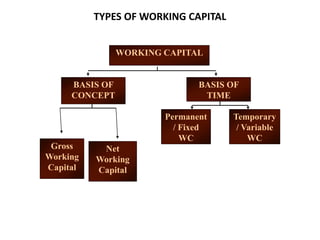
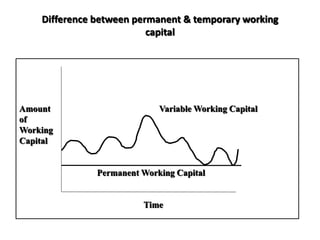
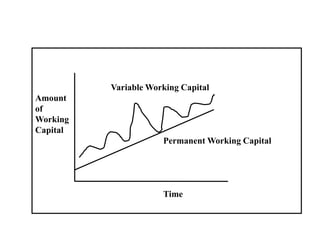
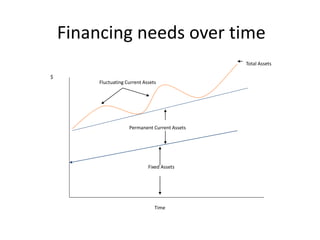
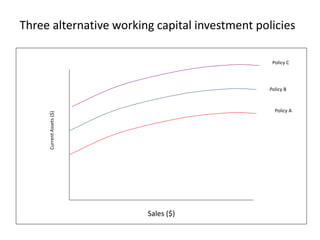
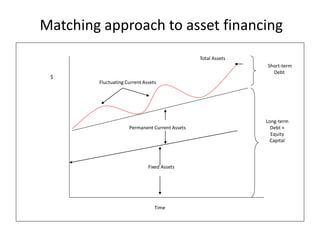
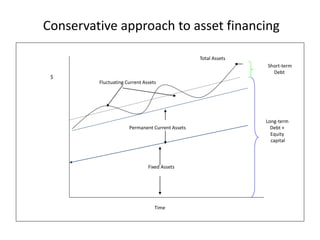
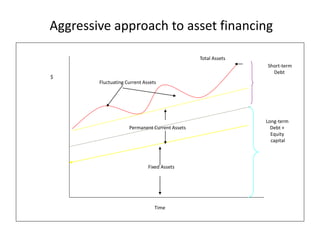
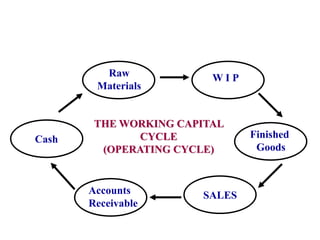
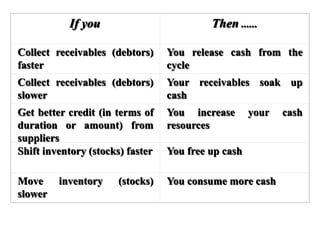
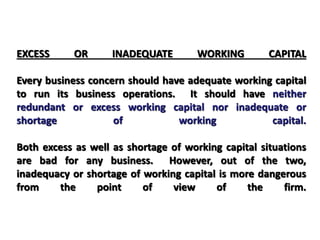
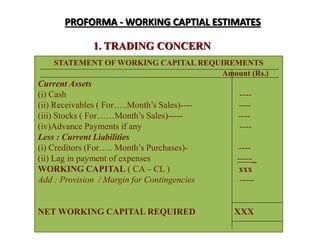
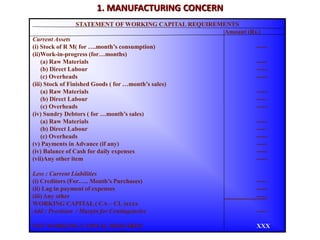
Working capital refers to a company's short-term assets and liabilities involved in day-to-day operations. It includes current assets like inventory, cash, and receivables, as well as current liabilities like payables and short-term debt. Managing working capital effectively ensures a company has enough cash to pay bills on time, maintains optimal inventory levels, collects receivables efficiently, and uses short-term financing at low cost. Both excess and inadequate working capital can hurt a business, so companies must forecast needs carefully based on factors like industry, sales, and production cycles.