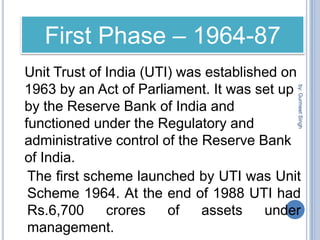
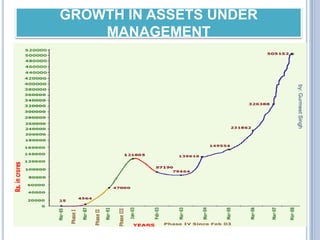
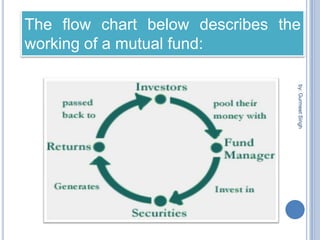
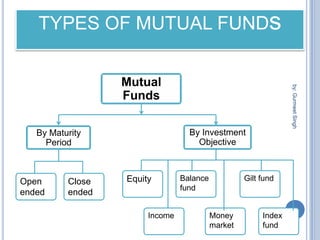
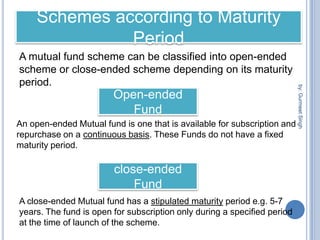
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on mutual funds and their types. It defines a mutual fund as a trust that pools investor savings and invests in stocks, bonds, and other securities. It outlines the history of mutual funds in India in four phases from 1964 to the present. It also describes the different types of mutual funds based on maturity period (open-ended or closed-ended) and investment objectives (growth, income, balanced, money market, gilt, and index funds). Finally, it lists some major Indian mutual fund companies and the advantages of investing in mutual funds.