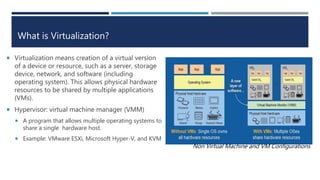
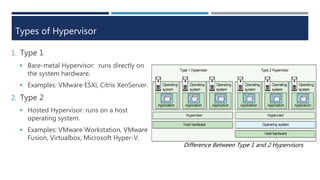
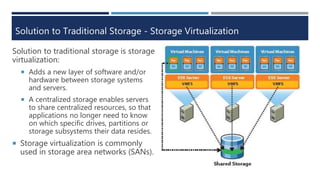
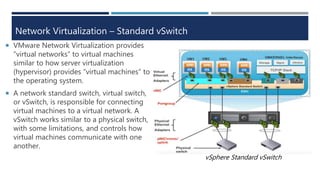
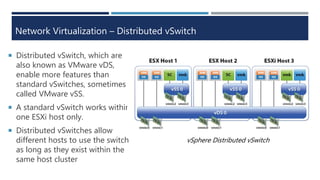
The document explains virtualization, highlighting virtual machines (VMs) as software-based computers that run operating systems and applications. It covers types of hypervisors, server virtualization, storage virtualization, and network virtualization, emphasizing their benefits such as cost reduction, improved efficiency, and business continuity. Additionally, it describes the role of virtualization in cloud computing, enabling scalability and operational efficiency for businesses.