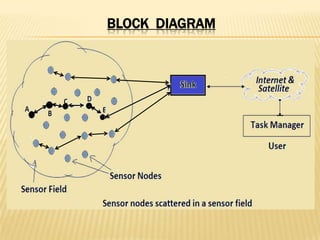
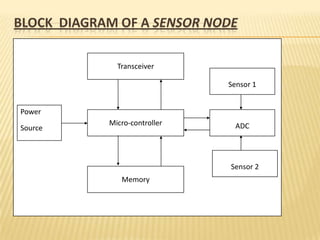
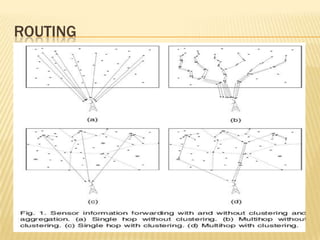
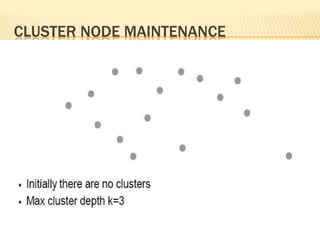
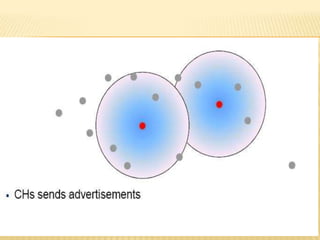
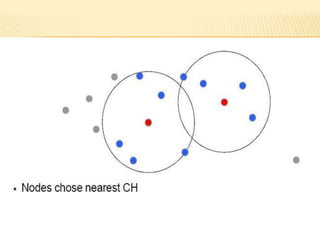
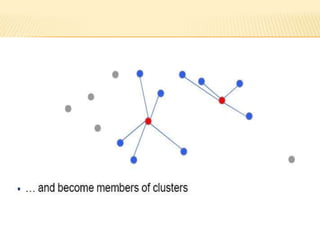
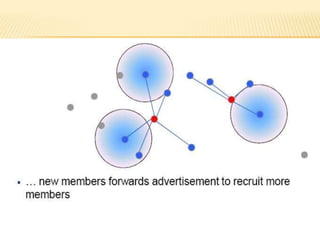
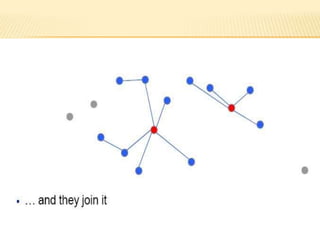
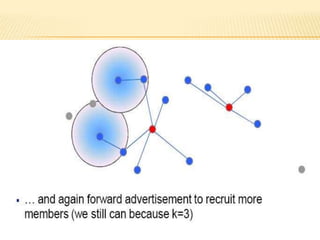
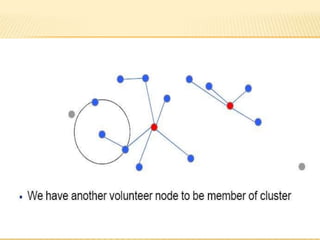
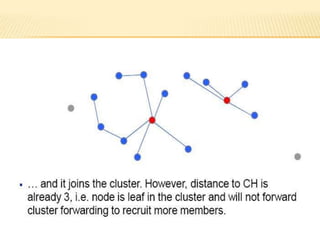
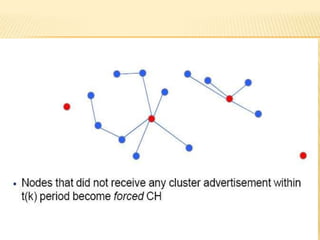
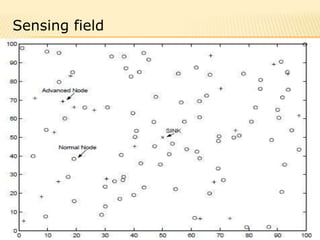
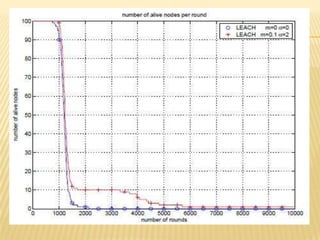
The document discusses the analysis of heterogeneous wireless sensor networks (WSNs) compared to homogeneous ones, focusing on parameters like stability, lifetime, and throughput. It outlines the components of WSNs, including sensor nodes that detect various physical conditions and the role of cluster heads in data management. Additionally, it highlights various application domains for WSNs, such as military, medical, industrial, and environmental monitoring.