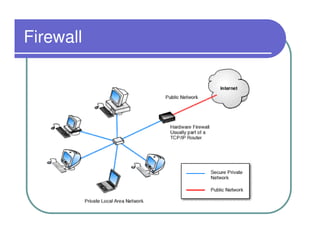
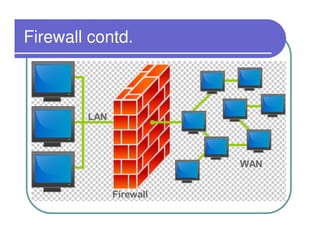
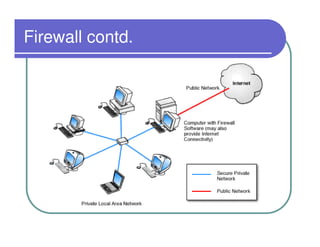
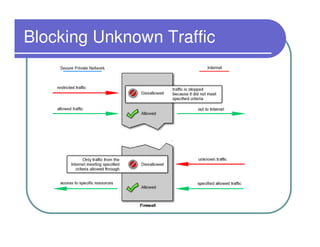
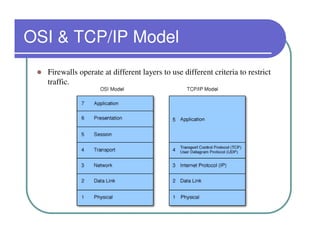
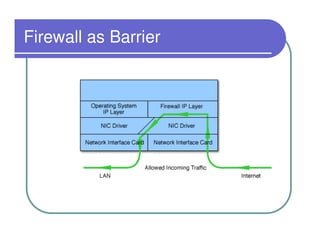
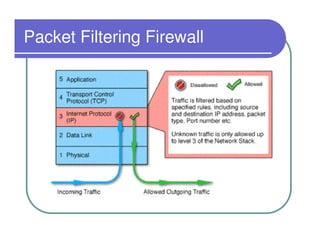
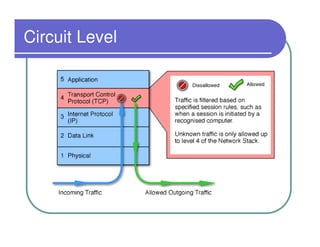
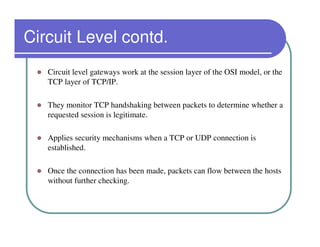
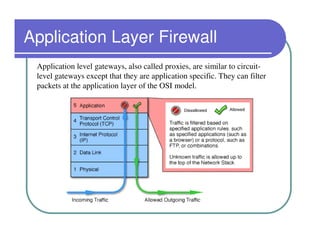
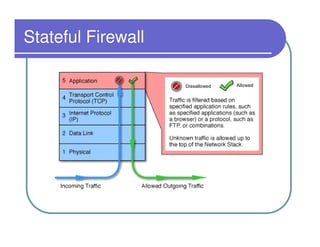
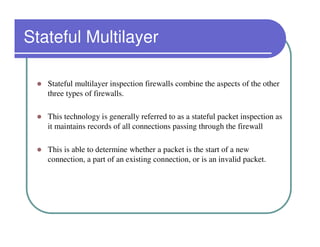
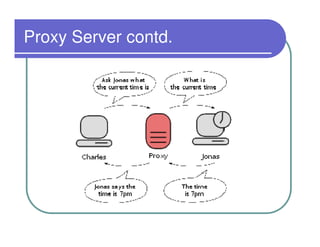
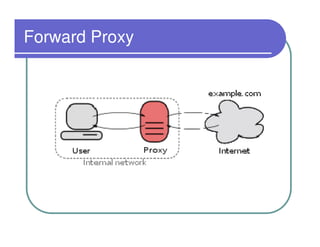
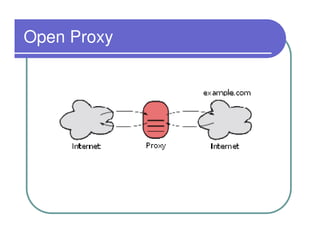
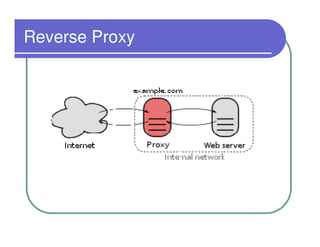
A firewall sits between private and public networks like the Internet to protect computers from unauthorized access. There are different types of firewalls that operate at different layers, including packet filtering firewalls that work at the network layer, circuit-level firewalls that work at the session layer, and application-level firewalls that filter at the application layer. Stateful multilayer firewalls combine aspects of these approaches and can determine if a packet is part of an existing connection. Proxy servers act as intermediaries for client requests to other servers and can filter traffic according to rules.