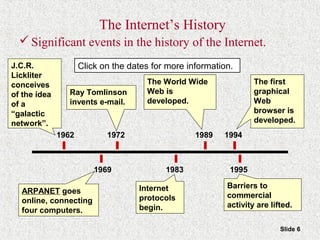
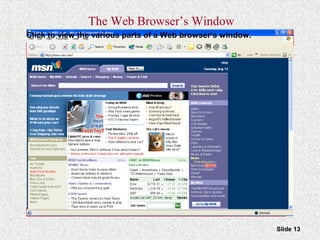
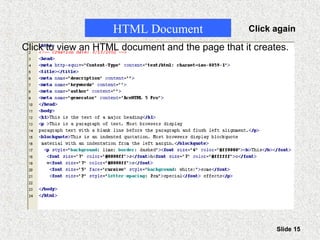
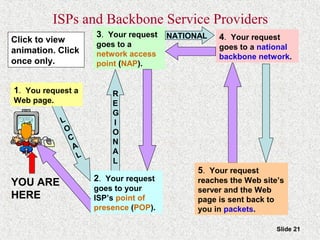
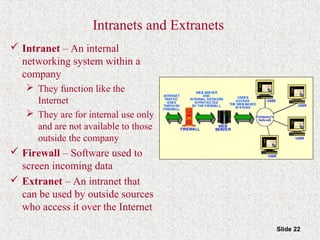
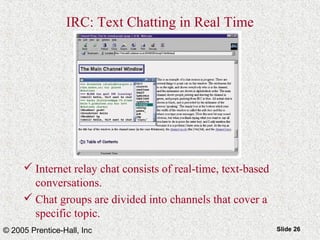
This document provides an overview of the Internet and World Wide Web. It discusses the history and significance of the Internet, how it works, common Internet protocols, accessing the Internet, popular Internet services like email and the World Wide Web. It also covers how to effectively search the Web using techniques like Boolean operators and keywords, and how to evaluate the reliability of information found on web pages.