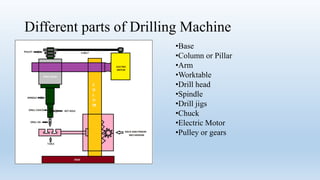
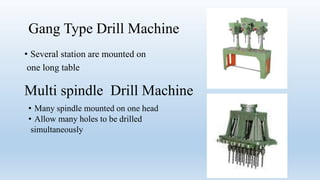
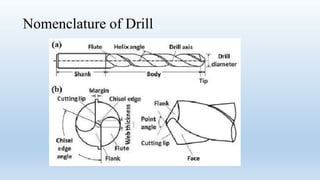
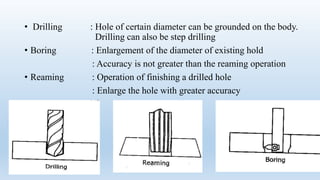
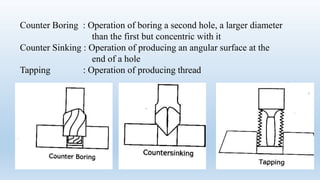
This document discusses drilling machines and drilling processes. It describes different types of drilling machines such as portable, sensitive, radial, upright, and multi-spindle machines. It also discusses the parts of a drilling machine like the base, column, arm, worktable, drill head, spindle, and chuck. Sensitive upright drilling machines are used for light-duty drilling of holes up to 15mm and can only be hand fed. Upright drilling machines are for medium and heavy-duty drilling of holes up to 50mm and can be hand or power fed. Radial arm drill machines allow the operator to position the spindle directly over the workpiece. Multi-spindle and gang-type drill machines can drill multiple holes simultaneously