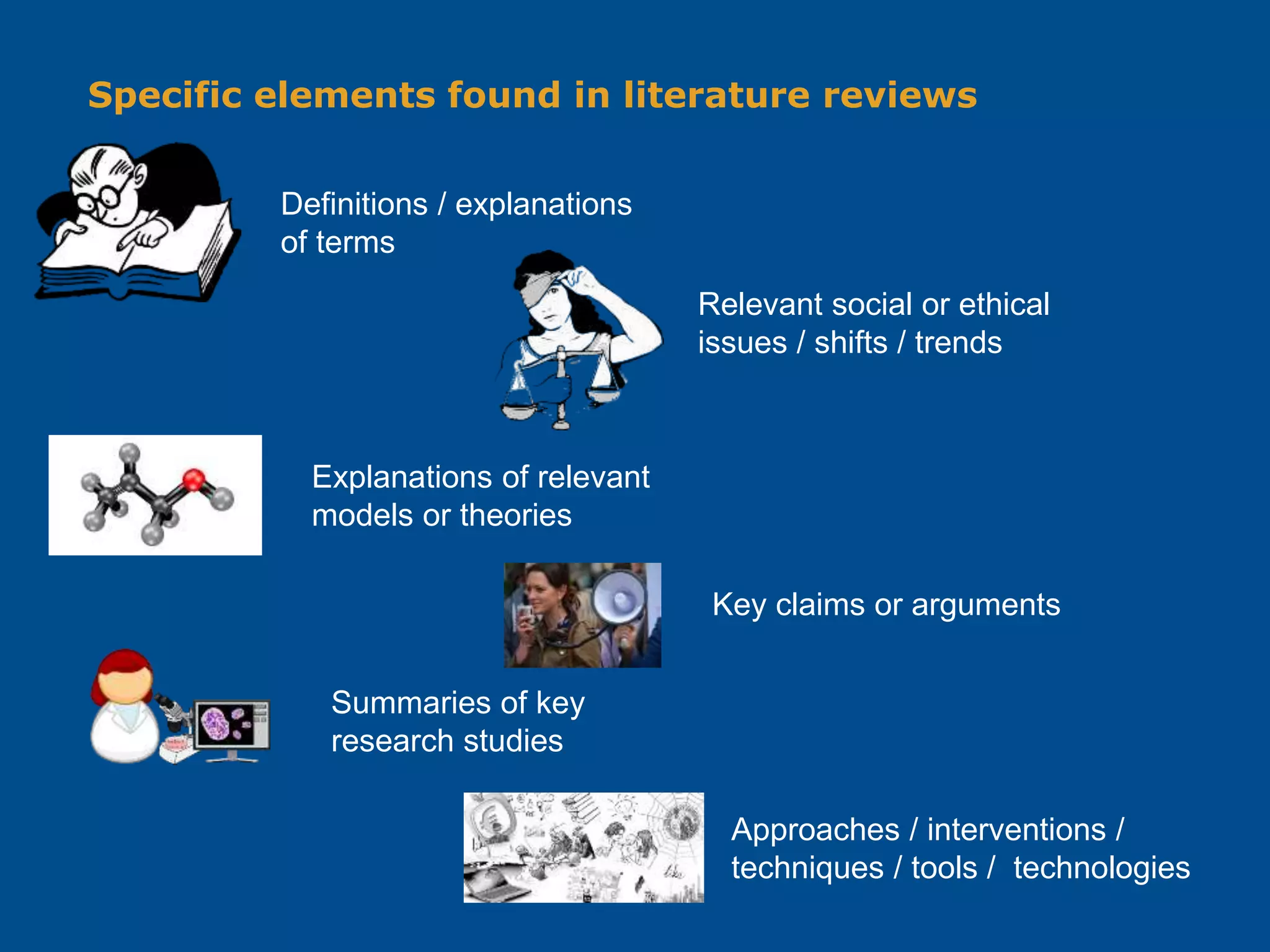
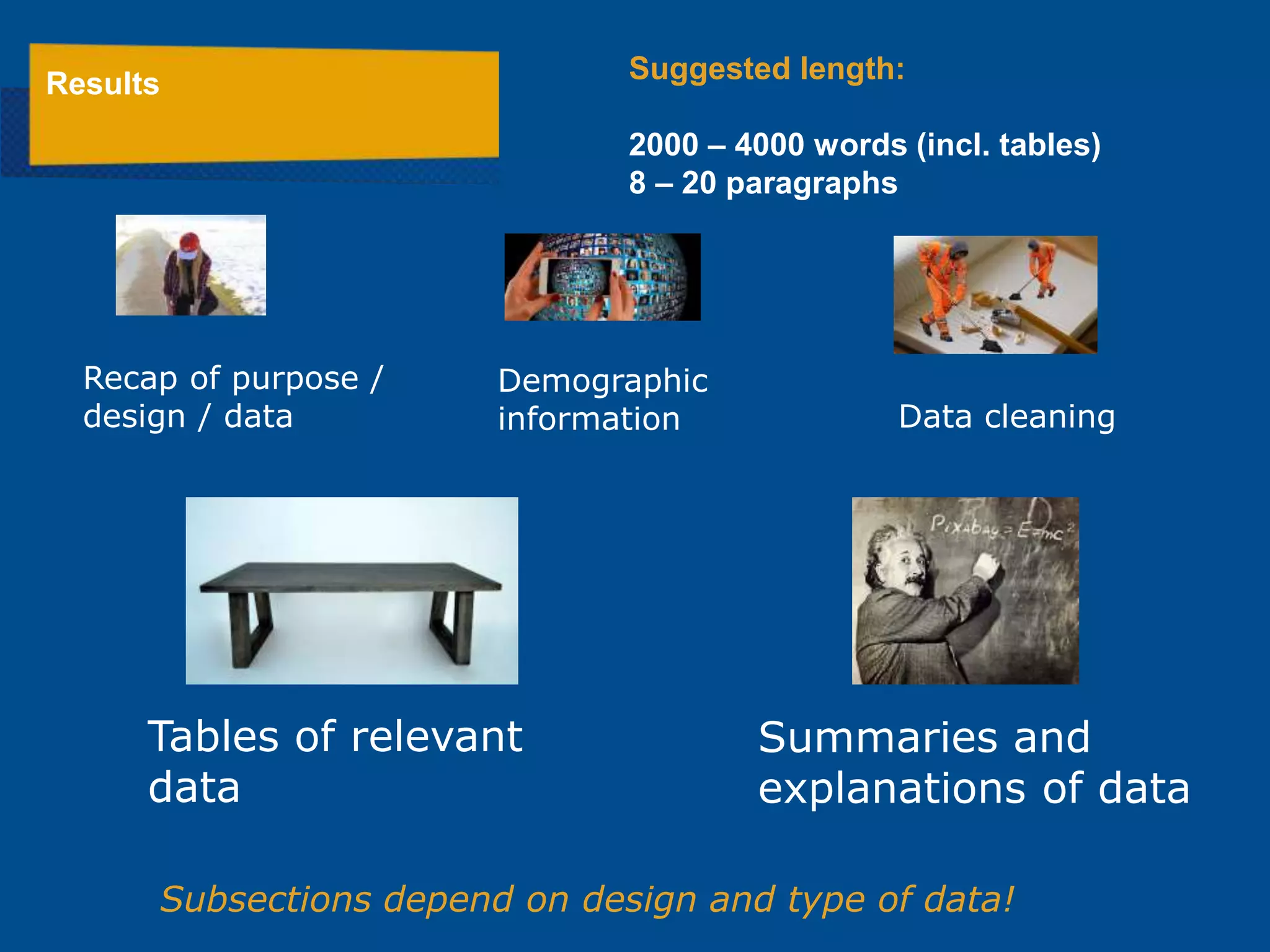
The document provides a comprehensive guide for writing a research report specific to the course 271.720 at the National Centre for Teaching & Learning. It outlines the structure of the report, including sections like introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion, along with sample phrases and lengths for each section. Additionally, it encourages interactive learning through quizzes and includes references to valuable readings on research methods.










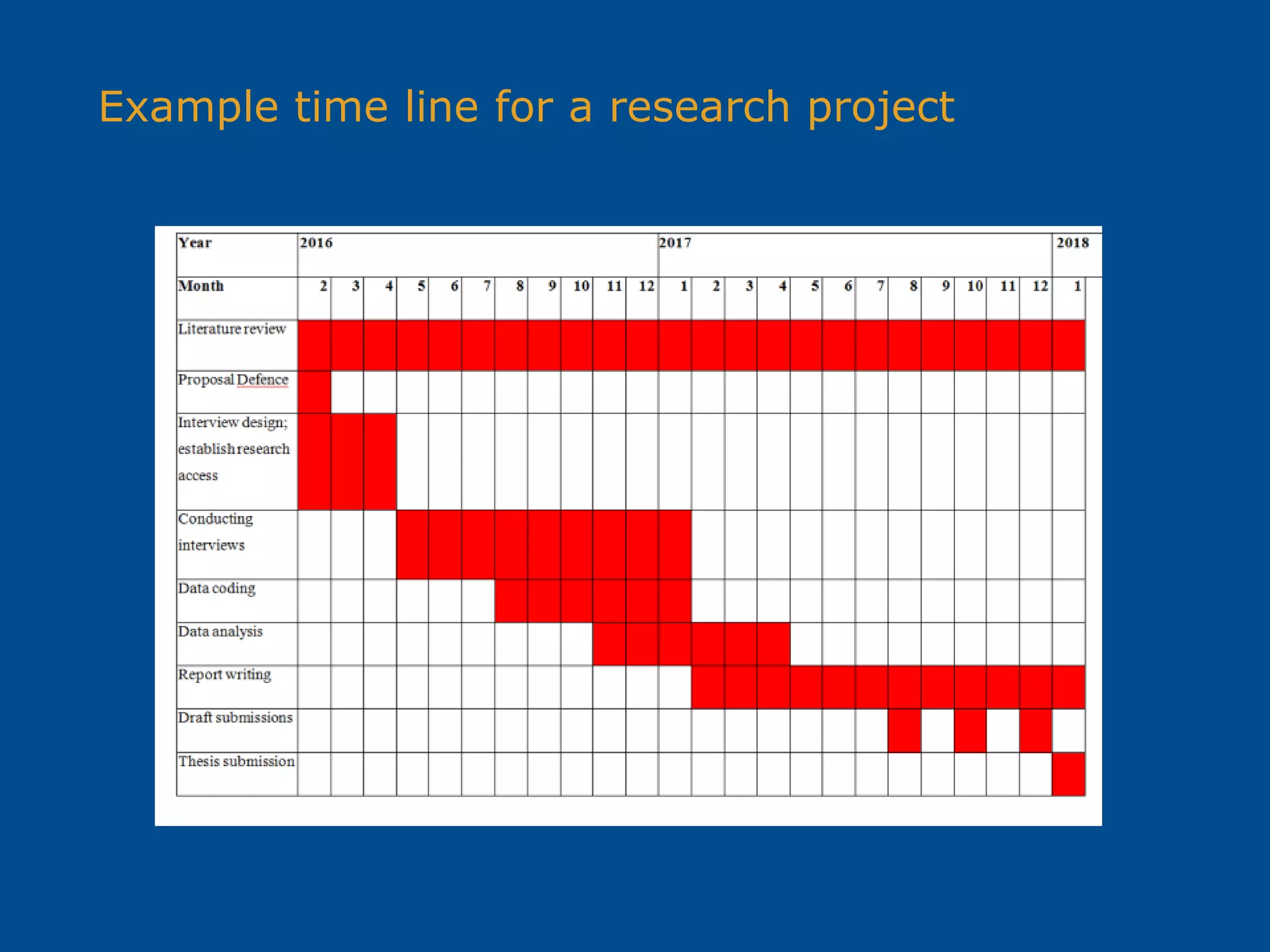


![Research report structure
Report A Report B Report C
Total Pages [excl.
refs & appendices]
29 36 24
Introduction
200 350 350
Lit review
1, 800 3, 700 1, 700
Method
1, 200 3, 500
(combined
350
Results
4, 000 (incl.
words in tables)
Method &
Results)
1, 350
Discussion
2, 800 2, 300 1, 000
Conclusion
200 300 500
References
33 60 25
Approximate word length of sections of selected 271.720 research reports](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017writingtheresearchreportfor271720-170319062346/75/Writing-a-research-report-14-2048.jpg)