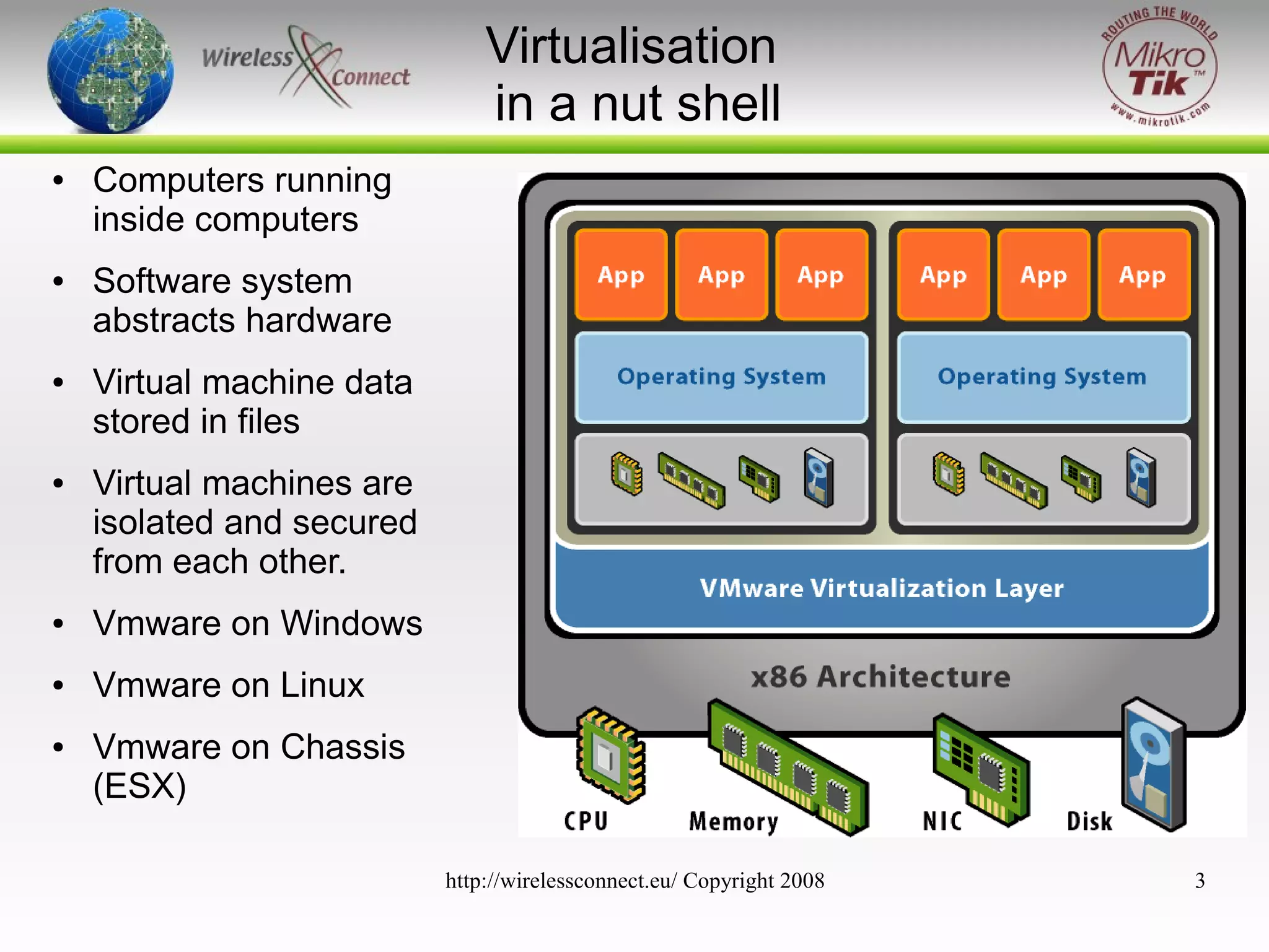
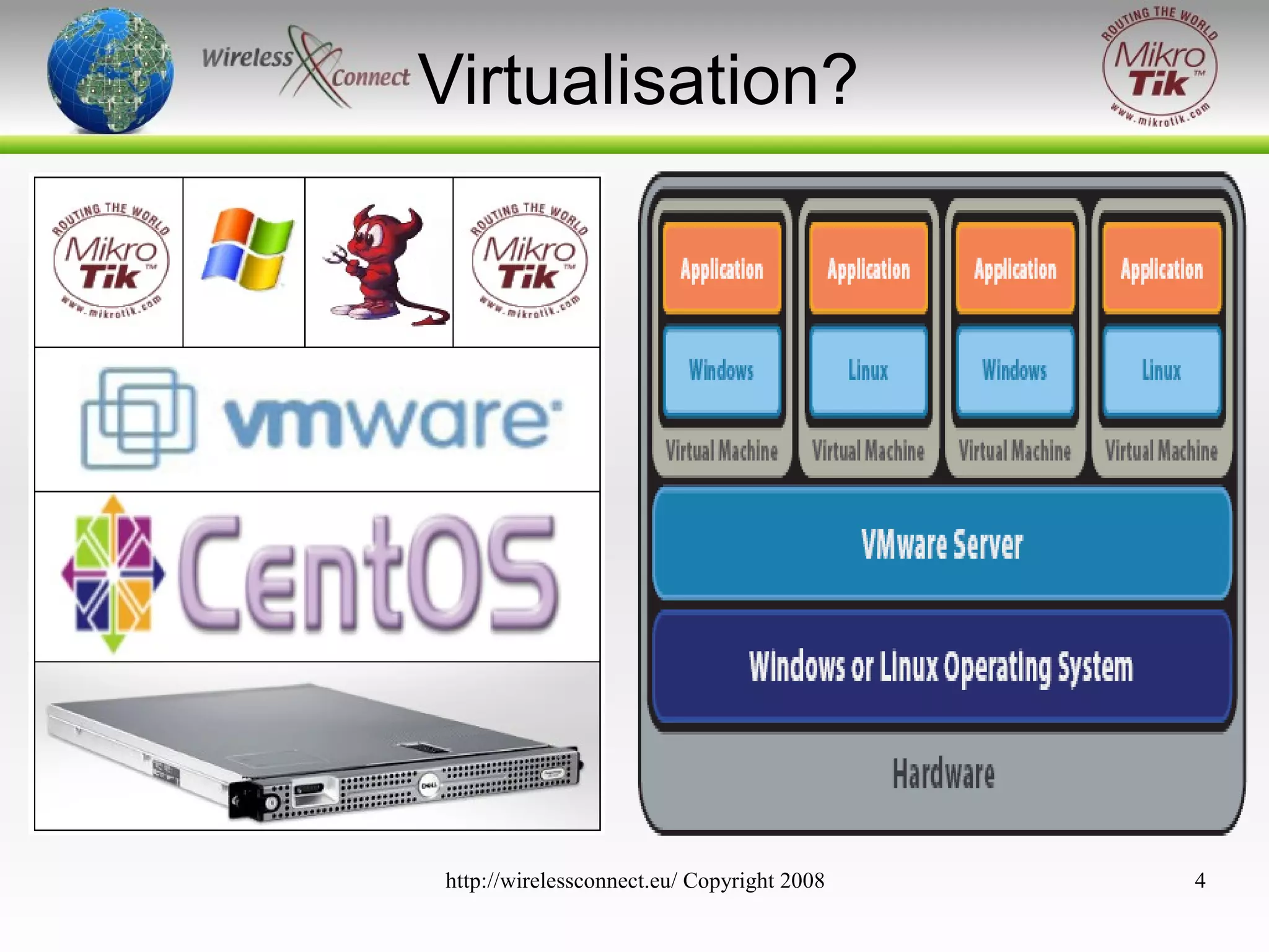
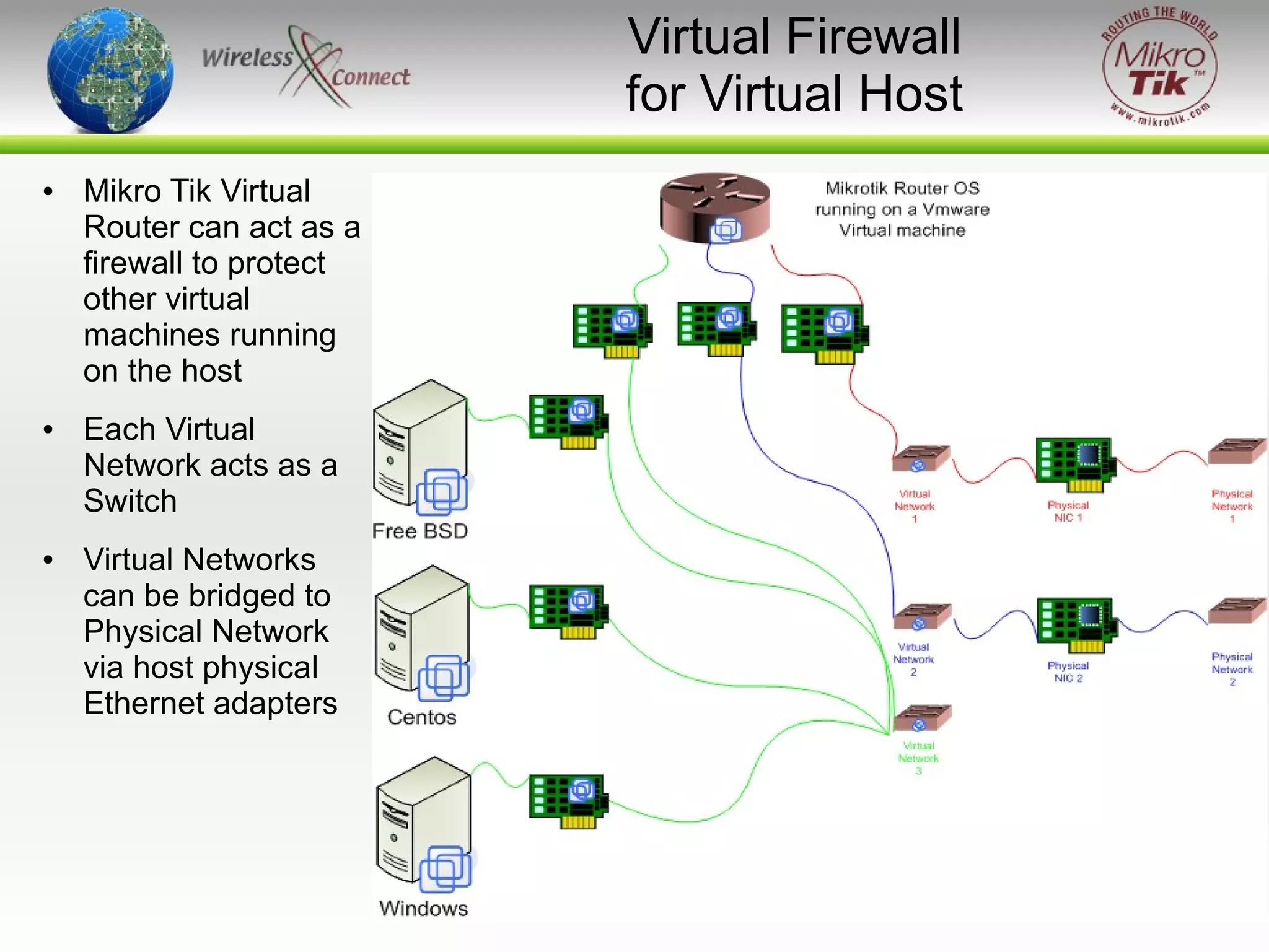
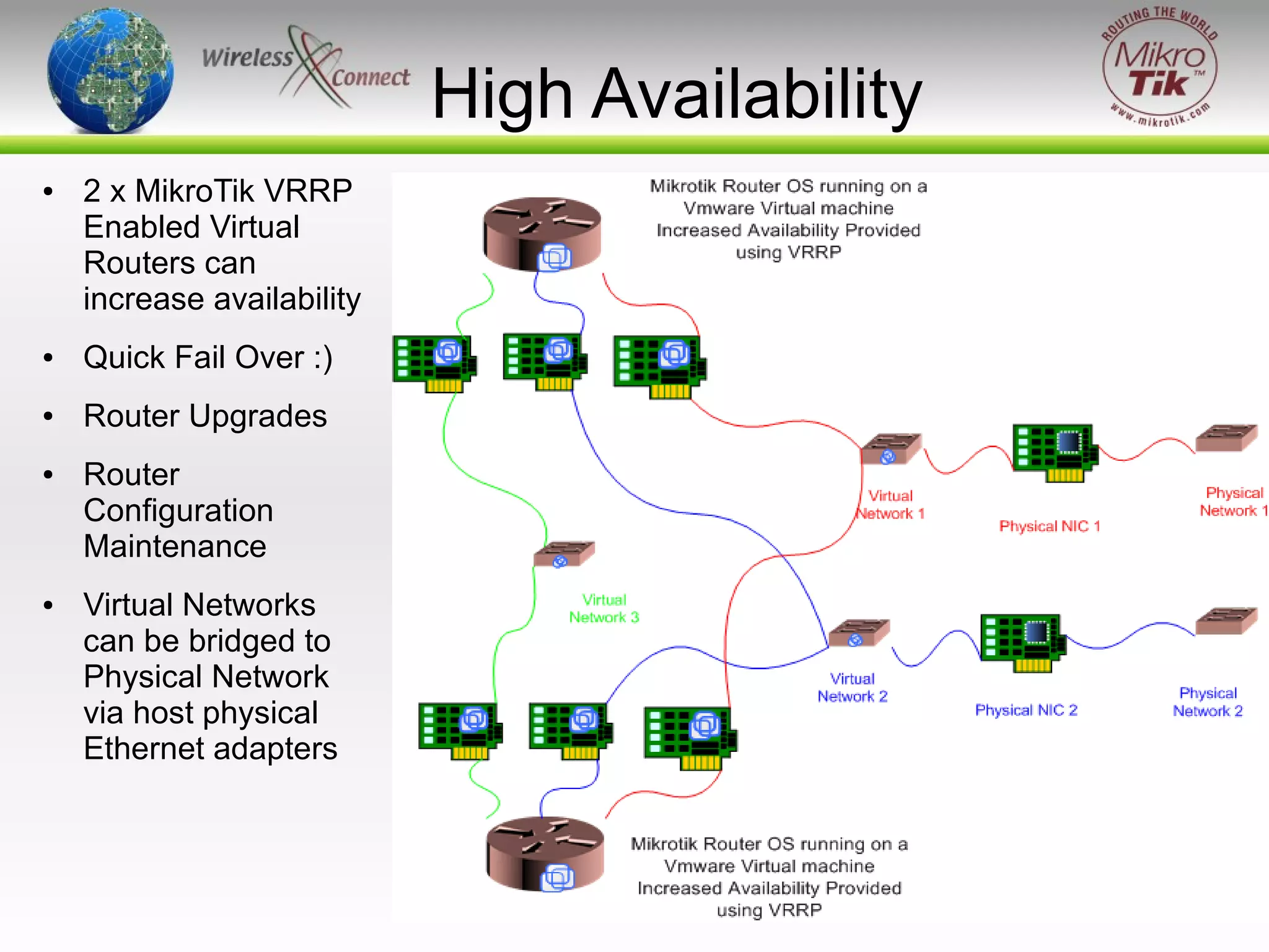
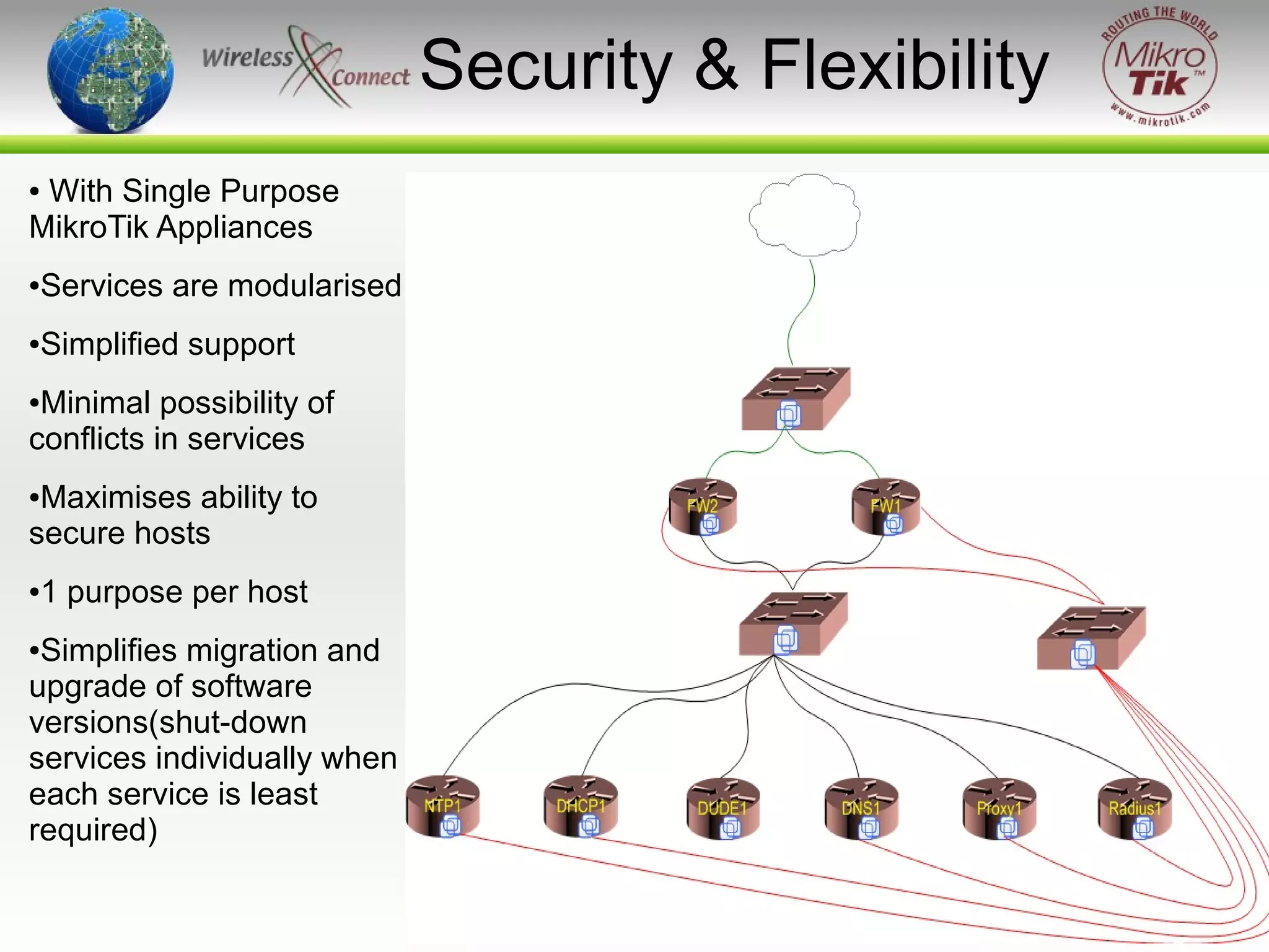
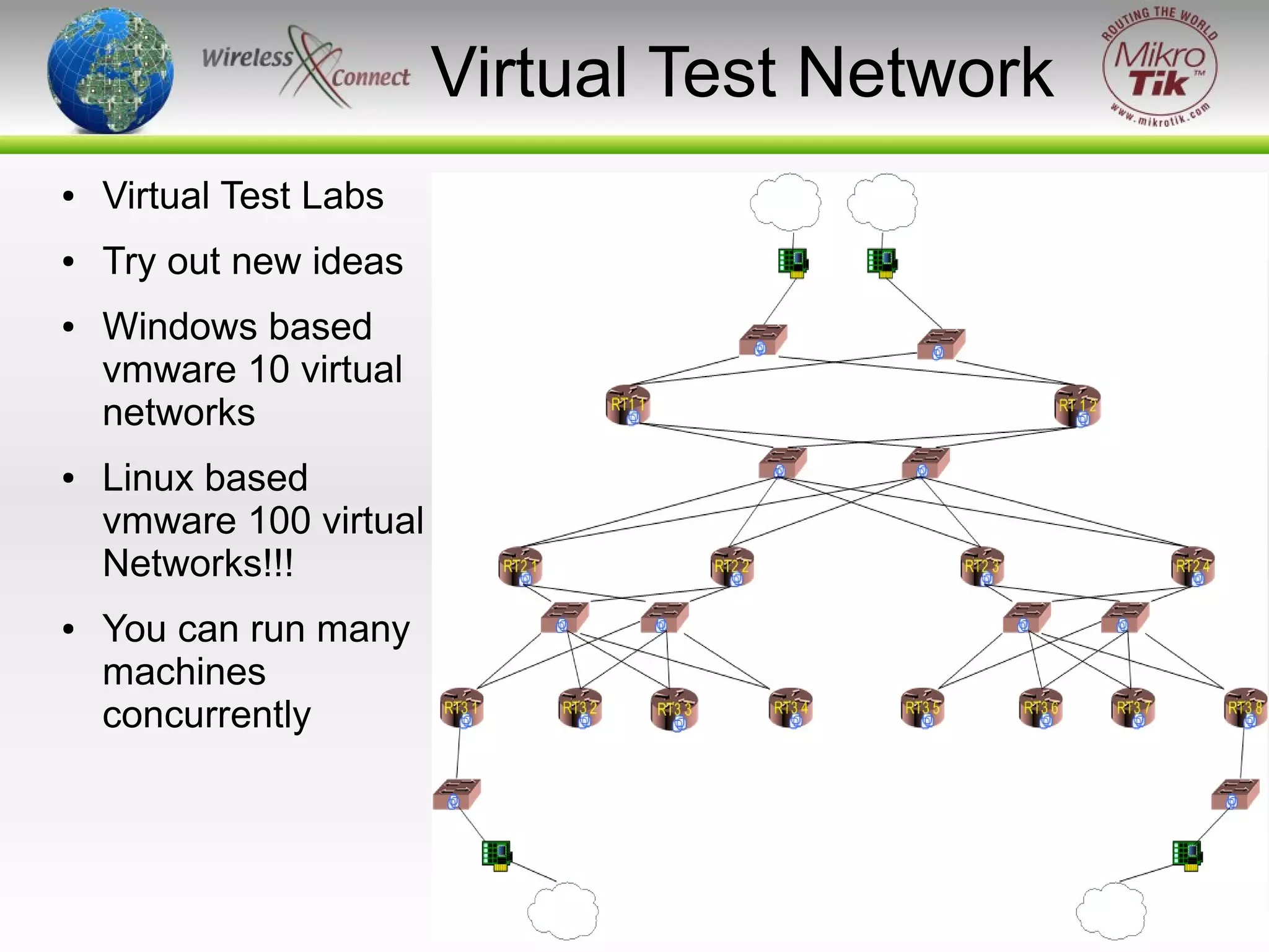
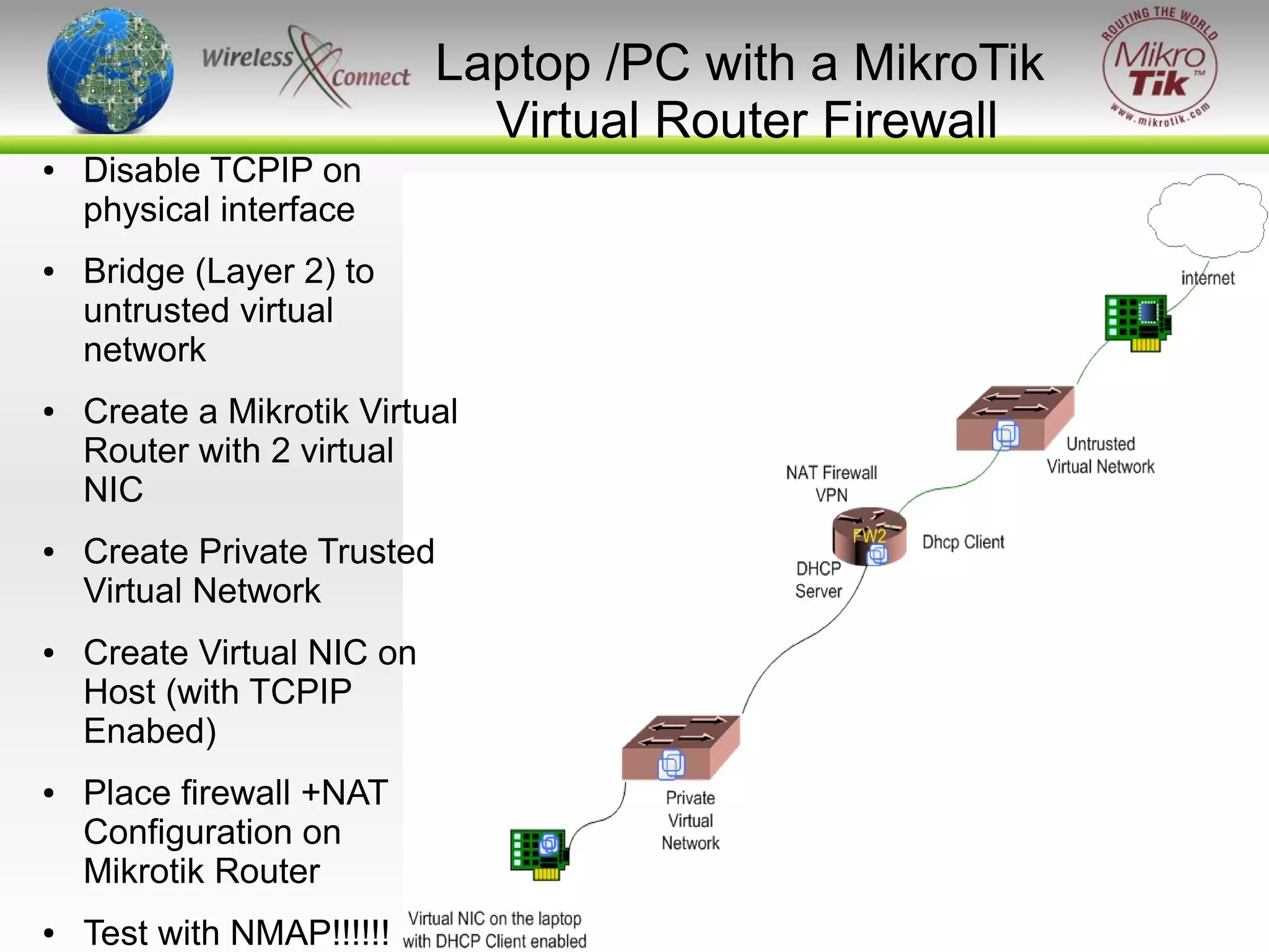
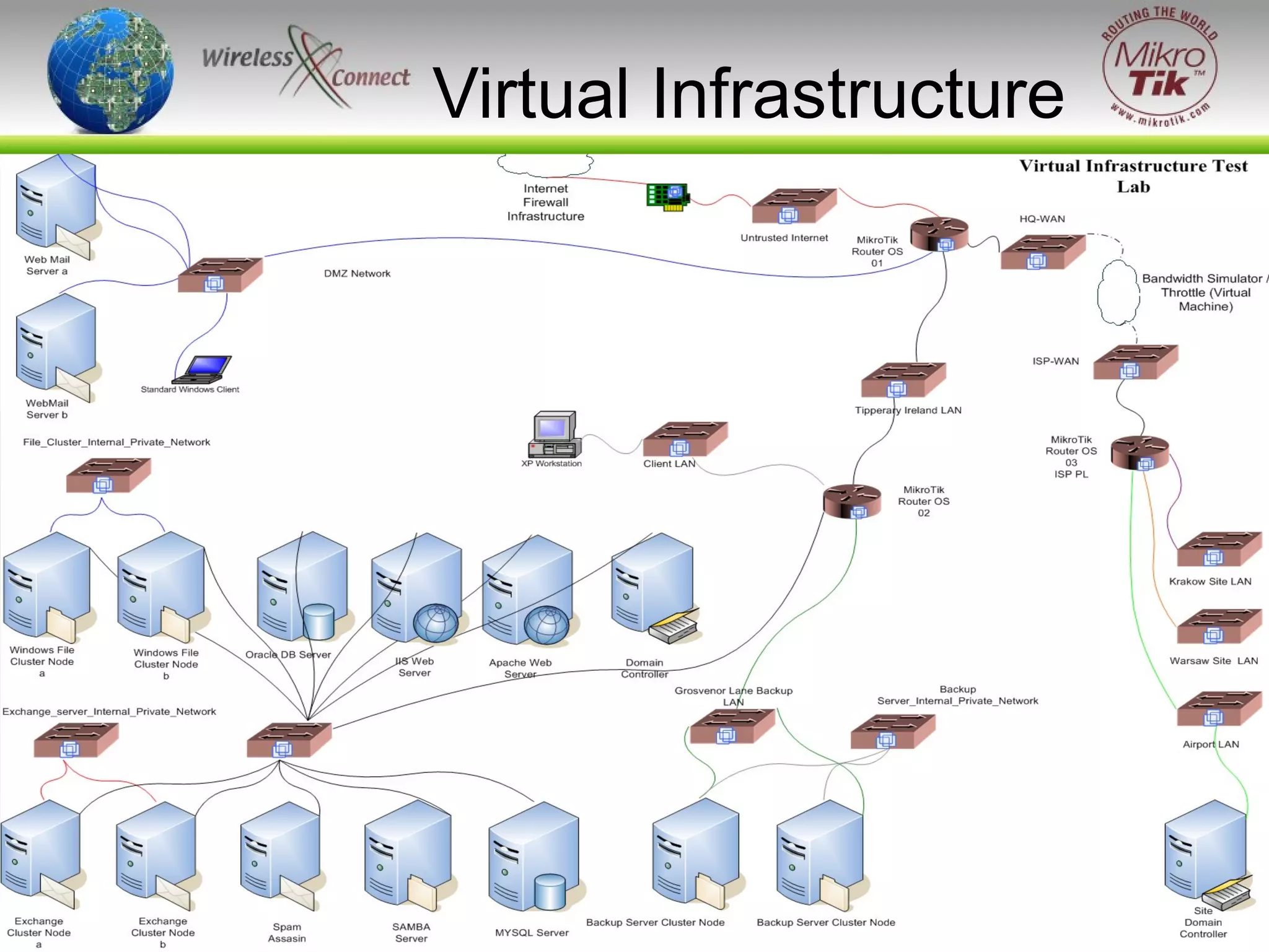
The document discusses virtualizing MikroTik routers. It provides an overview of virtualization and VMWare Server, how to configure virtual machines for RouterOS 2.9 and 3.x, and where virtualization can help or not help. Virtualizing allows MikroTik to run on incompatible hardware, provides flexibility for testing and disaster recovery, and isolates services for increased security. However, virtualization is not always practical and requires sufficient host hardware resources for good performance.