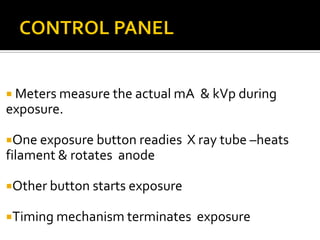
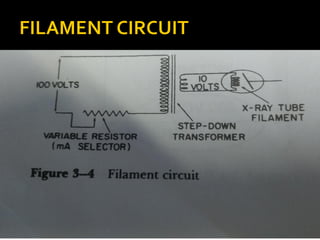
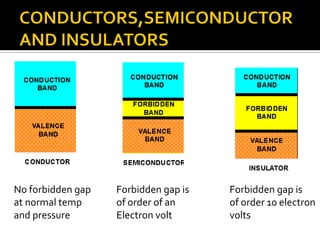
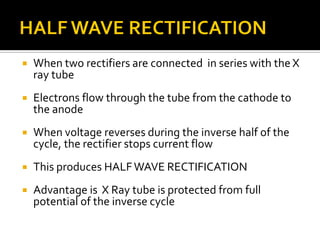
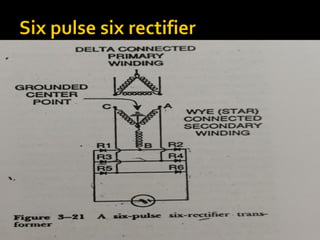
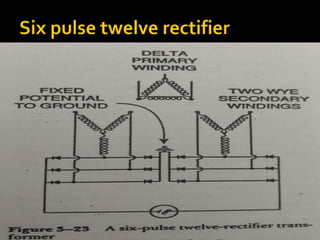
An x-ray generator uses a transformer assembly and control panel to supply electric power to the x-ray tube. The transformer assembly contains components like transformers, a rectifier, and capacitors that modify incoming alternating current into high voltage direct current needed by the x-ray tube. It increases the voltage using step-up transformers by factors of 600 or more. The control panel contains components that allow adjusting and monitoring of exposure parameters like kVp and mA, as well as buttons to initiate and terminate x-ray exposures. Modern x-ray generators use advanced rectification and switching circuits to provide stable, ripple-free power for short exposures like in angiography and fluoroscopy.