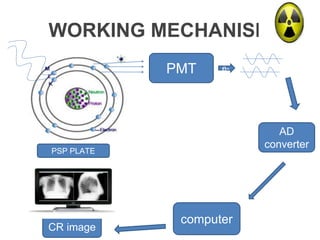
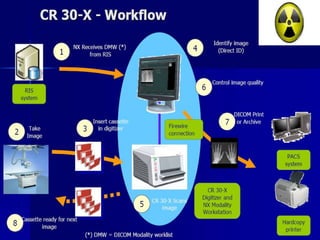
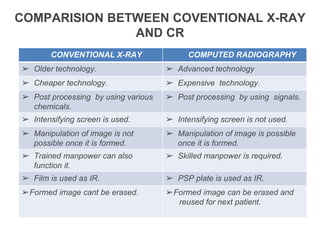
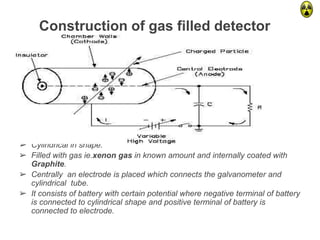
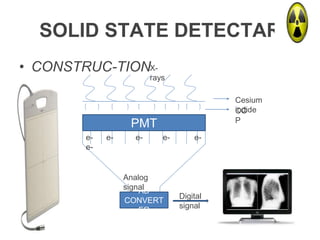
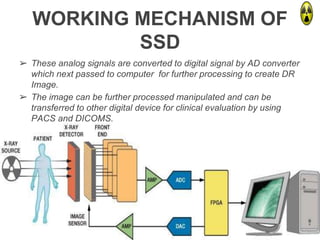
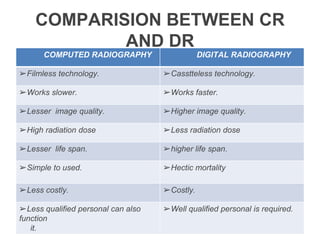
This document provides an overview of computed radiography (CR). It discusses the history and components of CR, including imaging plates, digitizers, and printers. The working mechanism is explained, from image acquisition using an imaging plate exposed to X-rays, to laser scanning to release photons detected by a photomultiplier tube and digitized to form the image. Advantages include comparable image quality to film and ability to process images digitally. The document also compares CR to conventional X-ray and digital radiography.