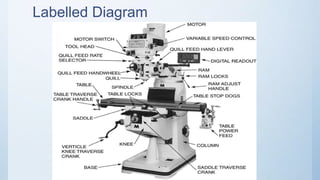
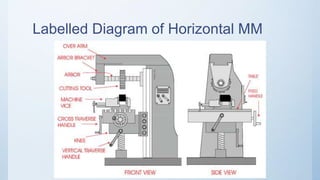
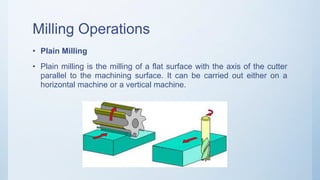
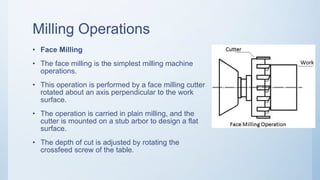
The document provides a comprehensive overview of milling machines, including their types (horizontal and vertical), cutting tools, and typical milling operations. It details the structure and function of various machine parts, such as the spindle, knee, and table, and outlines specific milling processes like face milling and gear cutting. Additionally, the document compares vertical and horizontal milling machines regarding cost, surface finish, and operational efficiency.