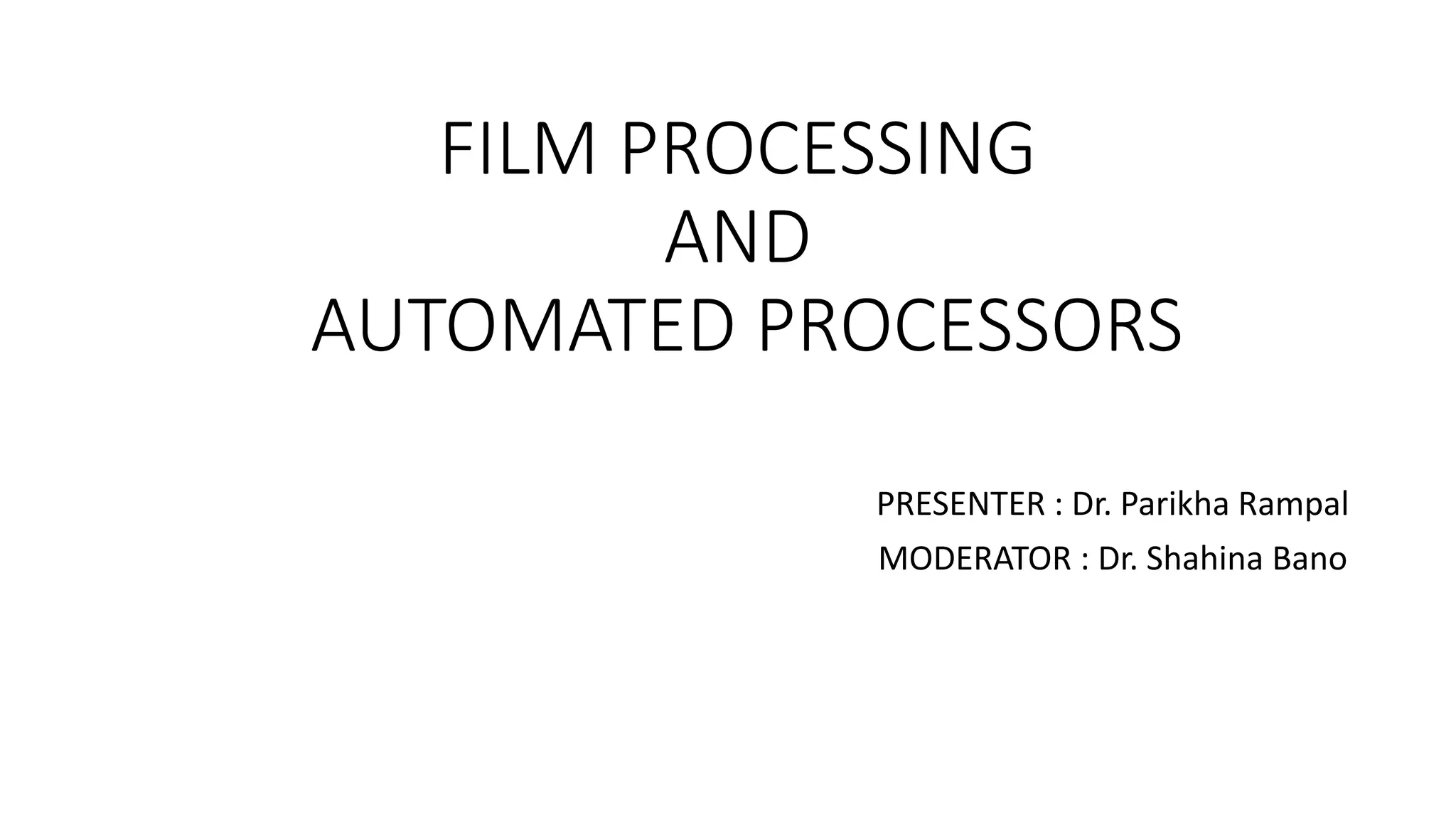
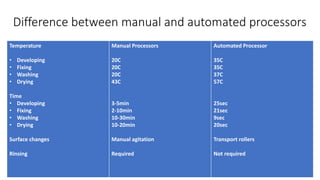
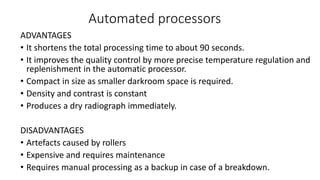
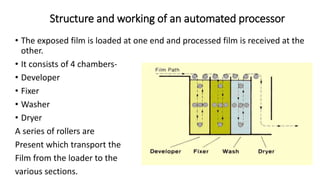
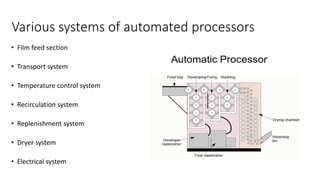
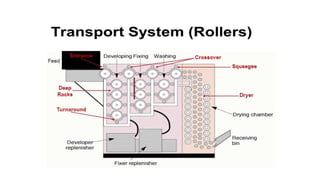
The document outlines the film processing steps for X-ray films, including development, fixing, washing, and drying, detailing the chemical reactions and agents involved. It contrasts manual and automated processing methods, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of automated systems. Additionally, it discusses the factors affecting each processing stage and the structure and functioning of automated processors.