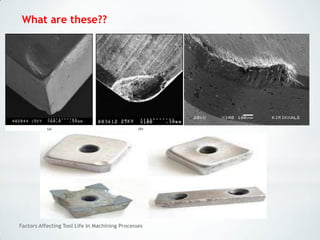
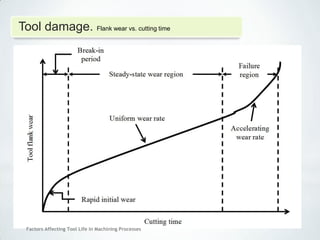
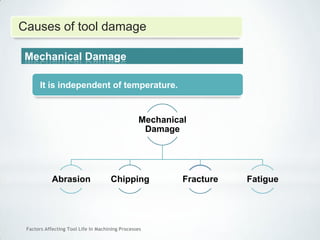
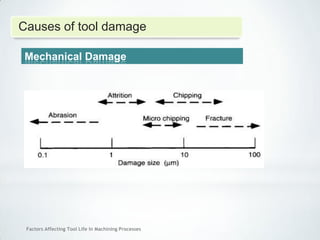
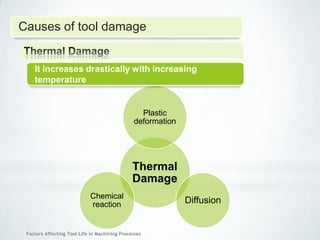
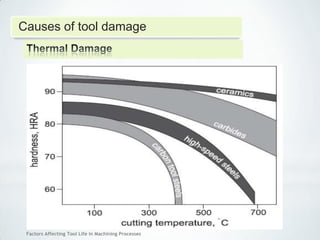
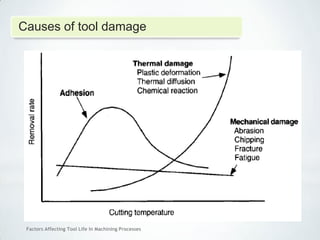
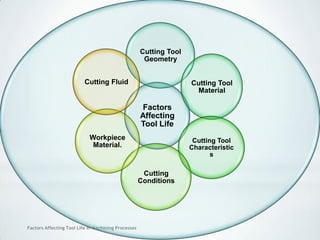
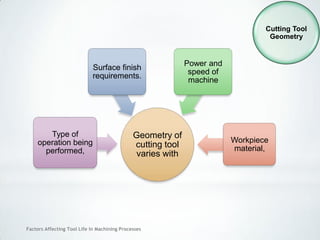
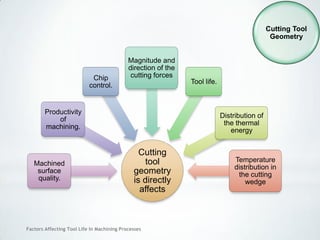
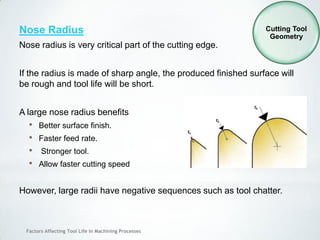
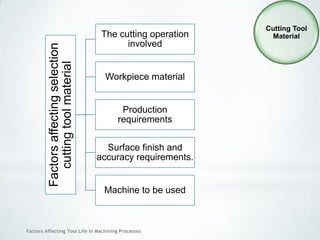
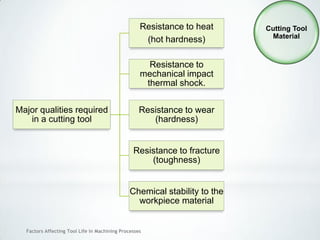
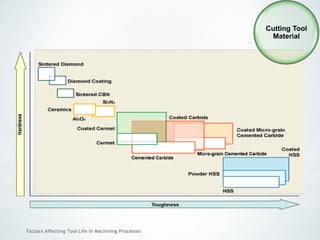
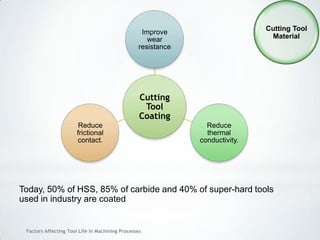
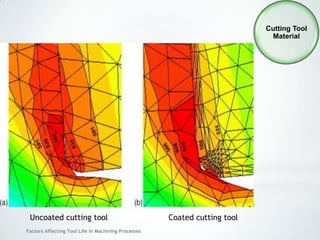
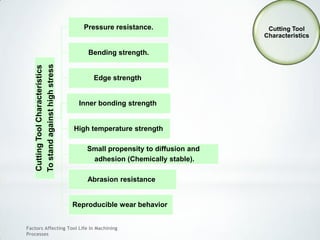
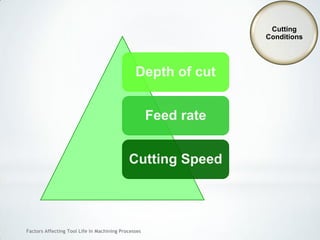
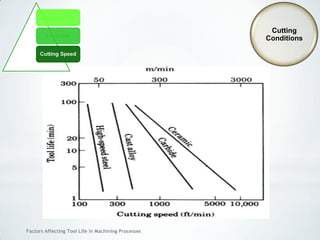
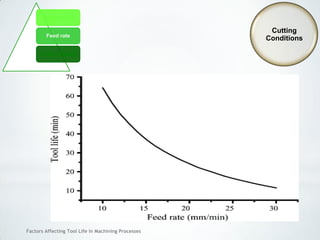
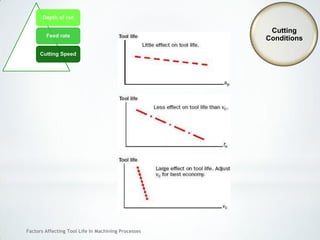
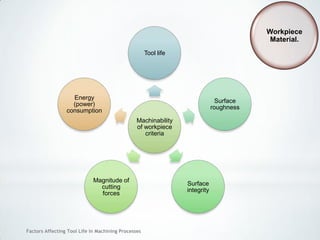
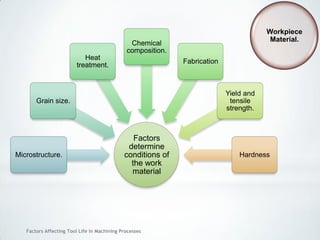
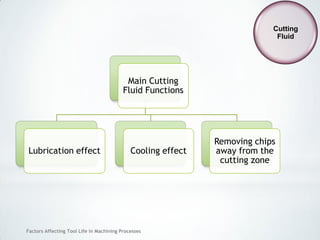
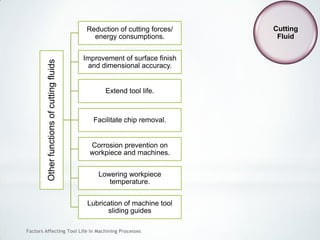
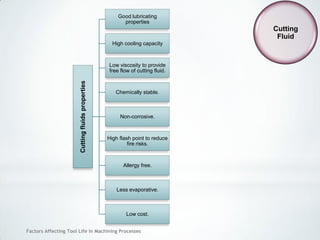
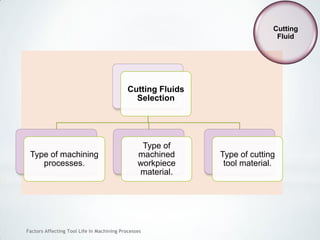
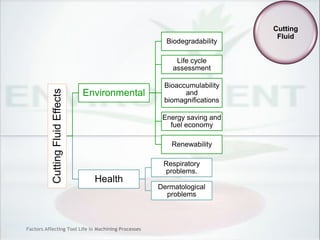
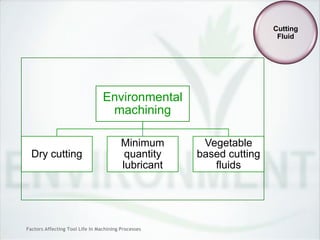
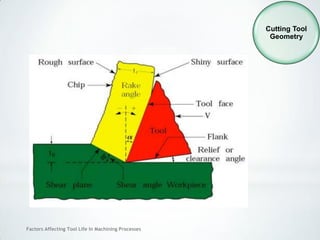
This document discusses factors that affect tool life in machining processes. It identifies the main factors as cutting tool geometry, material, characteristics, cutting conditions, workpiece material, and cutting fluid. Cutting tool geometry influences machined surface quality, productivity, chip control, and forces/temperatures. Cutting tool material and coatings must have properties like heat/wear resistance. Cutting conditions like depth of cut, feed rate, and cutting speed also impact tool life. Workpiece material properties and machinability affect tool performance. Cutting fluids provide lubrication, cooling and chip removal to extend tool life. Environmental impacts of fluids are also considered.