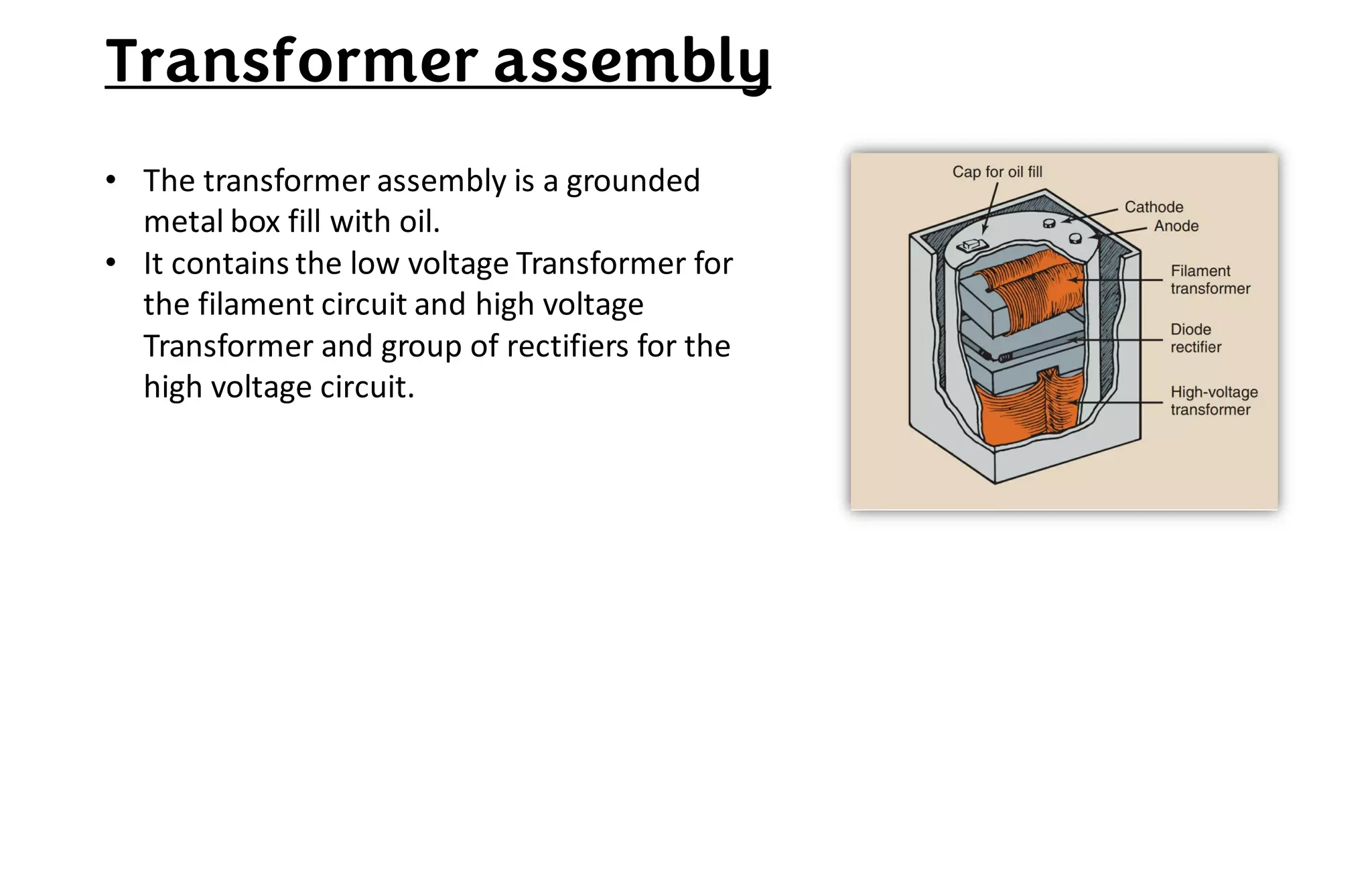
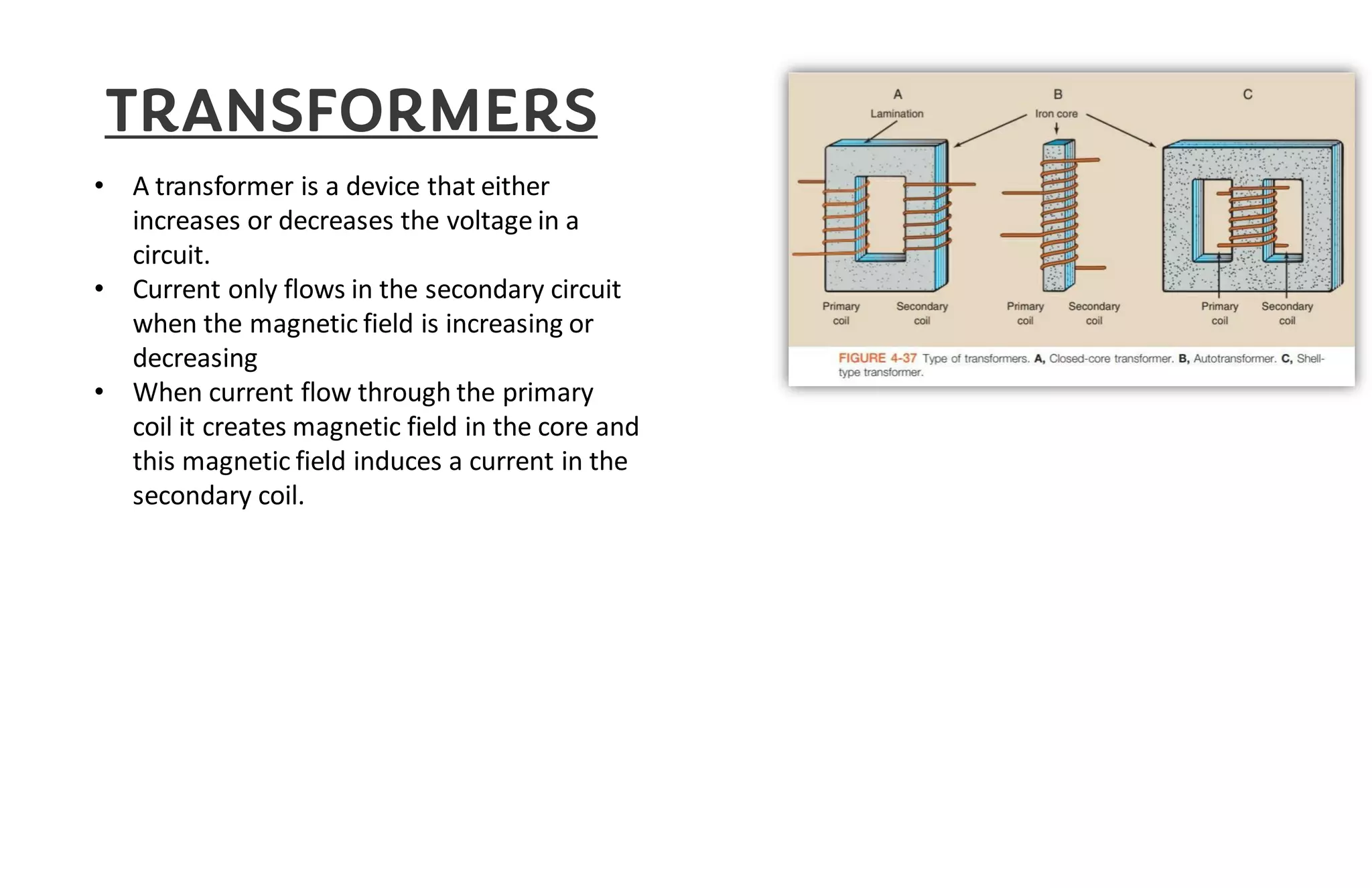
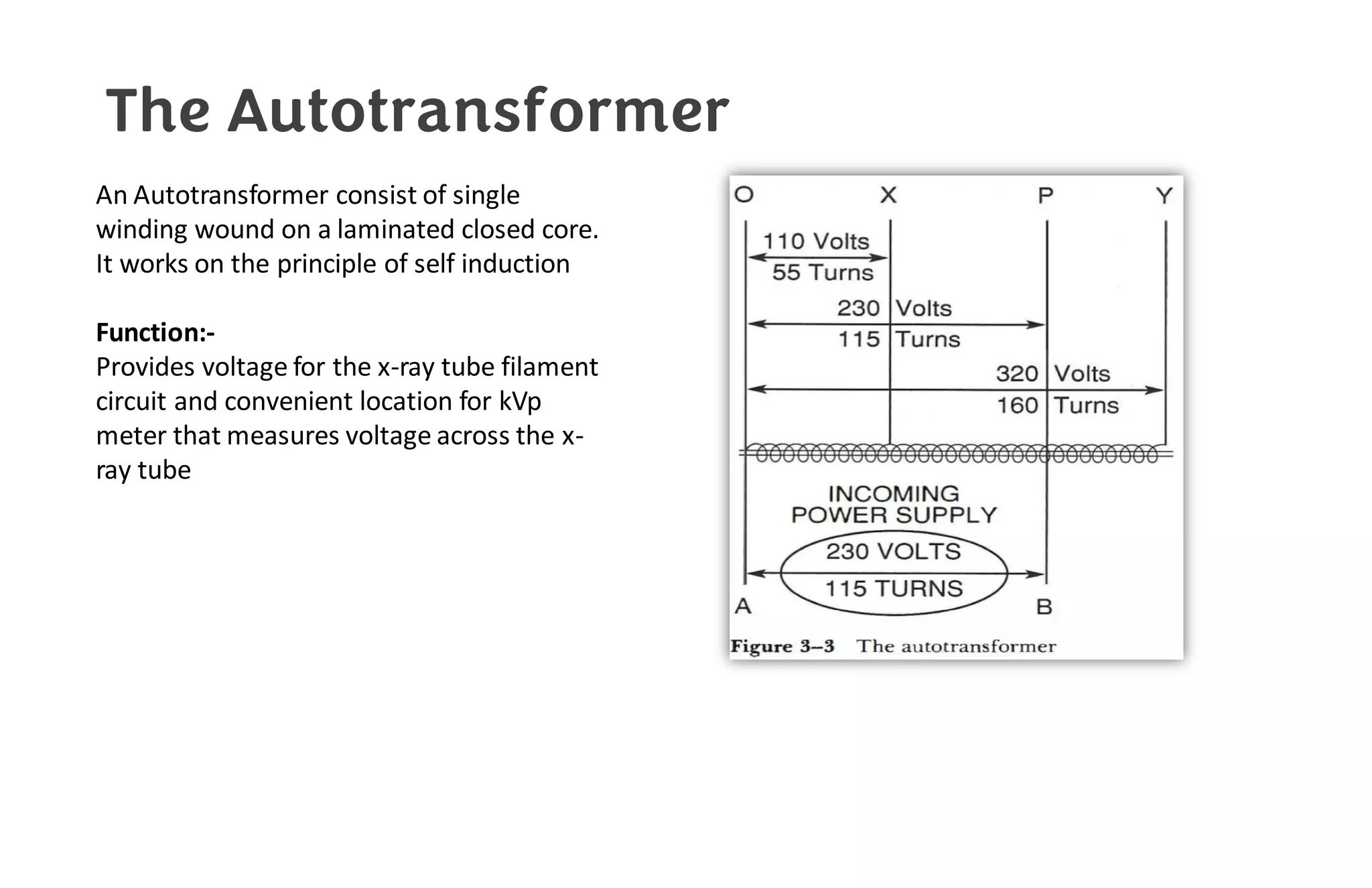
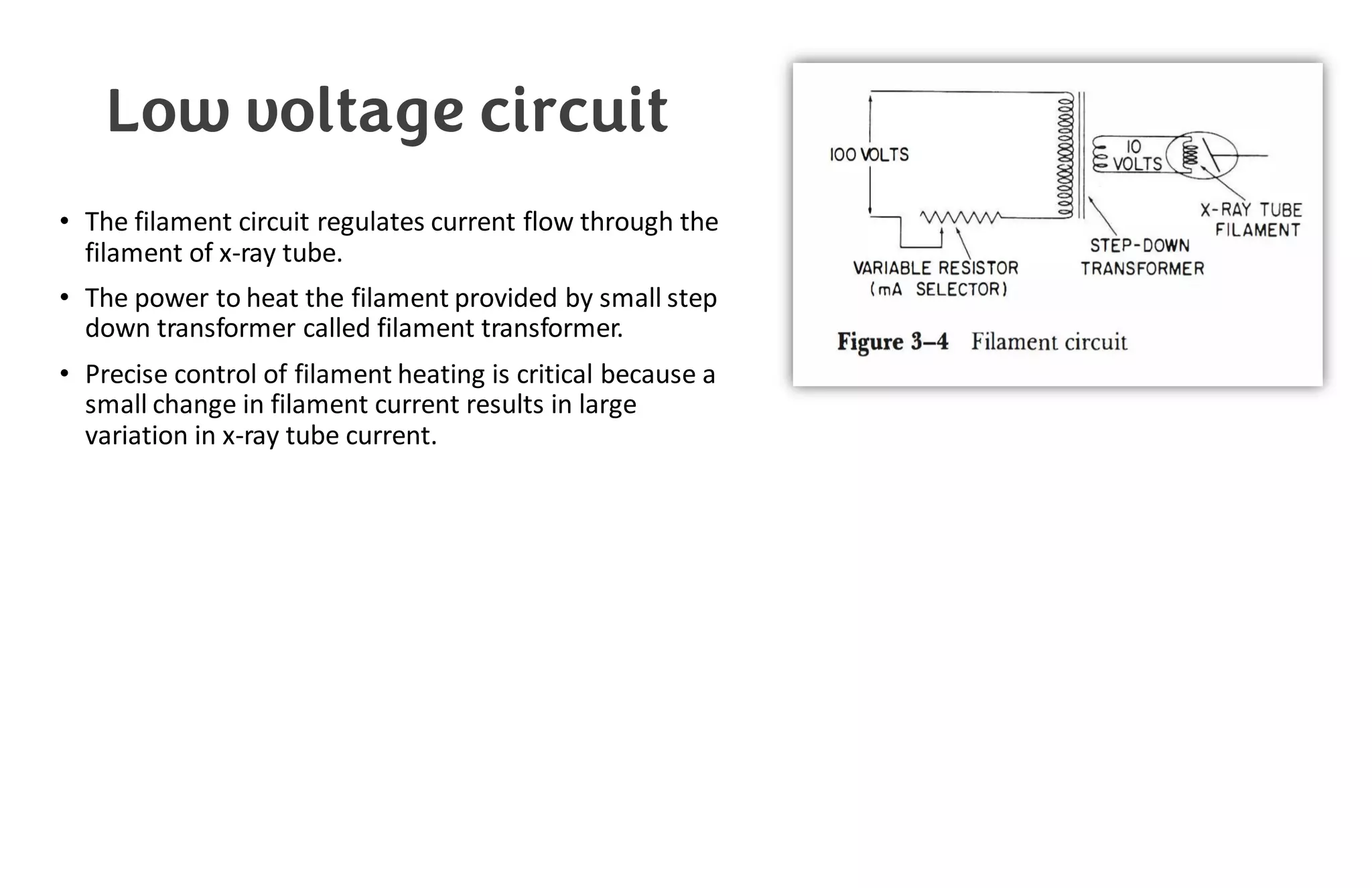
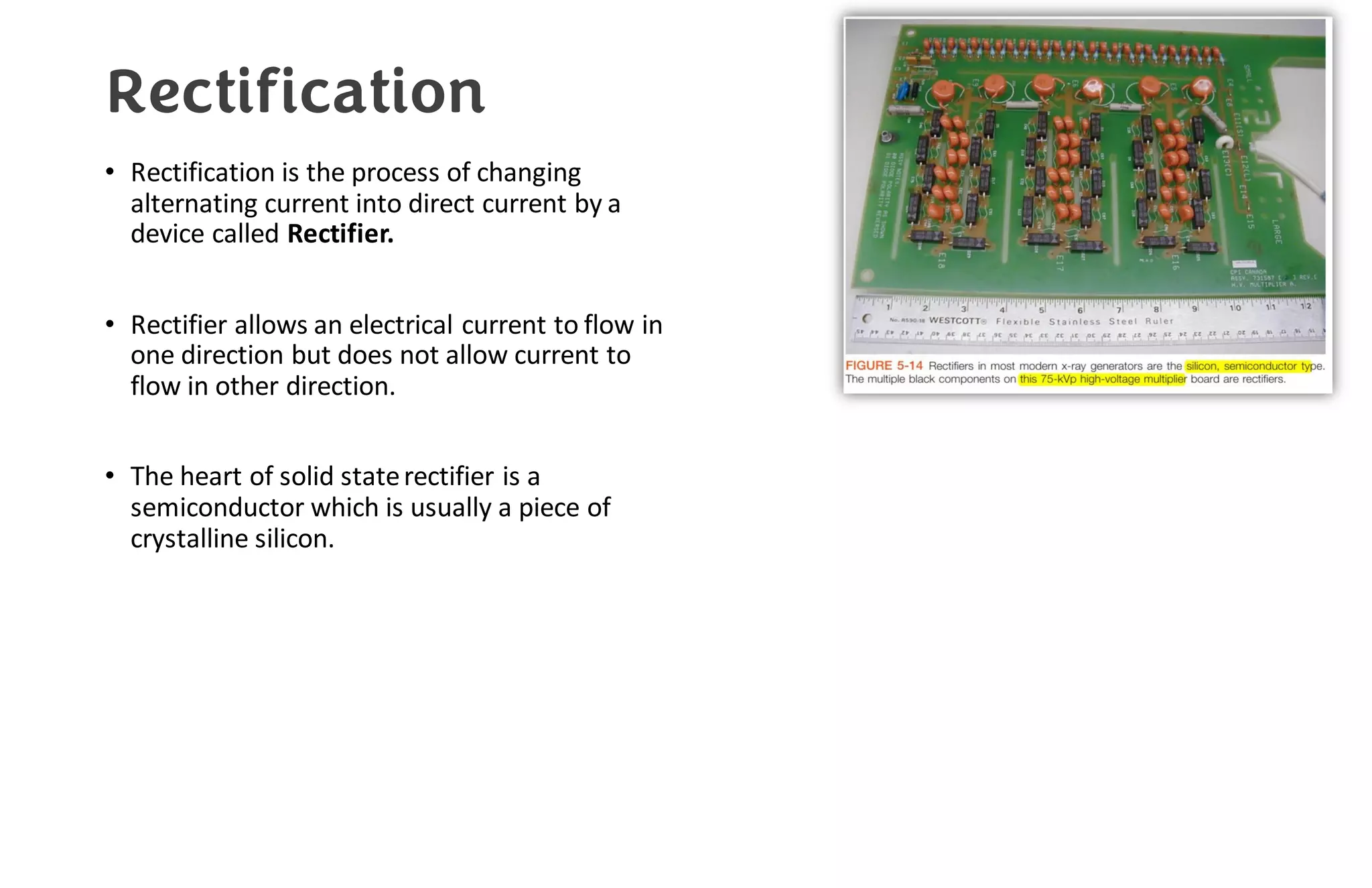
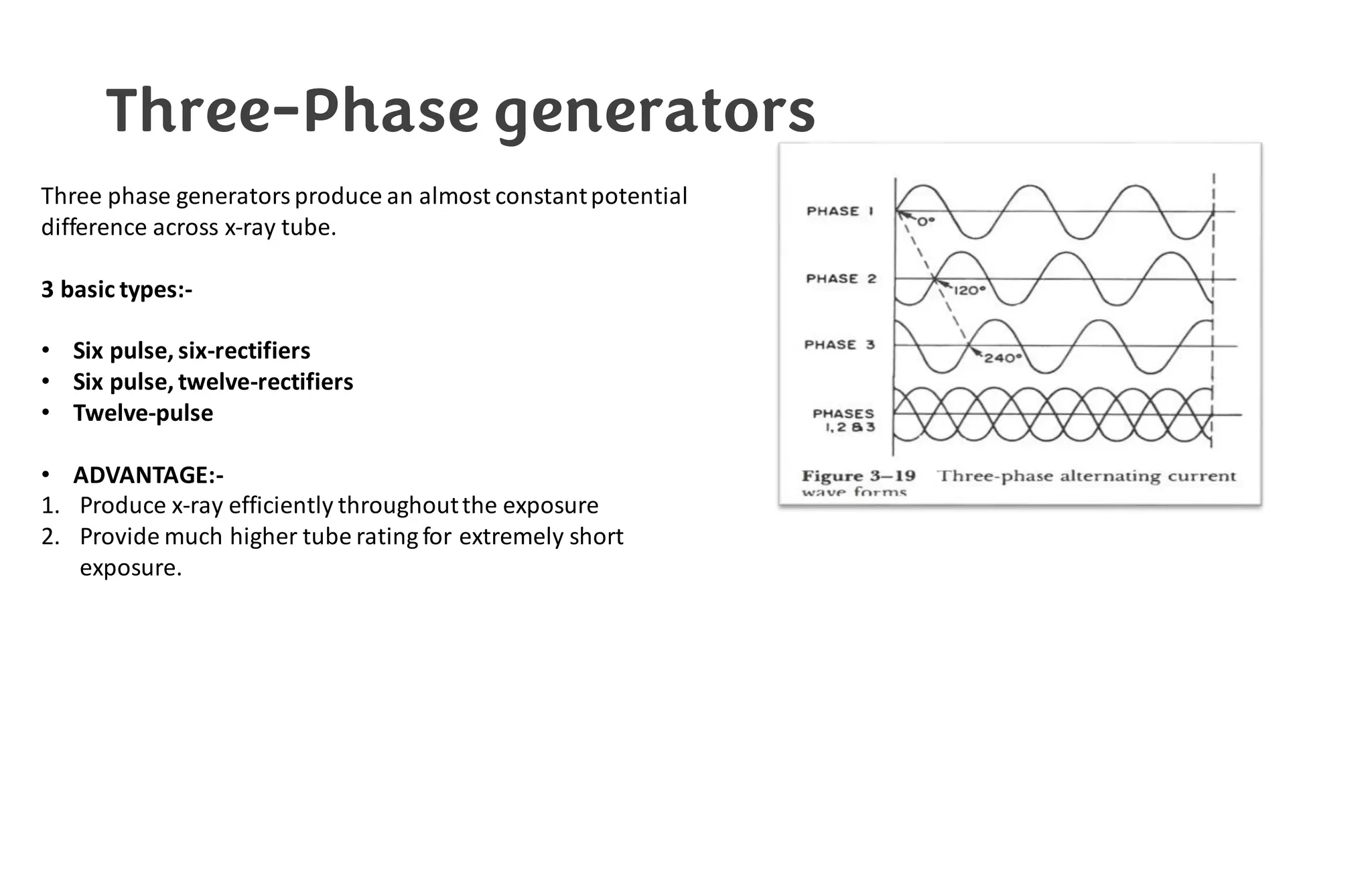
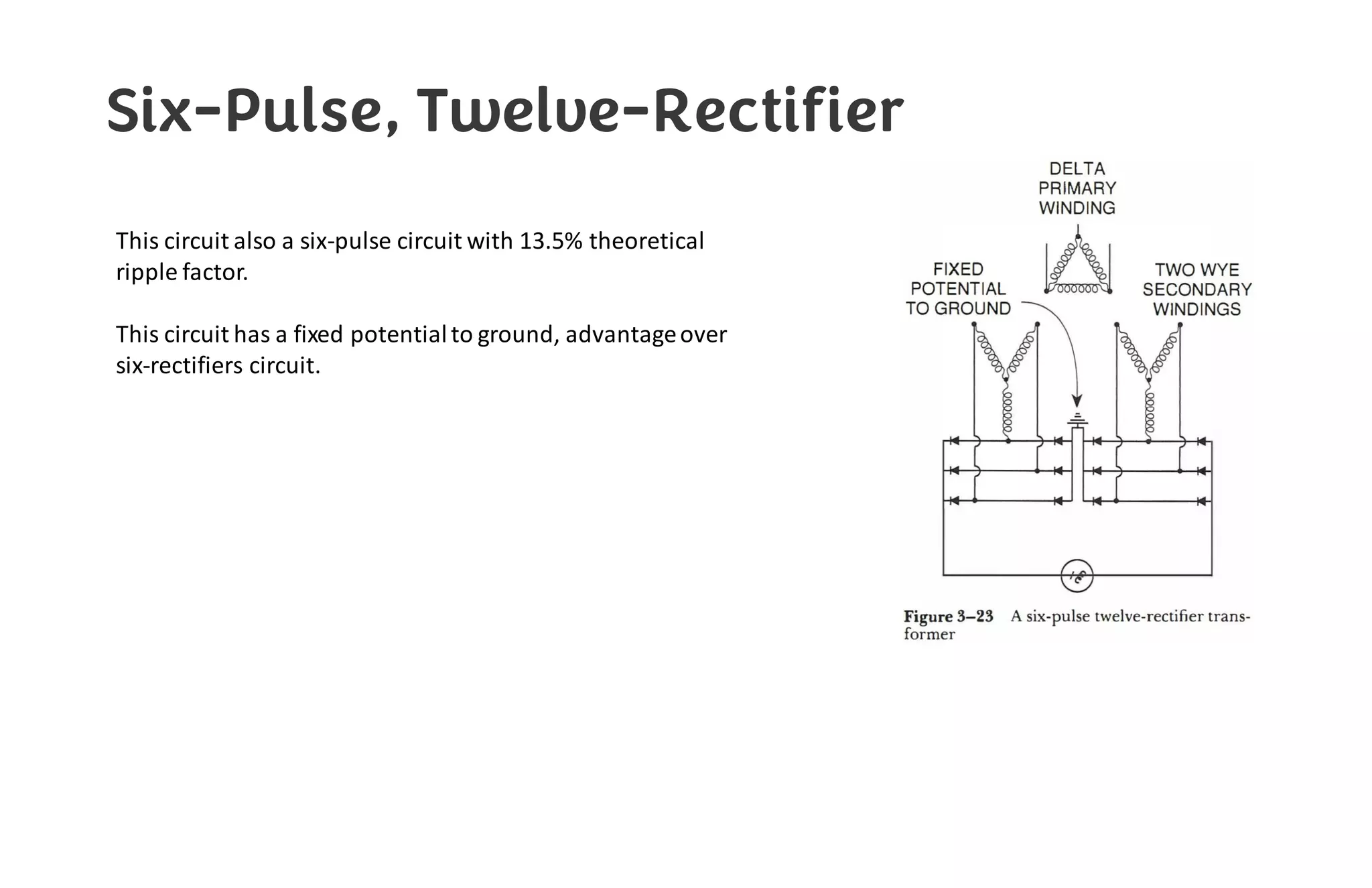
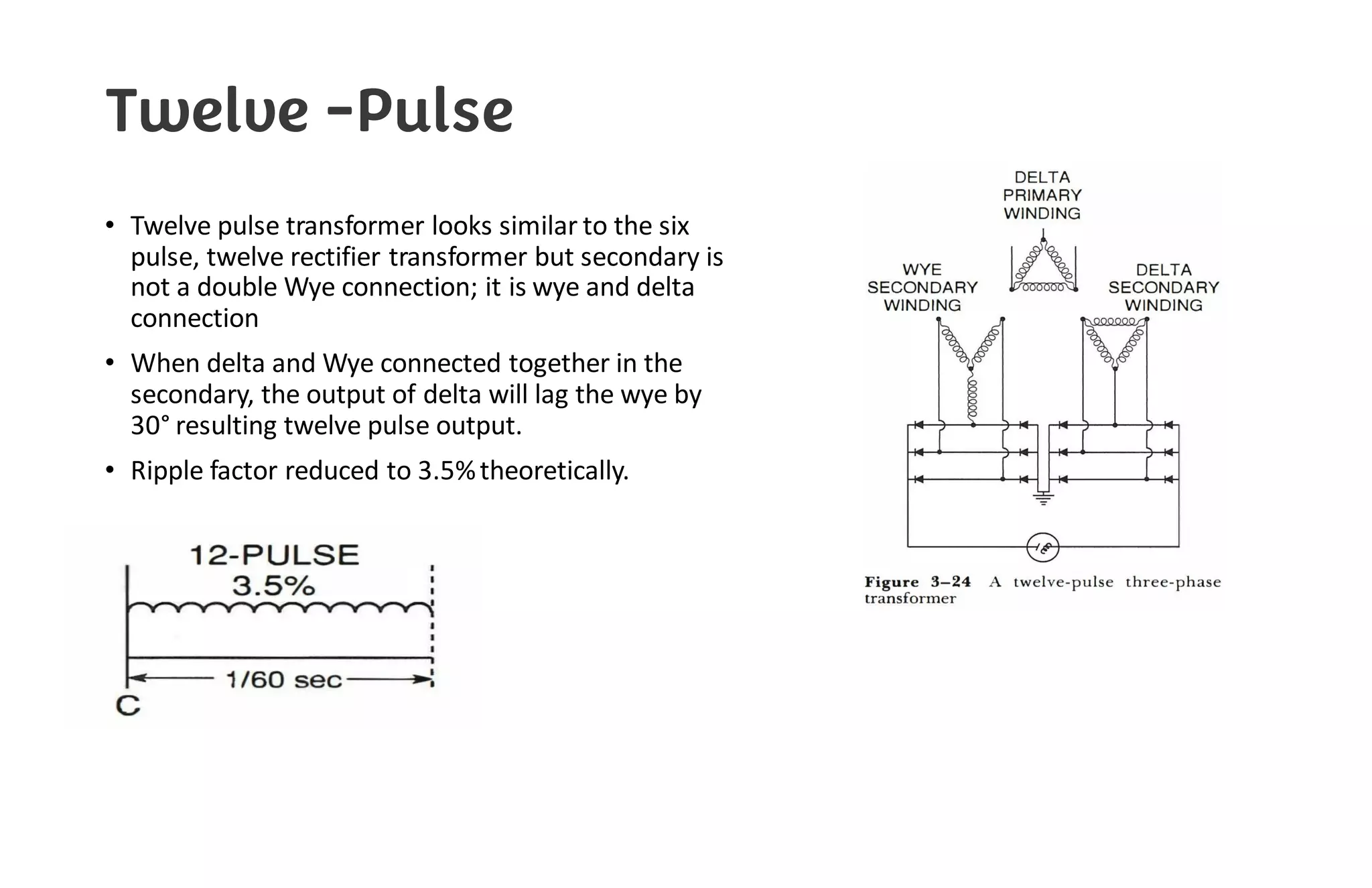
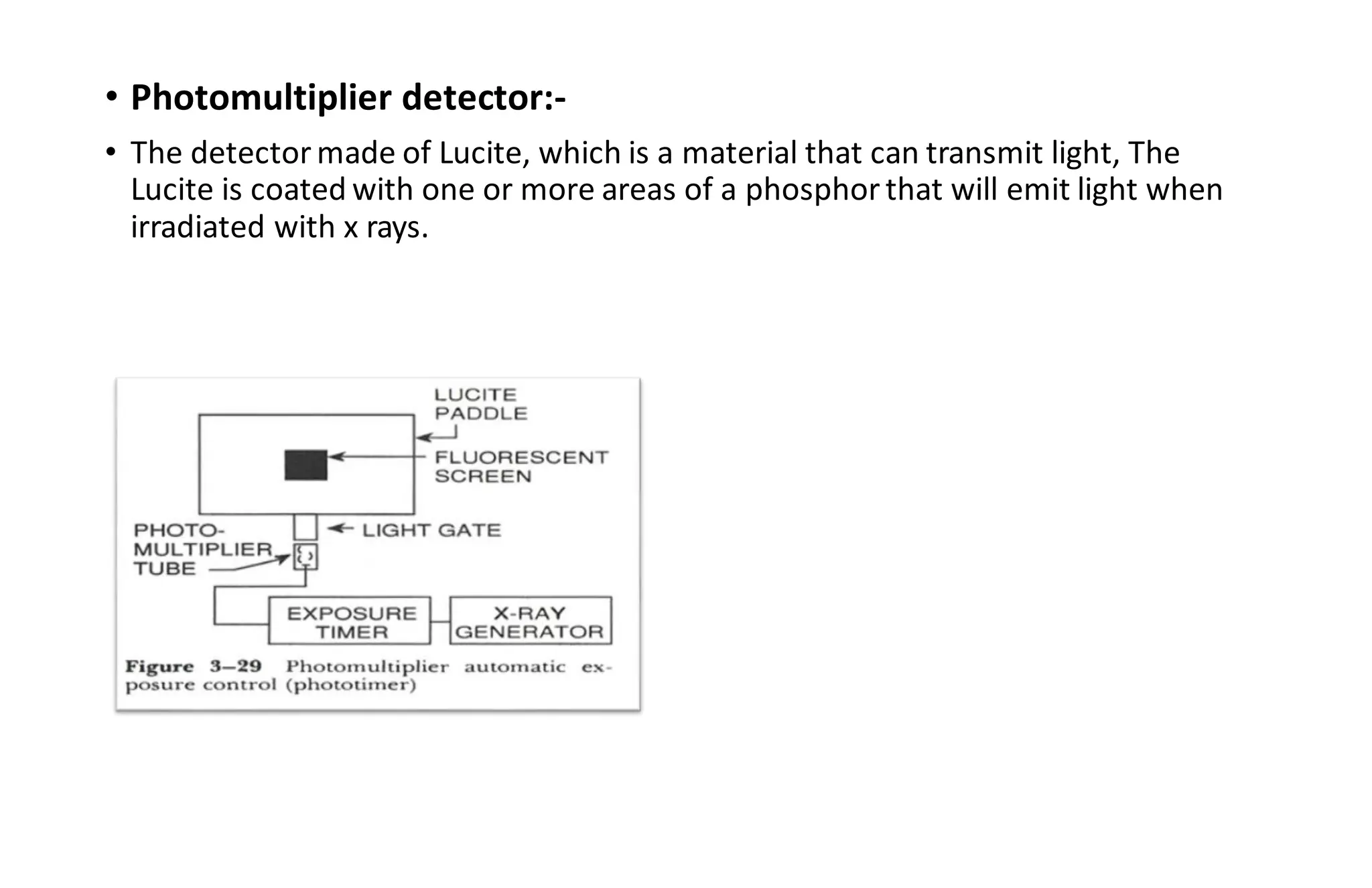
This document provides information about x-ray generators. It discusses the key components of x-ray generators including transformers, rectifiers, and exposure timers. The transformers are used to increase or decrease voltage in the circuit. Rectifiers convert alternating current to direct current. Exposure timers control the length of x-ray exposures. The document also describes different types of x-ray generators such as three-phase generators, power storage generators, and automatic exposure control systems.