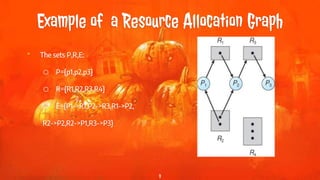
This document discusses deadlock prevention and recovery in computer systems. It begins by defining deadlock and describing the conditions required for deadlock to occur. It then presents a system model and characterizes deadlocks using resource allocation graphs. The document outlines four main methods for handling deadlocks: prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery. It focuses on prevention, describing four different approaches to ensure at least one deadlock condition does not hold: eliminating mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, or circular wait. The document also briefly discusses deadlock detection and two recovery methods: process termination and resource preemption.