The document discusses heap trees, which are tree-based data structures where all nodes follow a specific ordering. There are two main types: max-heaps, where the root node has the greatest value of its children, and min-heaps, where the root node has the minimum value. Heaps are often stored as arrays for efficient implementation of operations like insertion, deletion, and merging in logarithmic time. Common applications of heaps include priority queues, sorting algorithms, and finding order statistics.


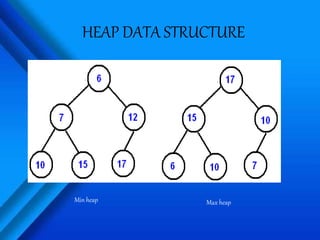
![REPRESENTATION OF A HEAP TREE
Heaps are built
on arrays
Heaps are often stored
as arrays, one node
after the other, like
this:
An array can be used
to simulate a tree in
the following way :
If we are storing one
element at
index I then
Parent :will be stored
at index I/2
Left child : will be
stored at [2∗I]
Right child : will be
stored at [2∗I+1].
Index of root will
be 1 in an array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heaptree-191025100033/85/Heaptree-4-320.jpg)






