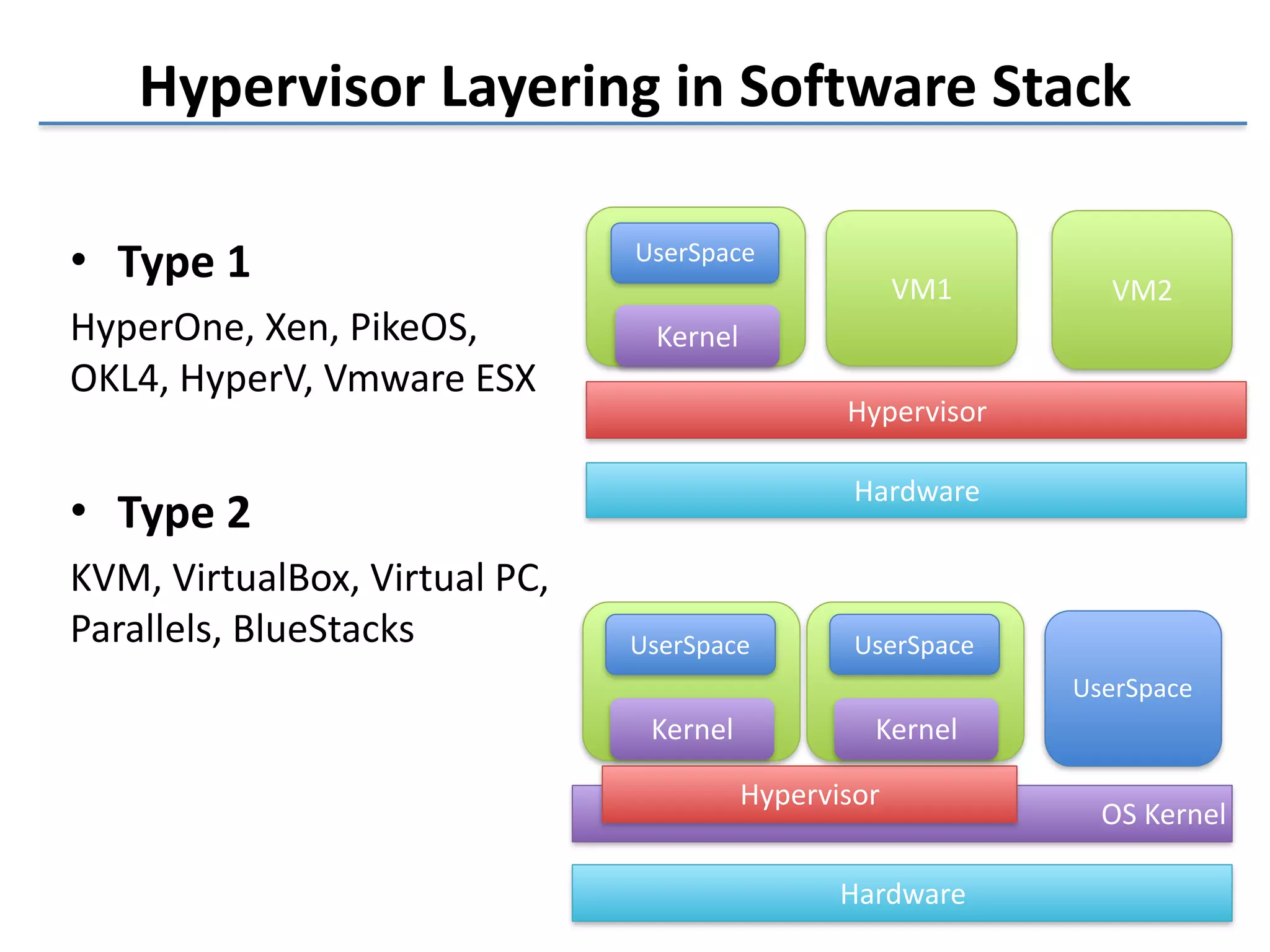
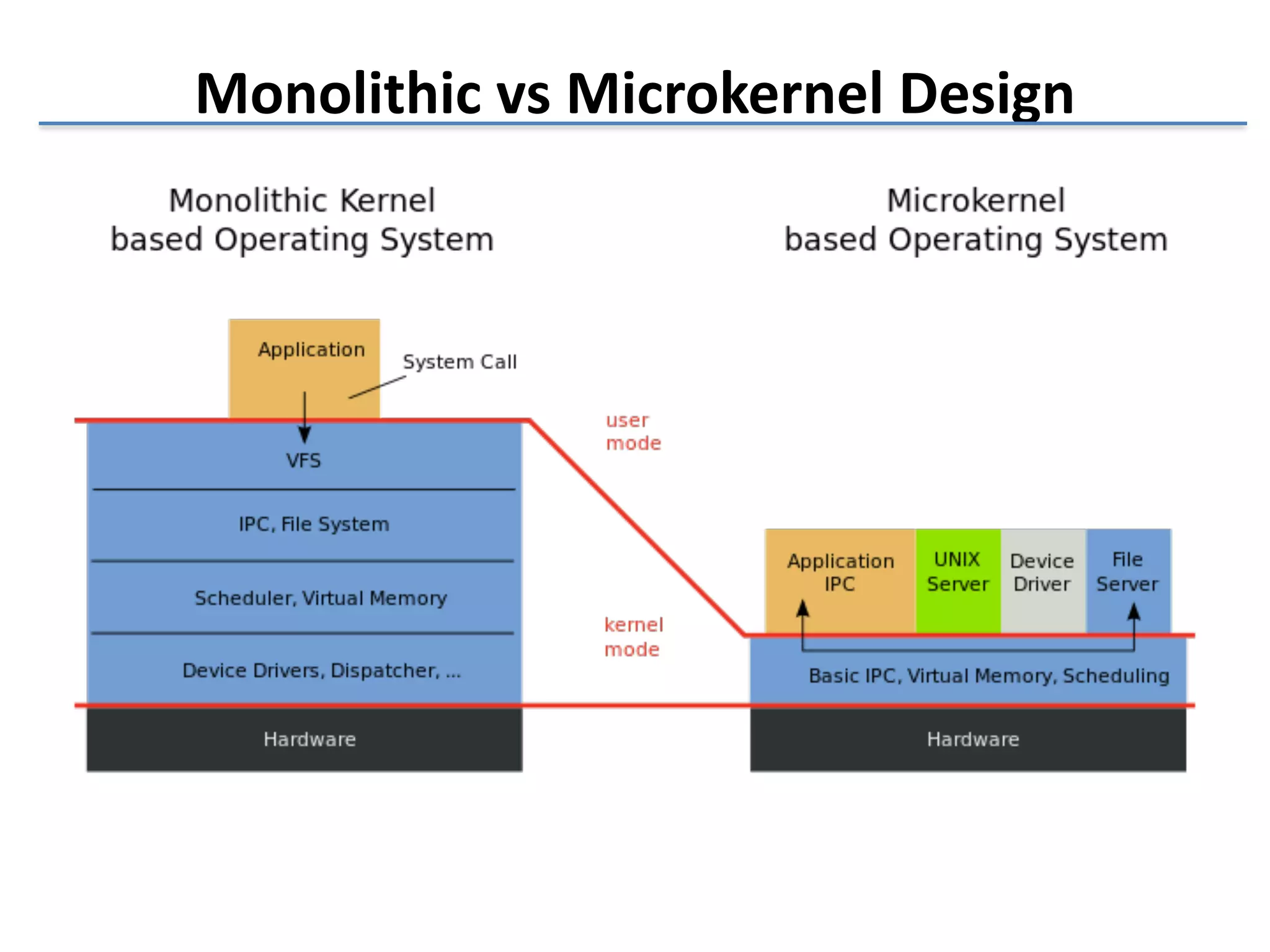
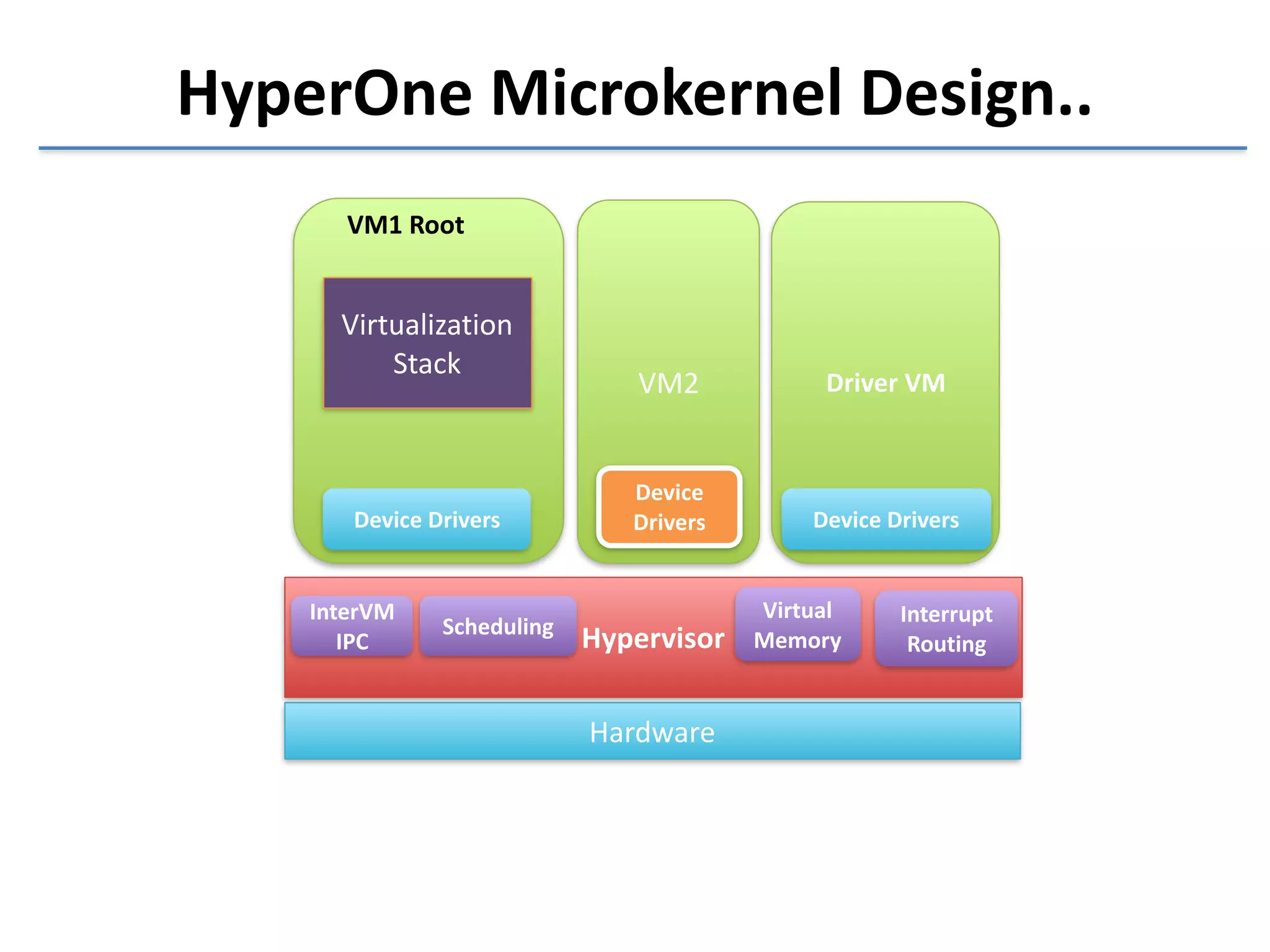
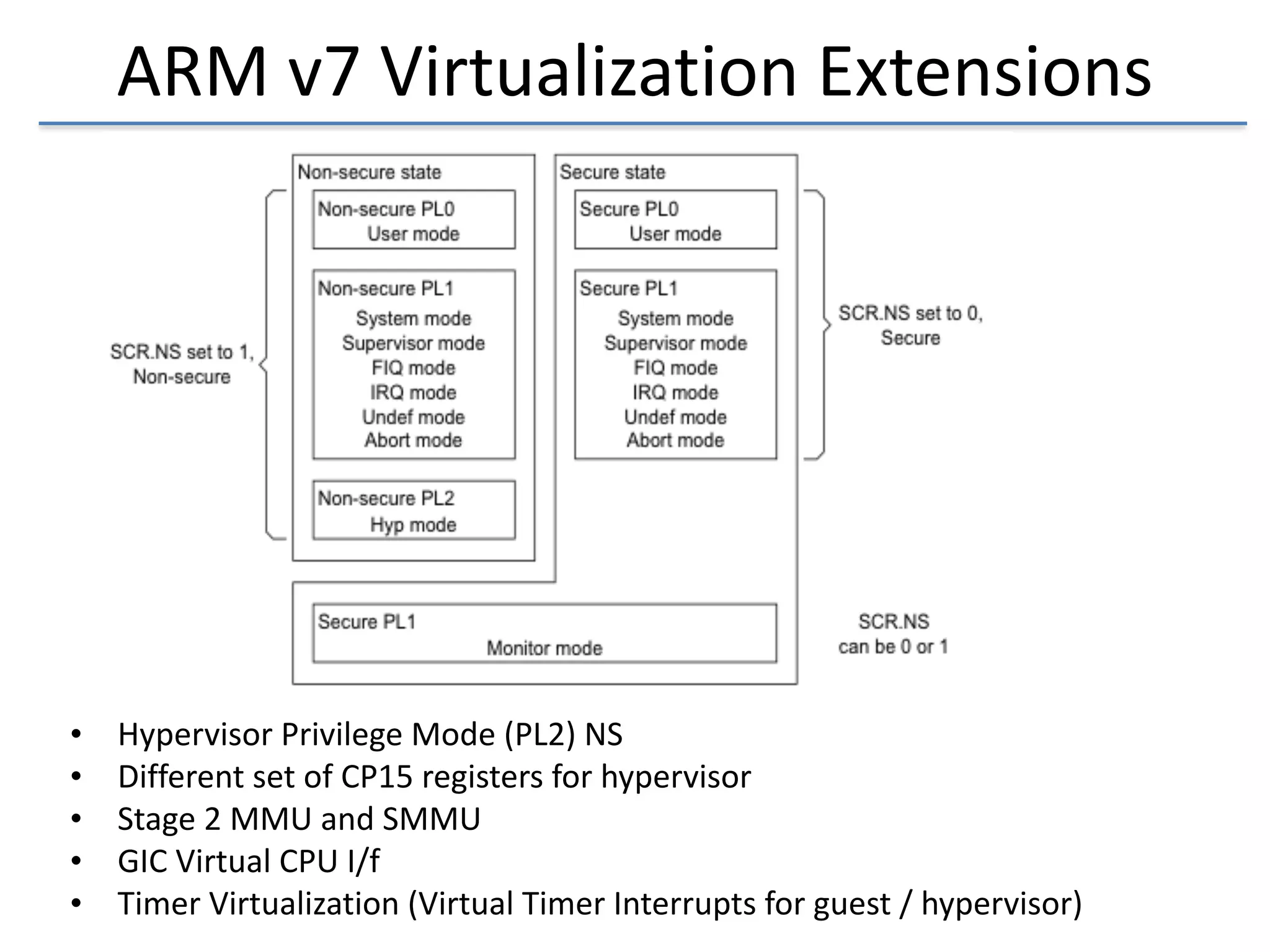
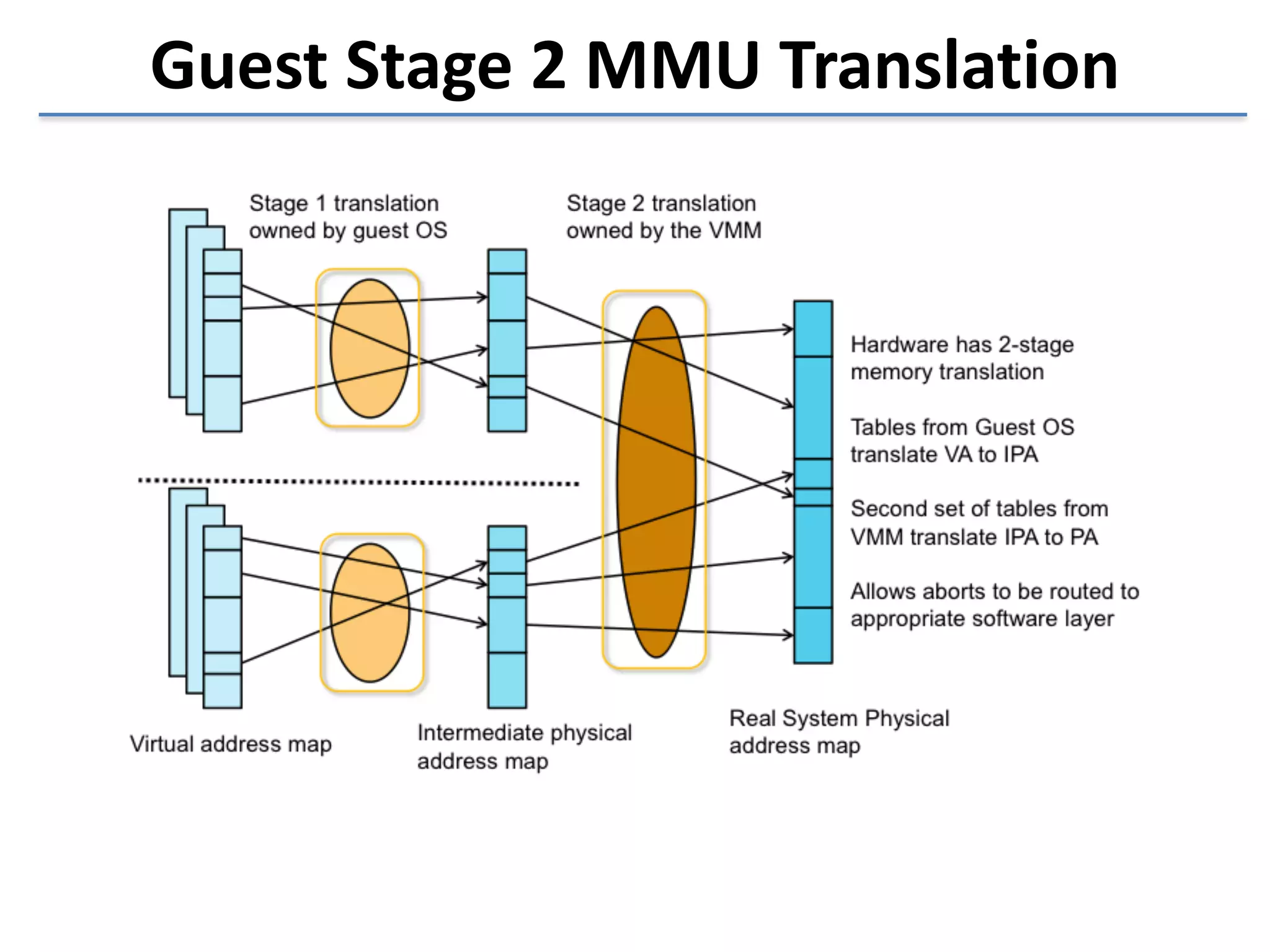
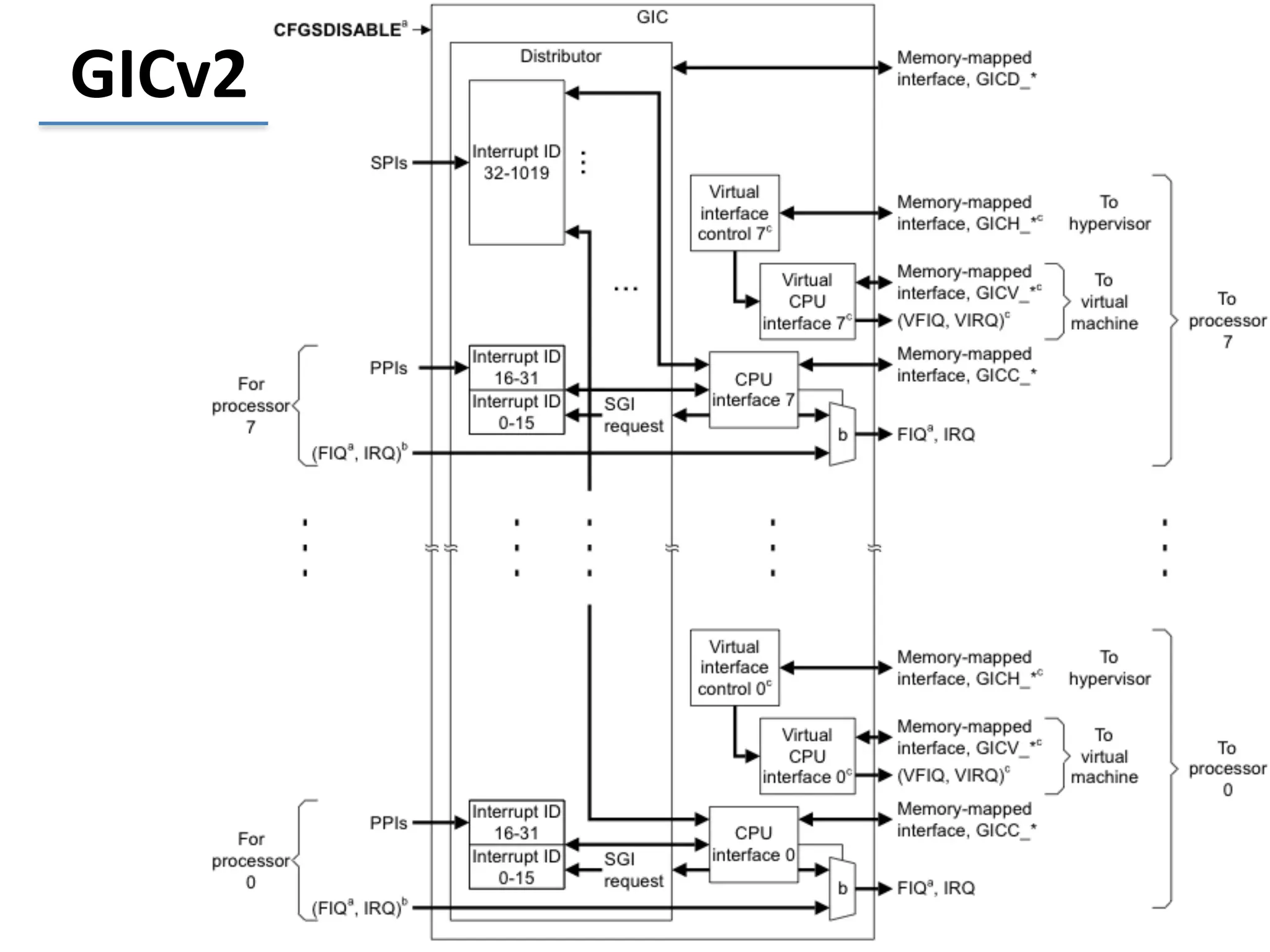
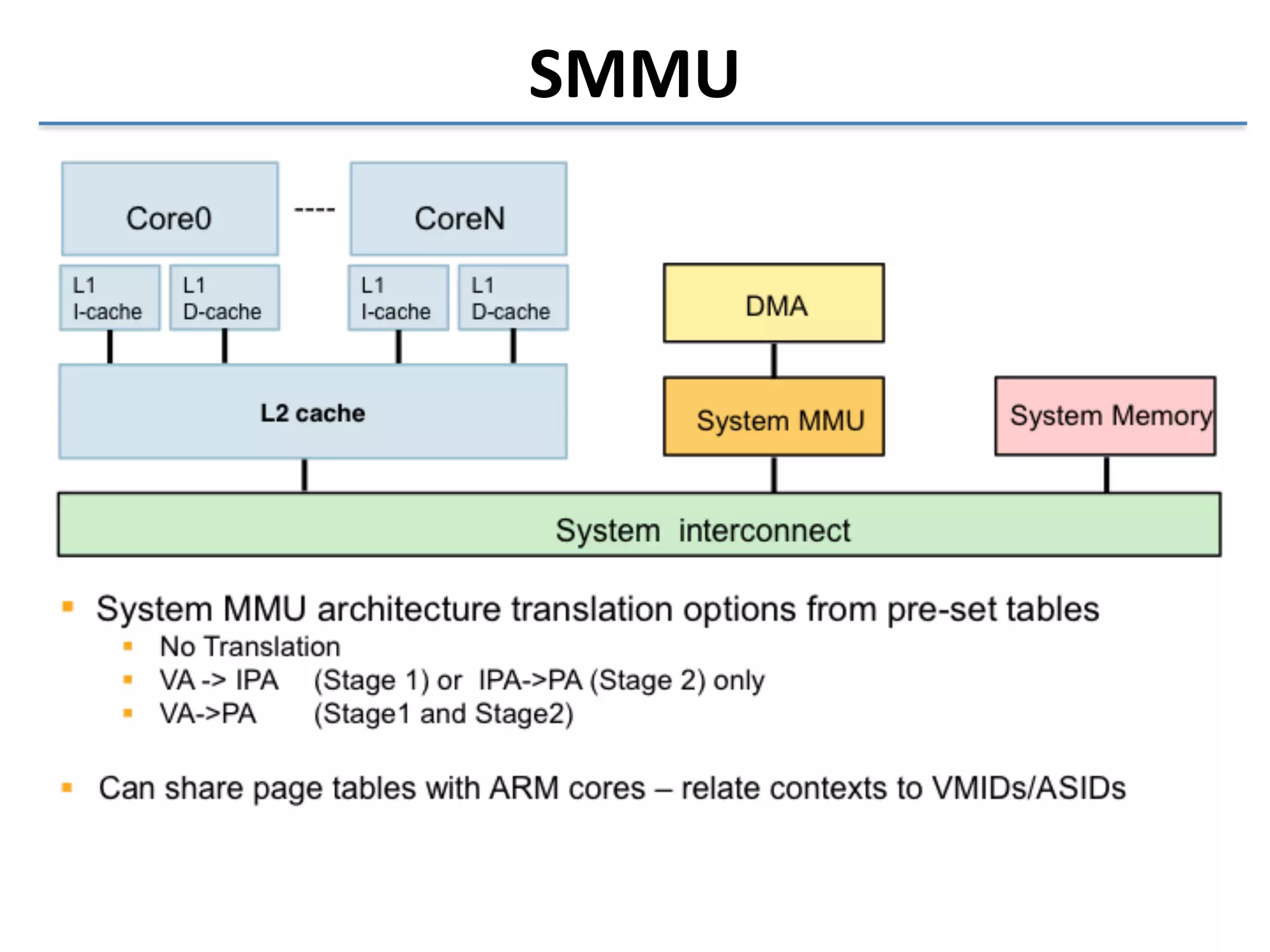
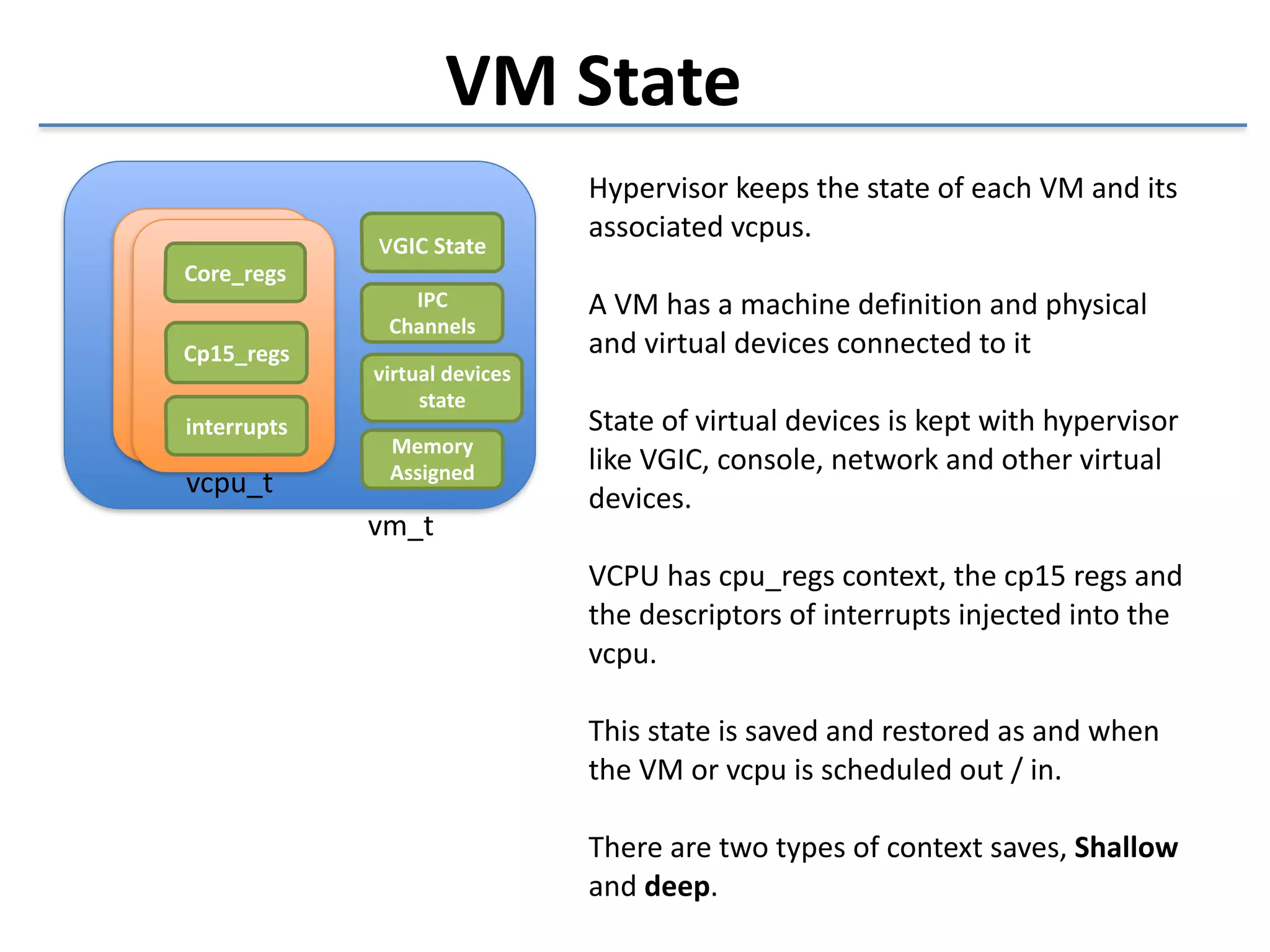
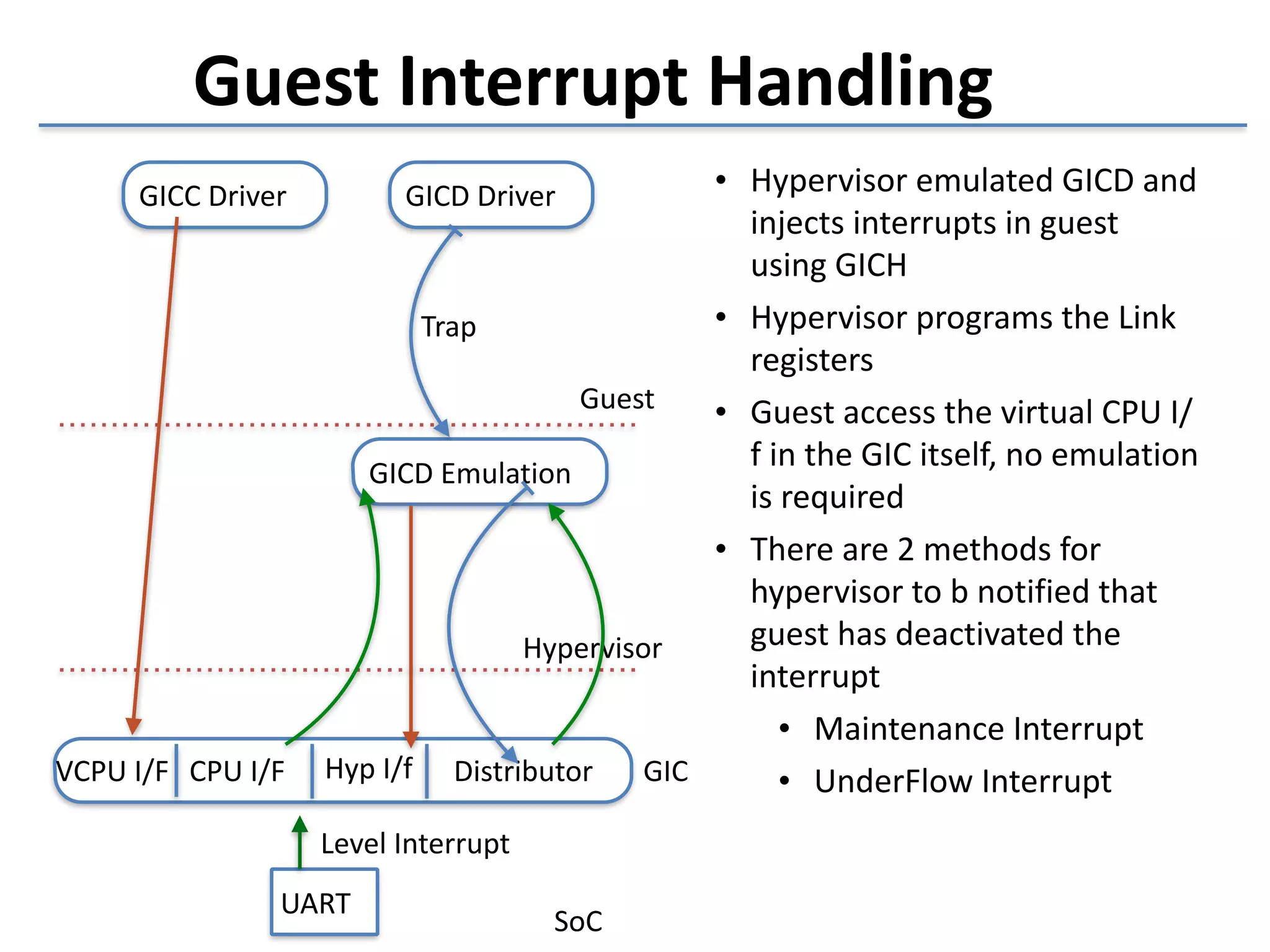
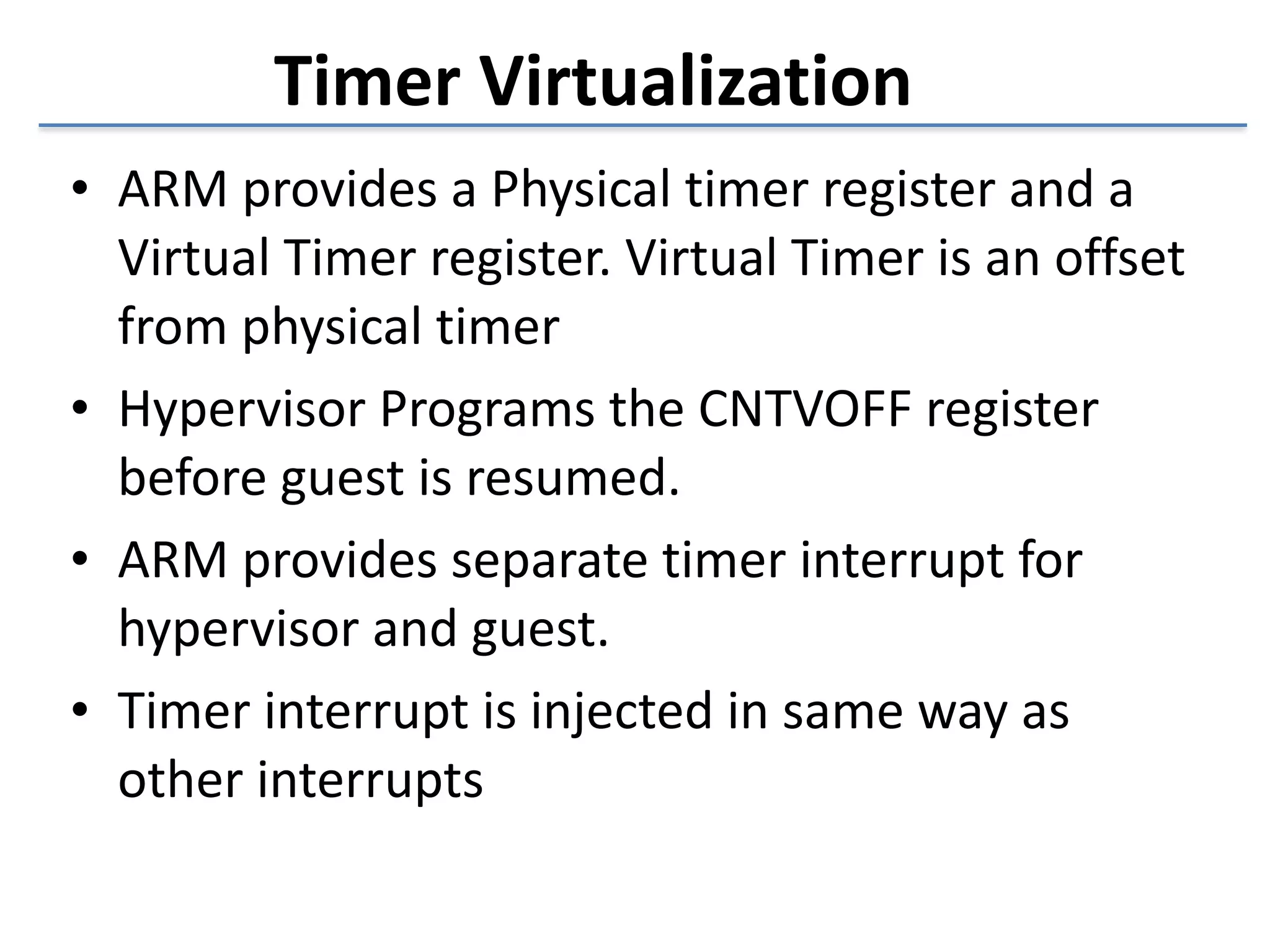
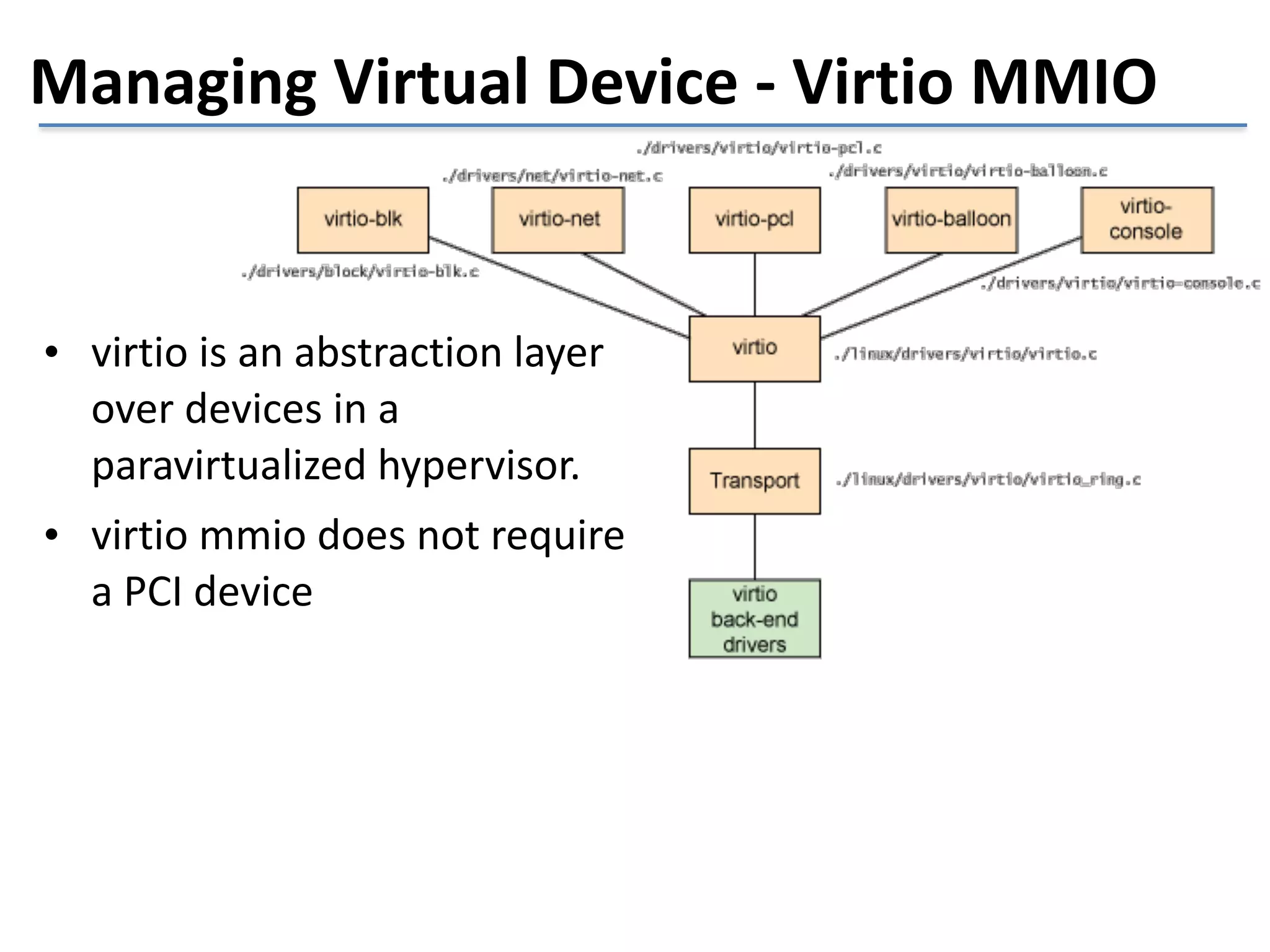
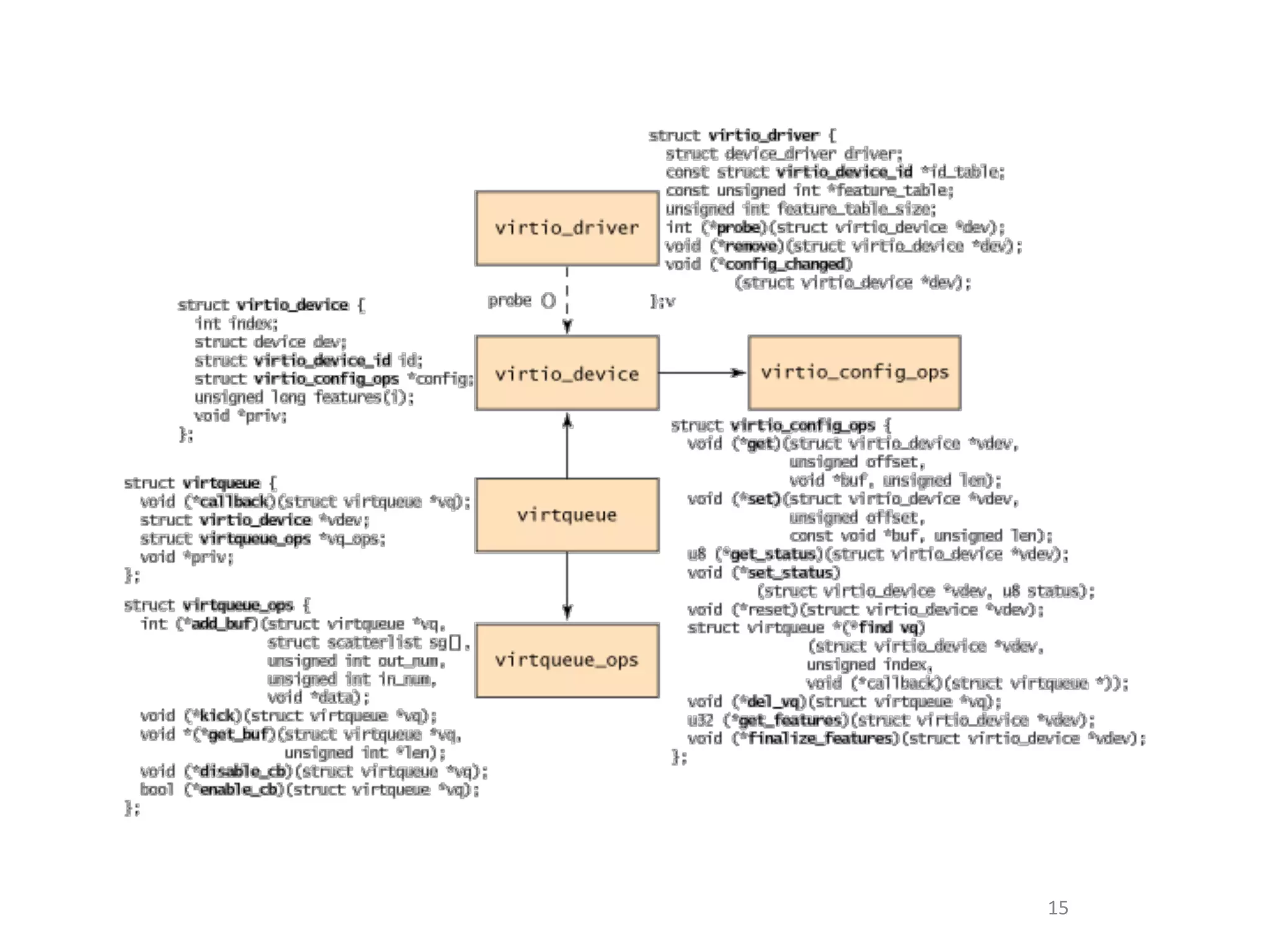
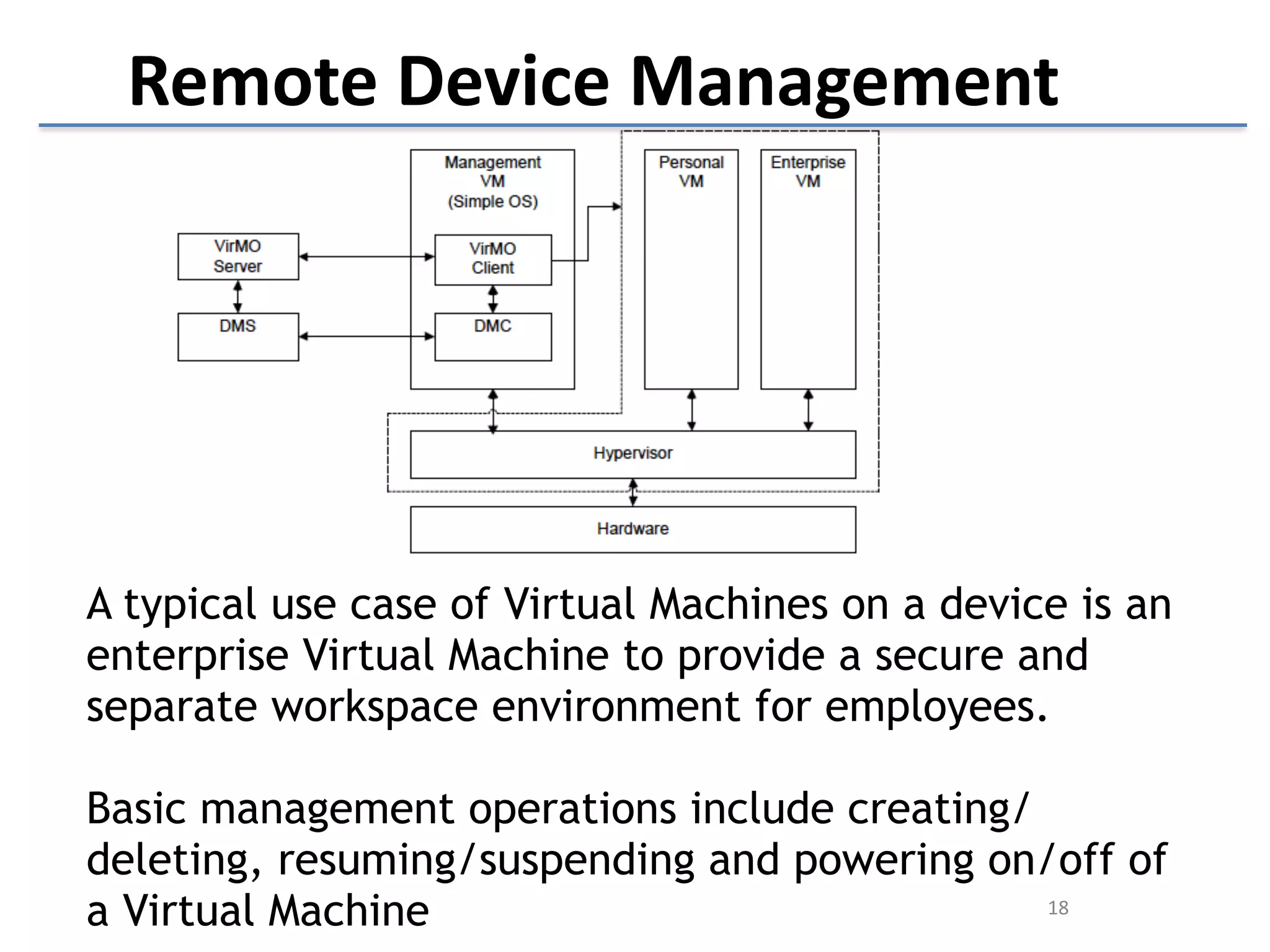
This document discusses the challenges in designing a type 1 hypervisor for ARM v7 virtualization extensions. It covers topics like hypervisor layering in software stack, monolithic vs microkernel design approaches, ARM v7 virtualization features, bare minimal hypervisor design, hypervisor exception handling, guest interrupt handling using GIC, timer virtualization, managing virtual devices using virtio MMIO, guest debugging support, VM management functions like context save/restore and scheduling, and remote device management use cases.