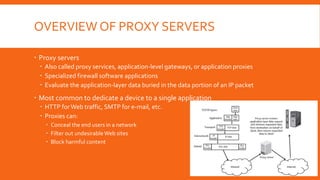
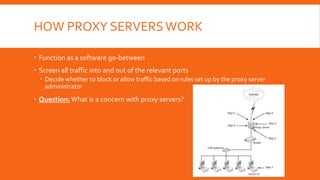
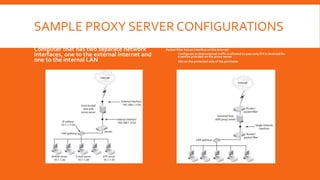
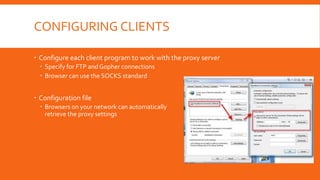
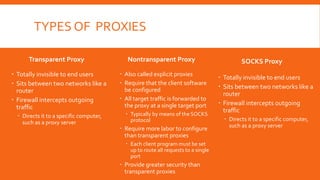
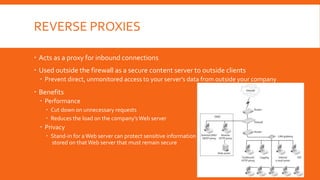
Proxy servers act as intermediaries between internal and external networks, screening traffic and enforcing security policies. They can conceal internal network structure, filter undesirable content, and provide detailed logs. Proxy servers differ from packet filters in that they operate at the application layer and can reconstruct packets with new source IP information to shield internal hosts. Common configurations involve a computer with two network interfaces, one internal and one external. Benefits include concealed clients, blocked URLs and content, and robust logging. Proper configuration of both the proxy server and client software is required.