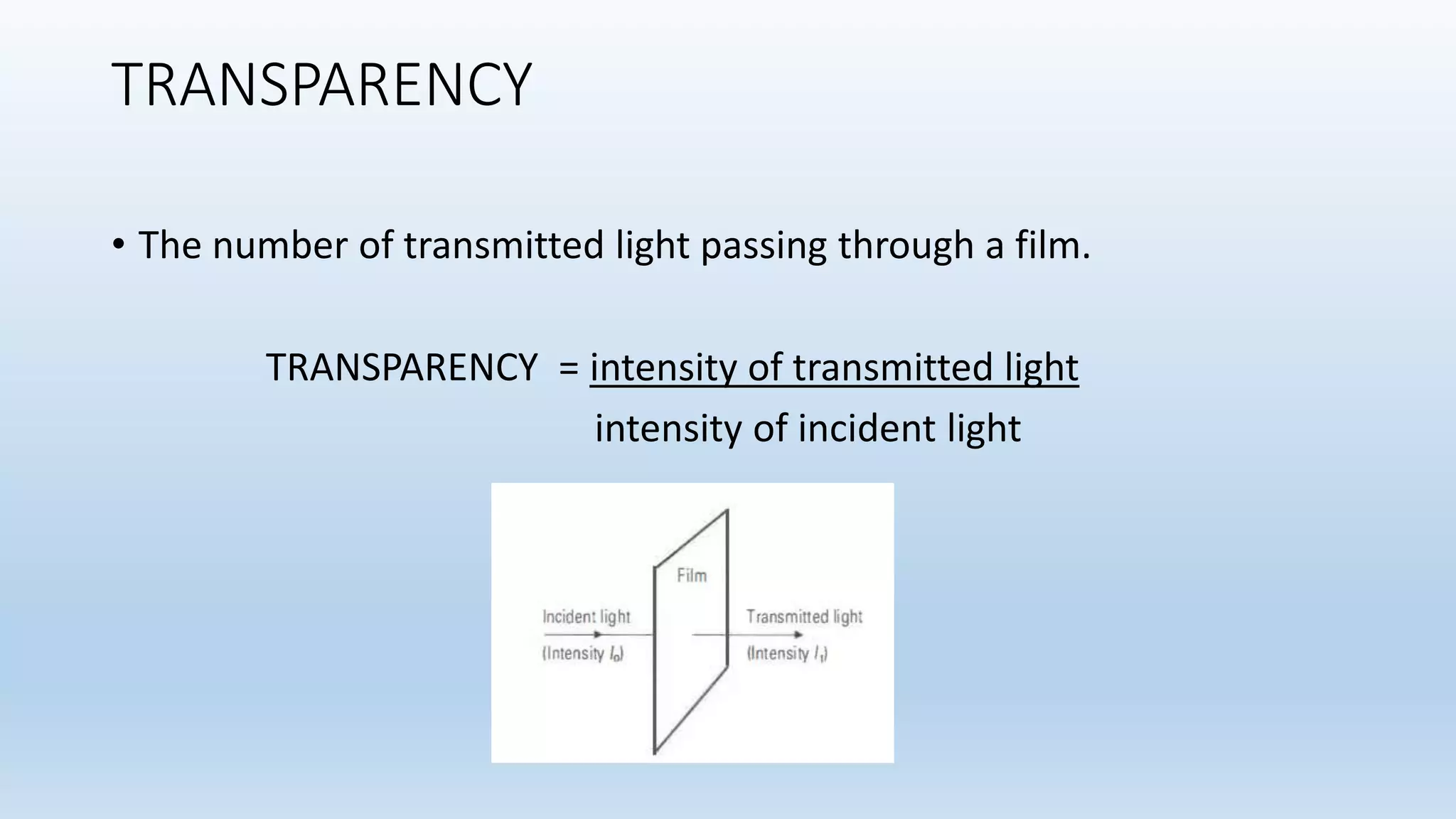
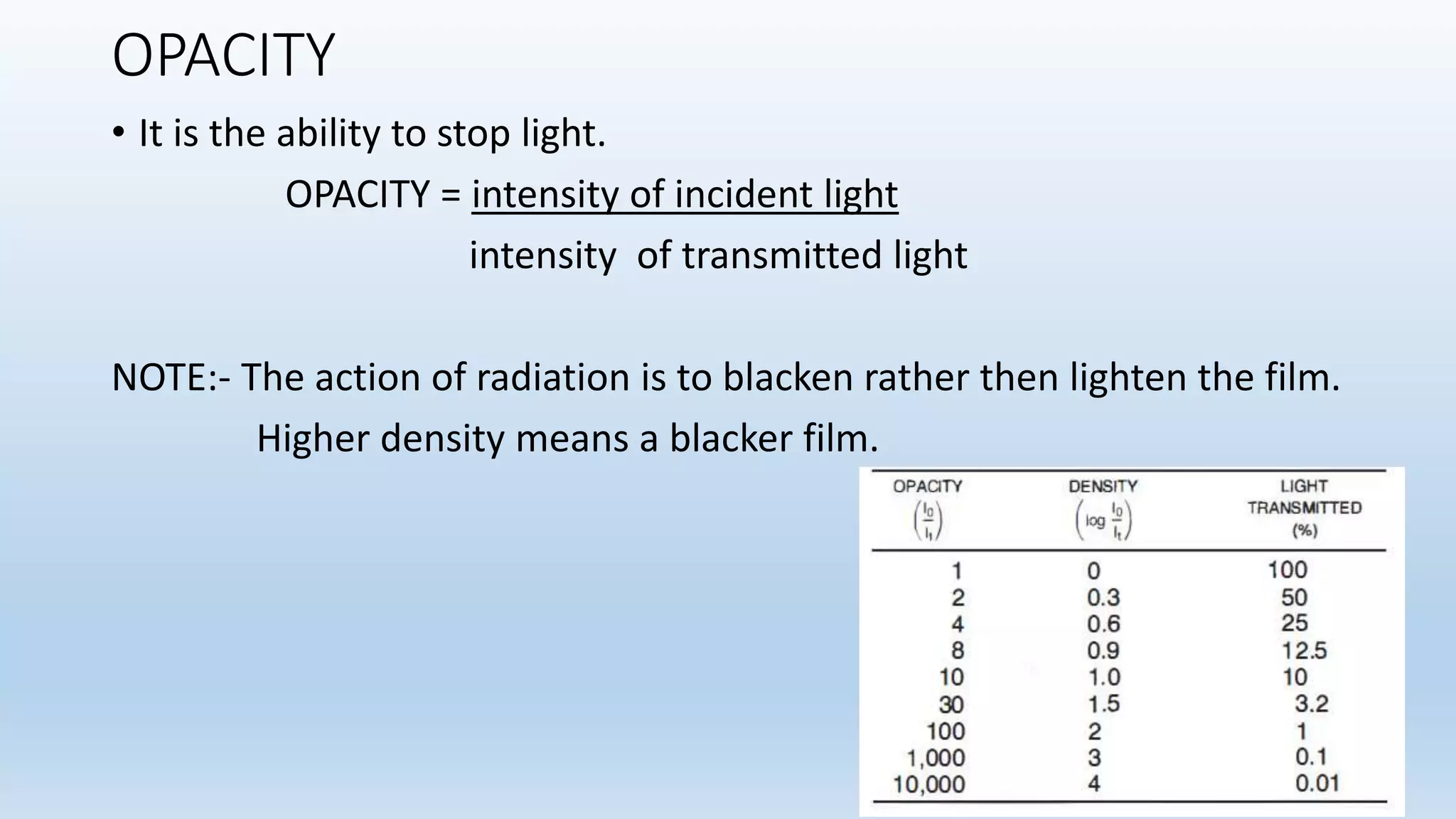
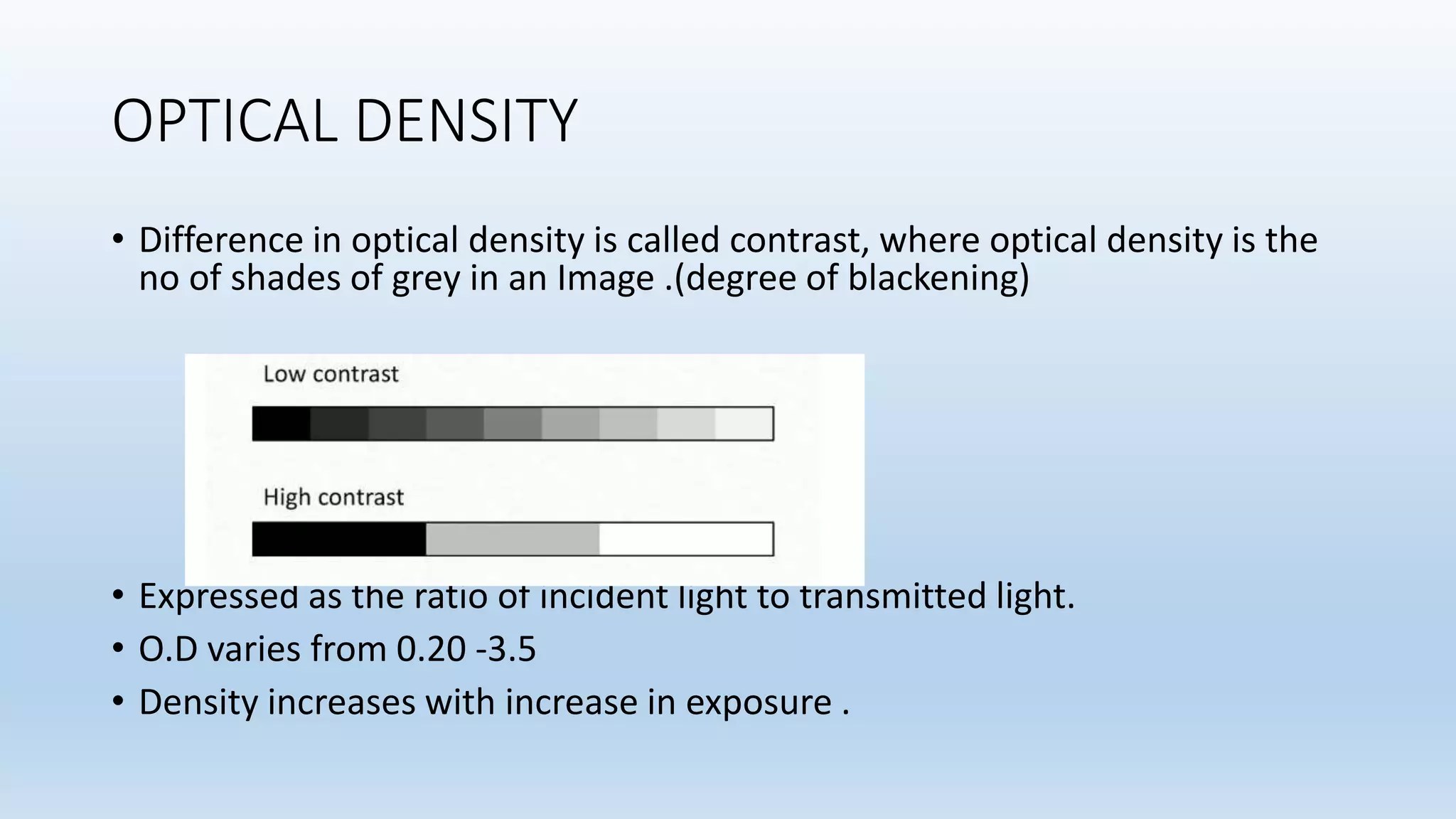
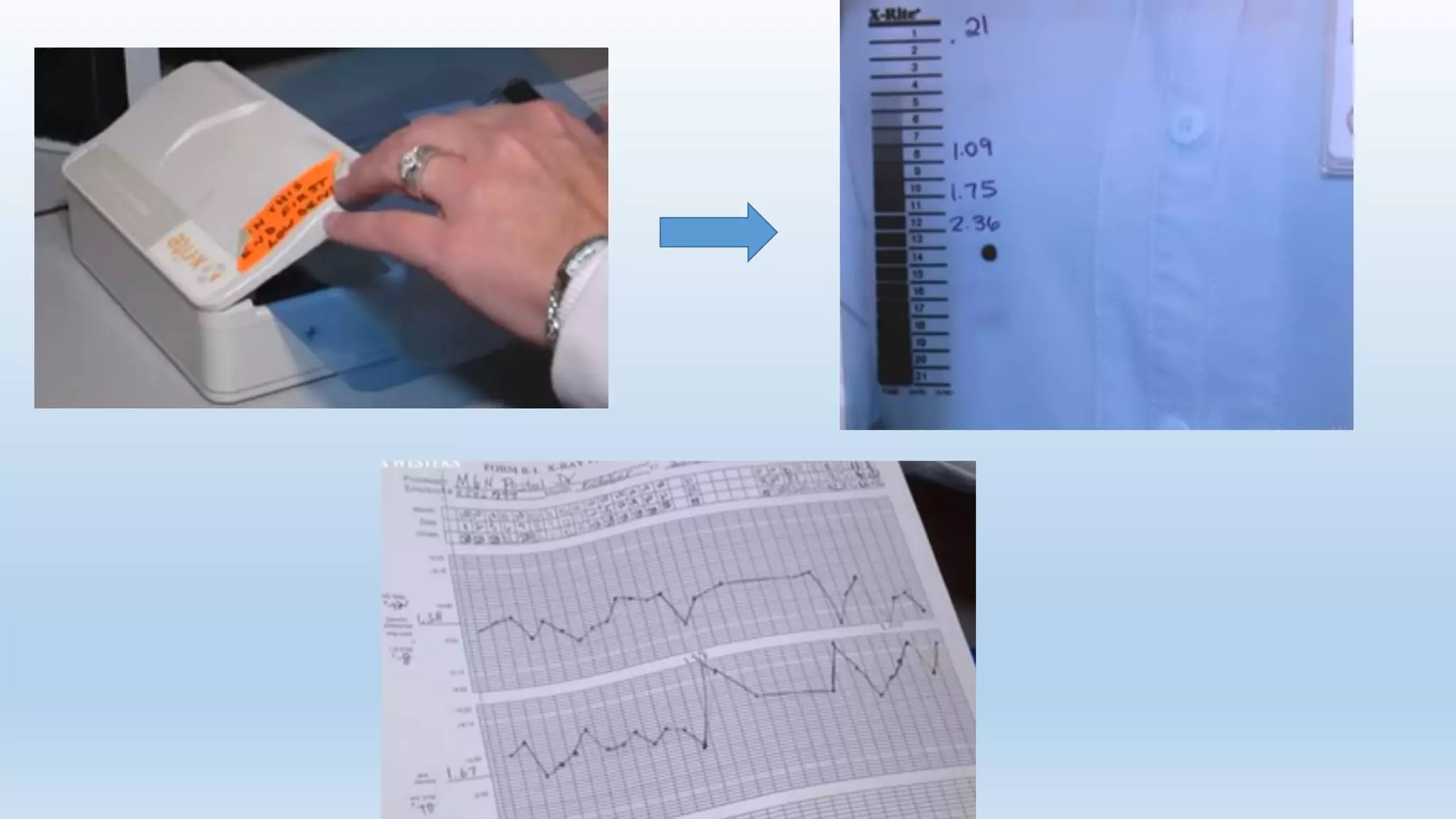
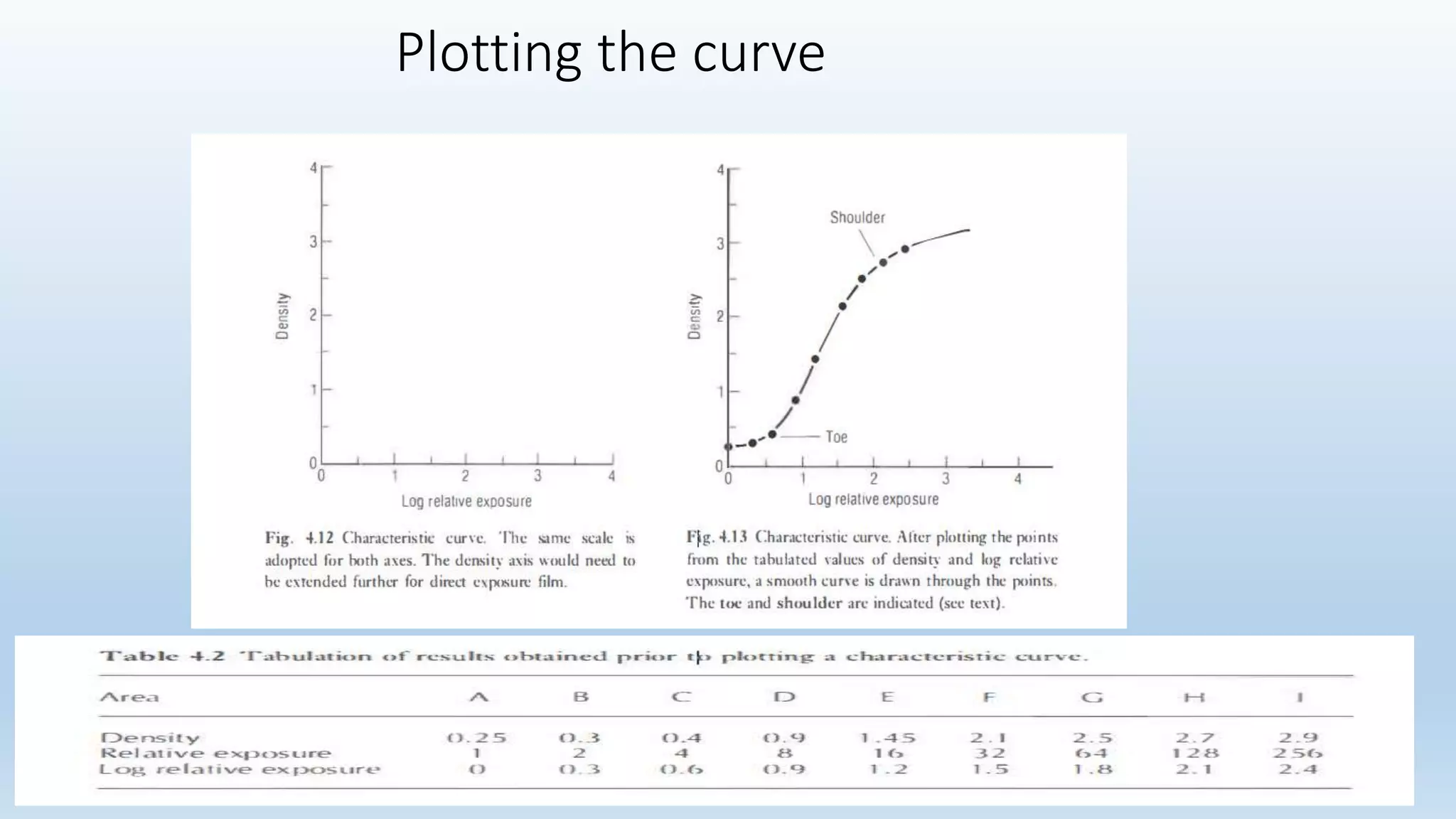
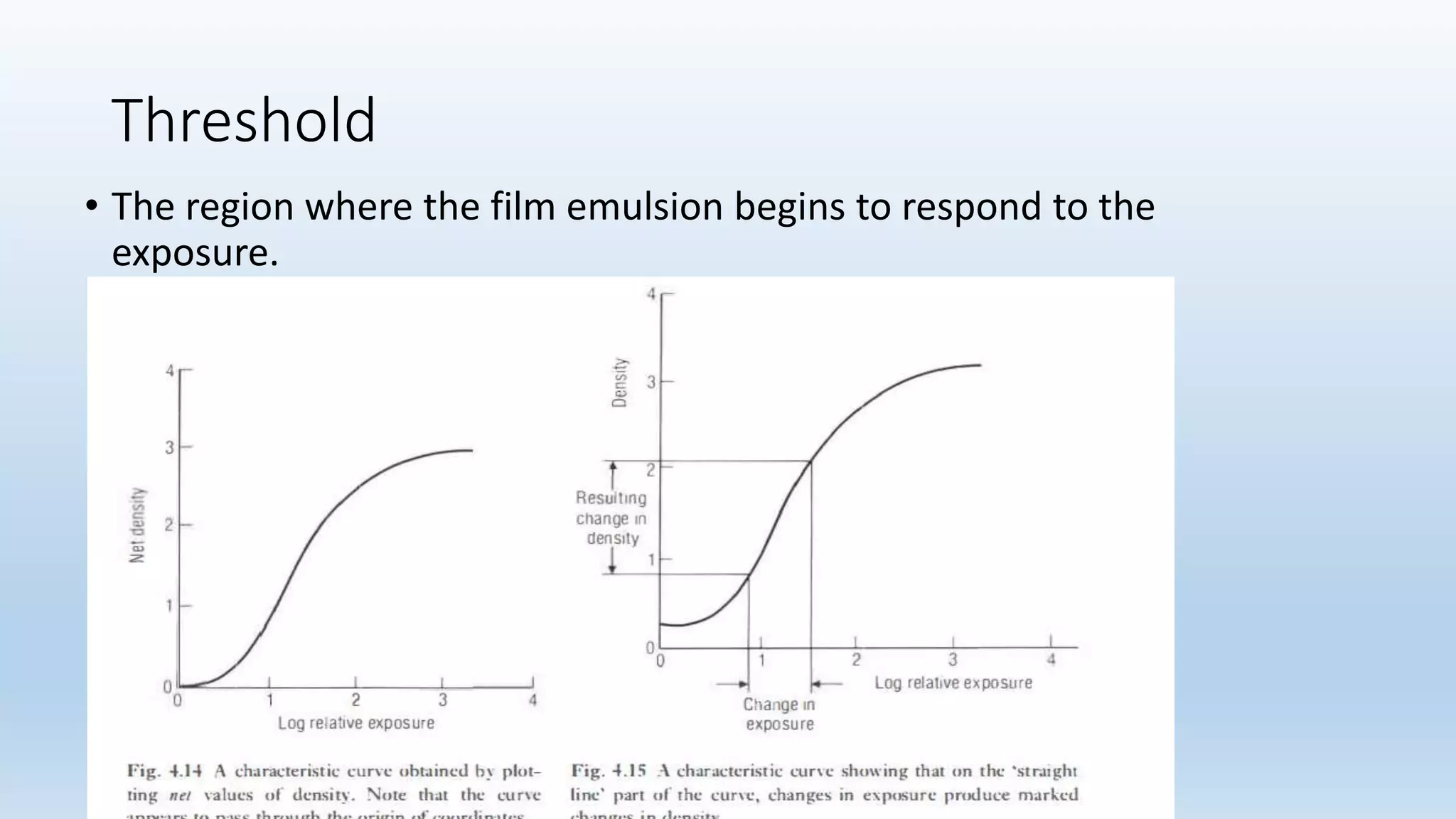
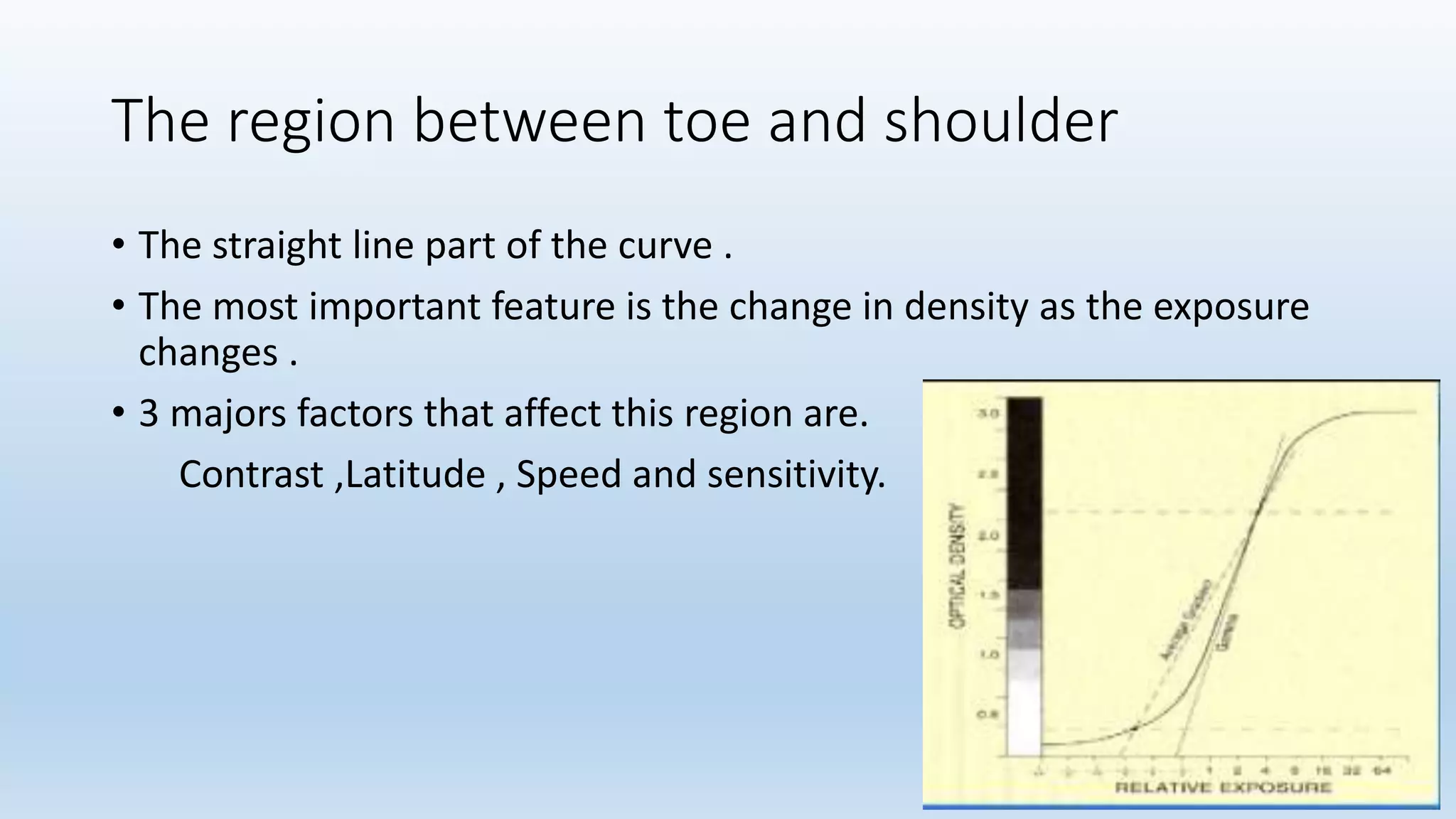
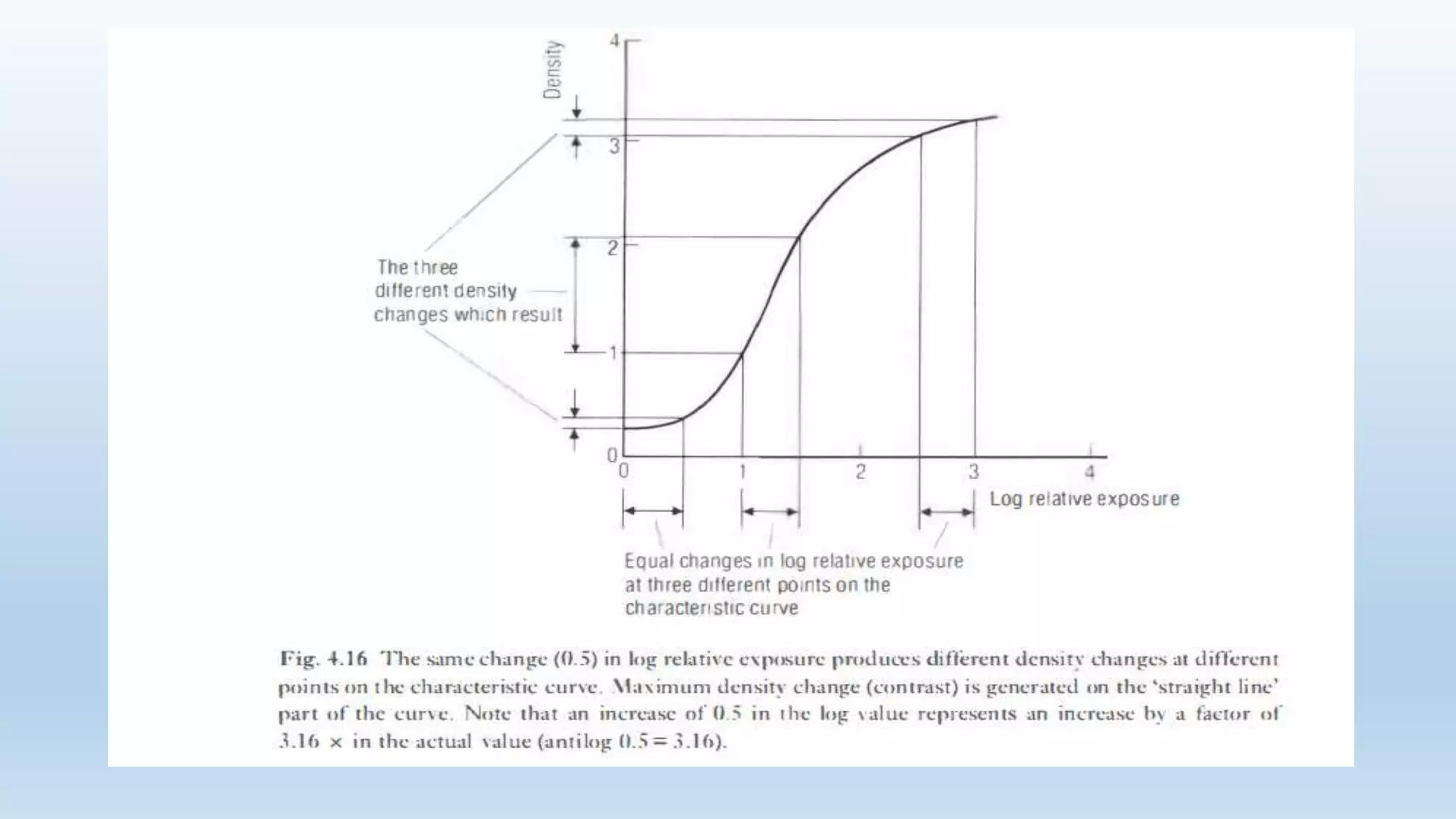
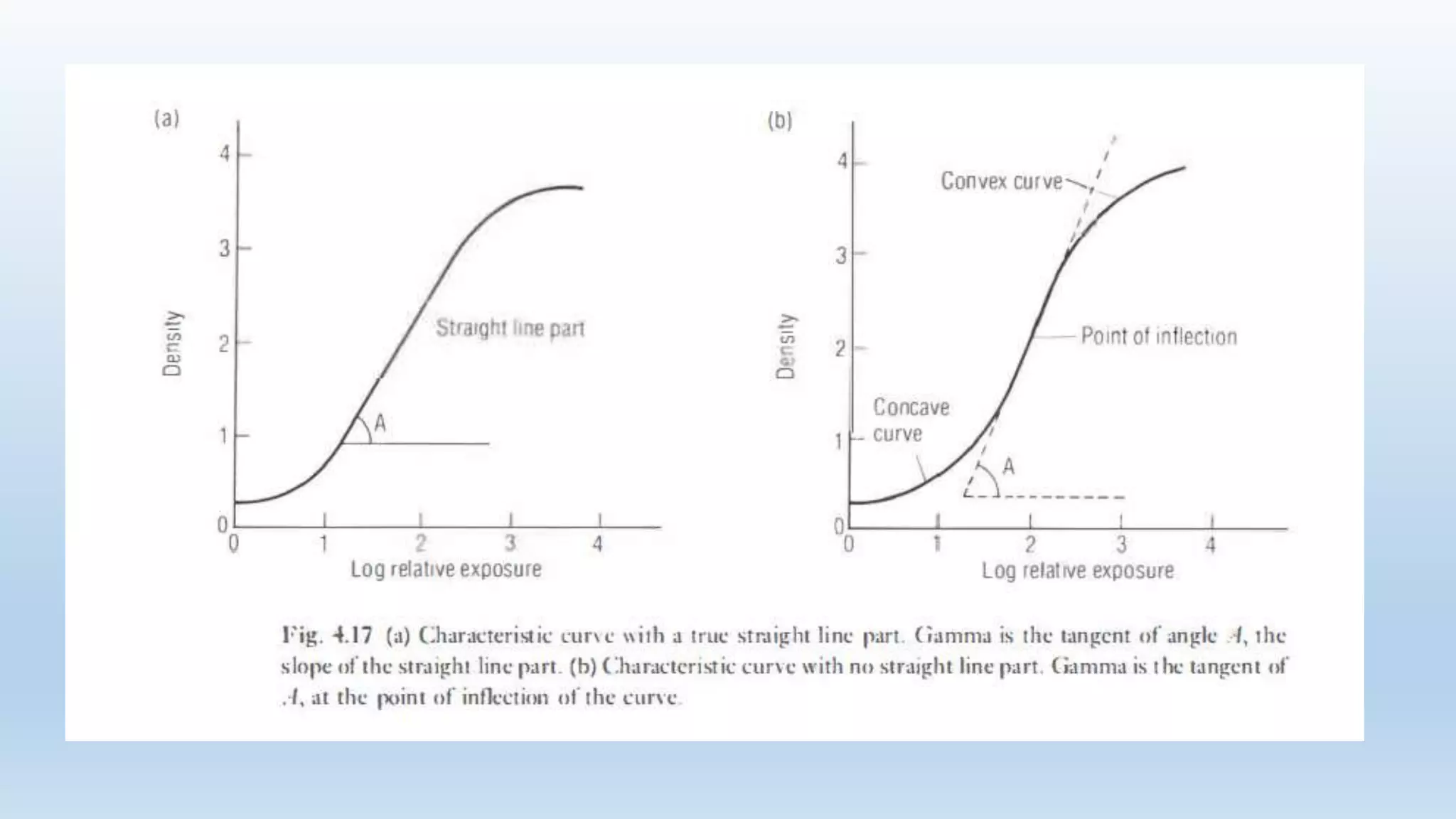
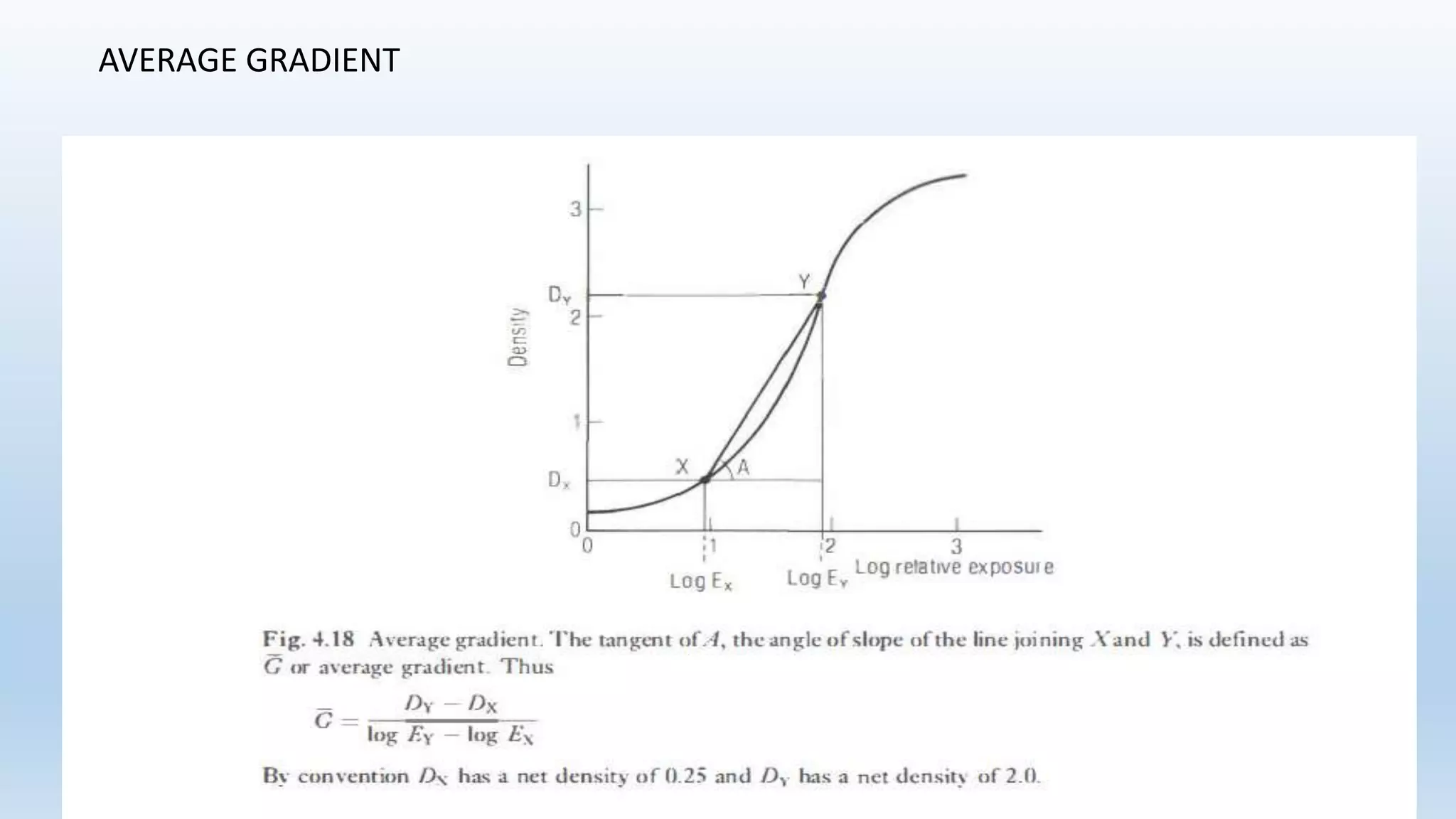
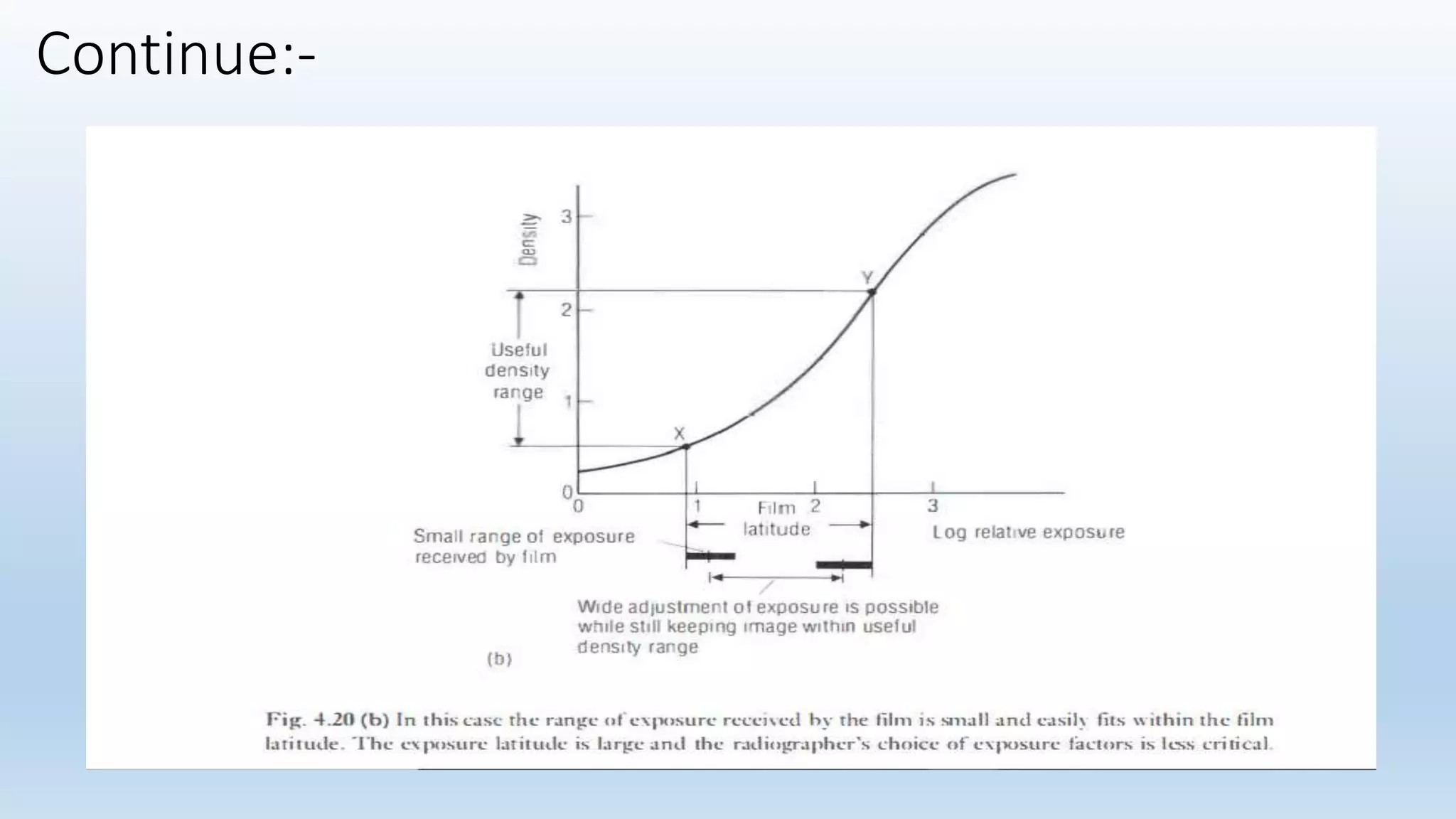
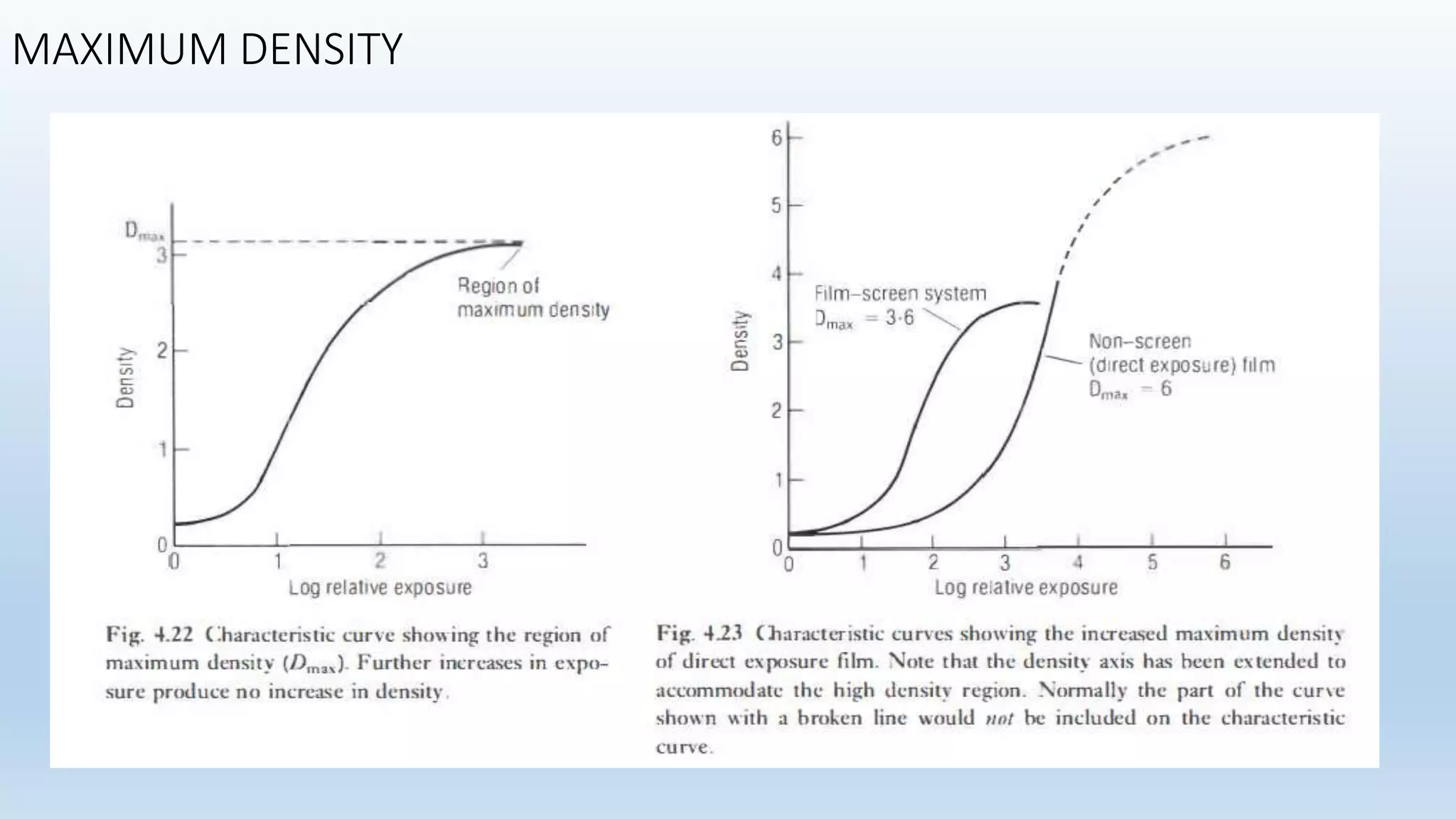
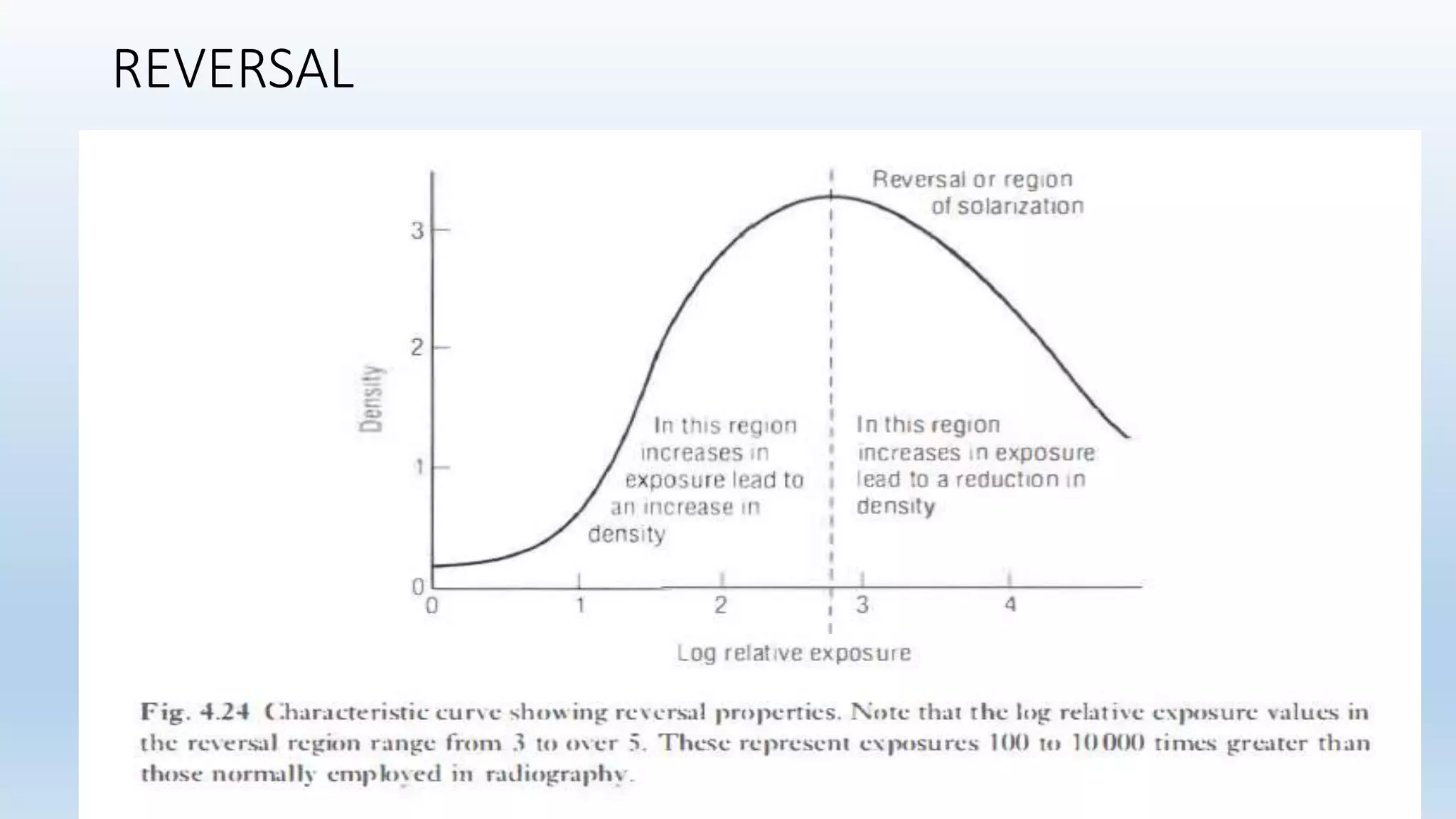
Sensitometry is the study of how photo-sensitive materials respond to radiation exposure. A characteristic curve plots optical density versus log relative exposure and shows the material's response. The curve has three key regions - the toe (minimum exposure), linear region (useful range), and shoulder (maximum exposure). Analyzing the curve provides information on film properties like speed, contrast, and latitude to optimize exposures and quality control.