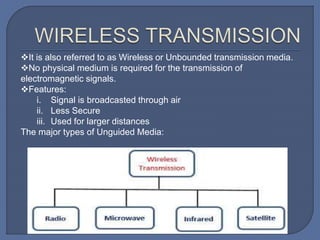
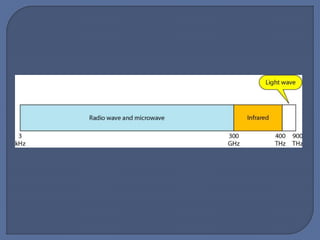
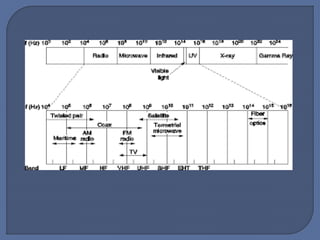
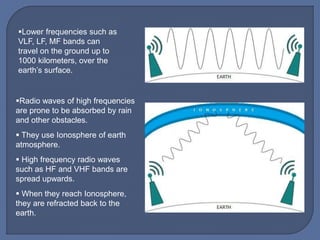
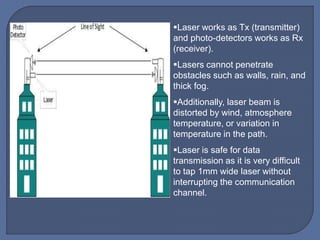
The document discusses unguided media for wireless communication, describing how electromagnetic signals are transmitted without physical links between devices. It covers key types such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, and laser transmission, along with their characteristics, frequency ranges, and typical applications. The material emphasizes factors like signal behavior, security, and environmental influences on transmission quality.