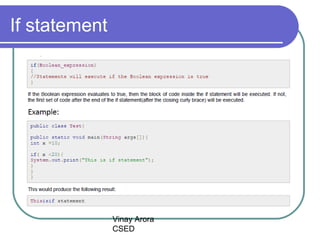
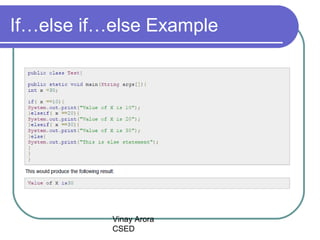
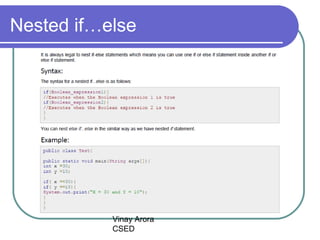
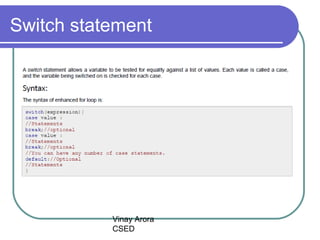
This document discusses decision making statements in Java, specifically if statements, if-else statements, if-else if-else statements, nested if statements, and switch statements. It explains that if statements and switch statements are the two types of decision making statements in Java. Switch statements can only use byte, short, int or char variables, and cases must contain a constant or literal of the same type as the switch variable. When a case matches the switch variable, code will execute until a break statement. A default case can specify code to run if no other cases match.