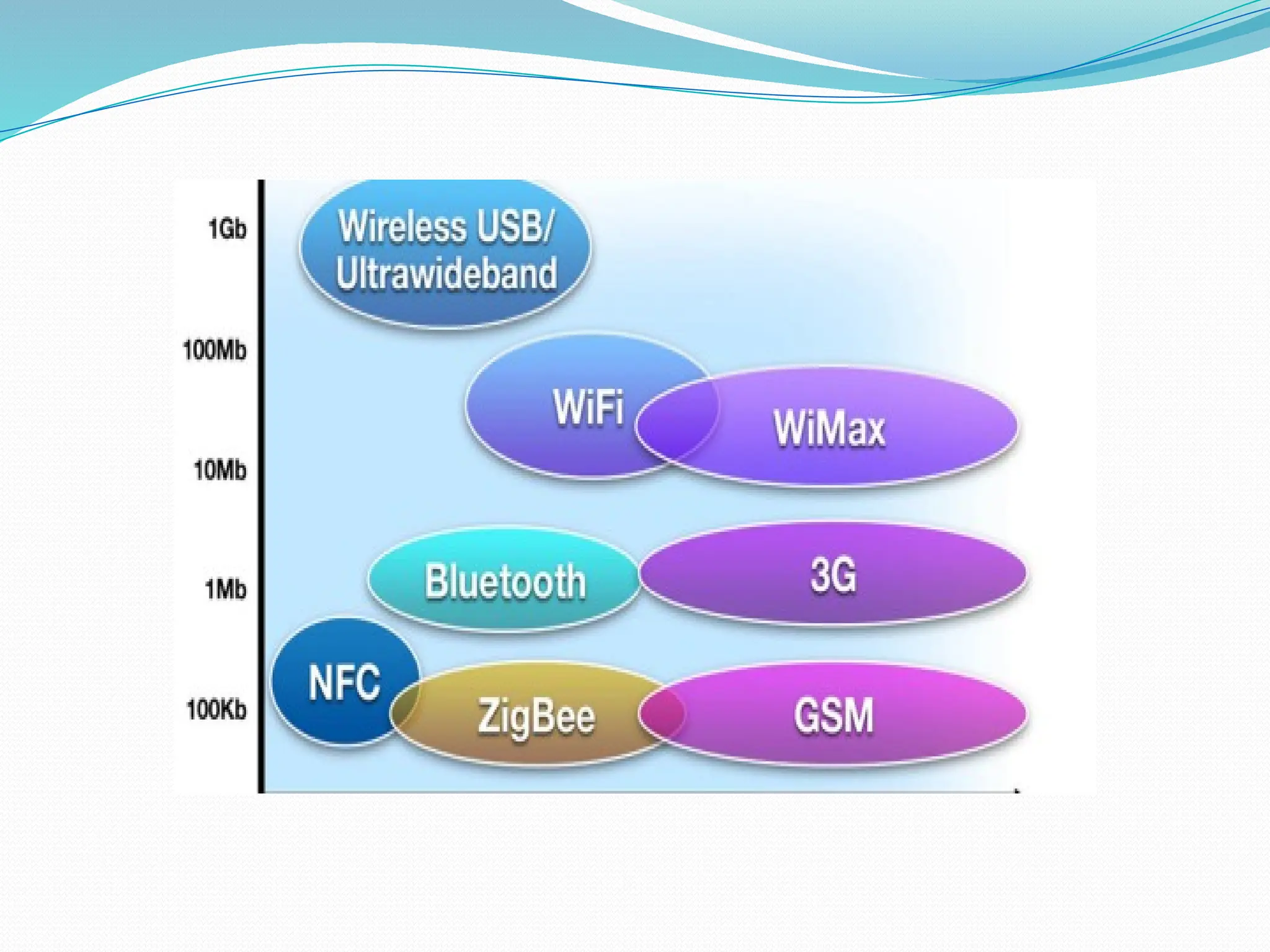
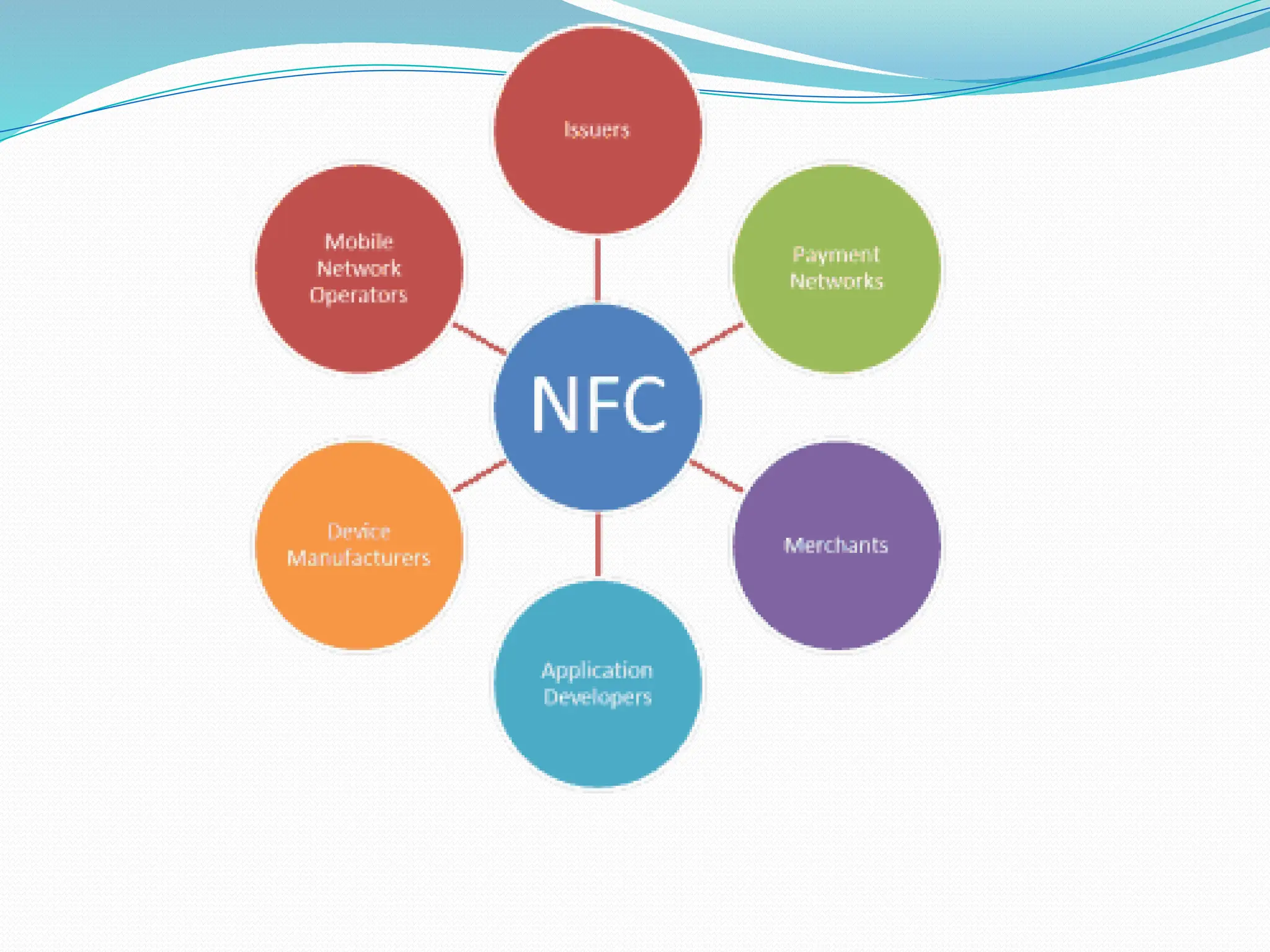
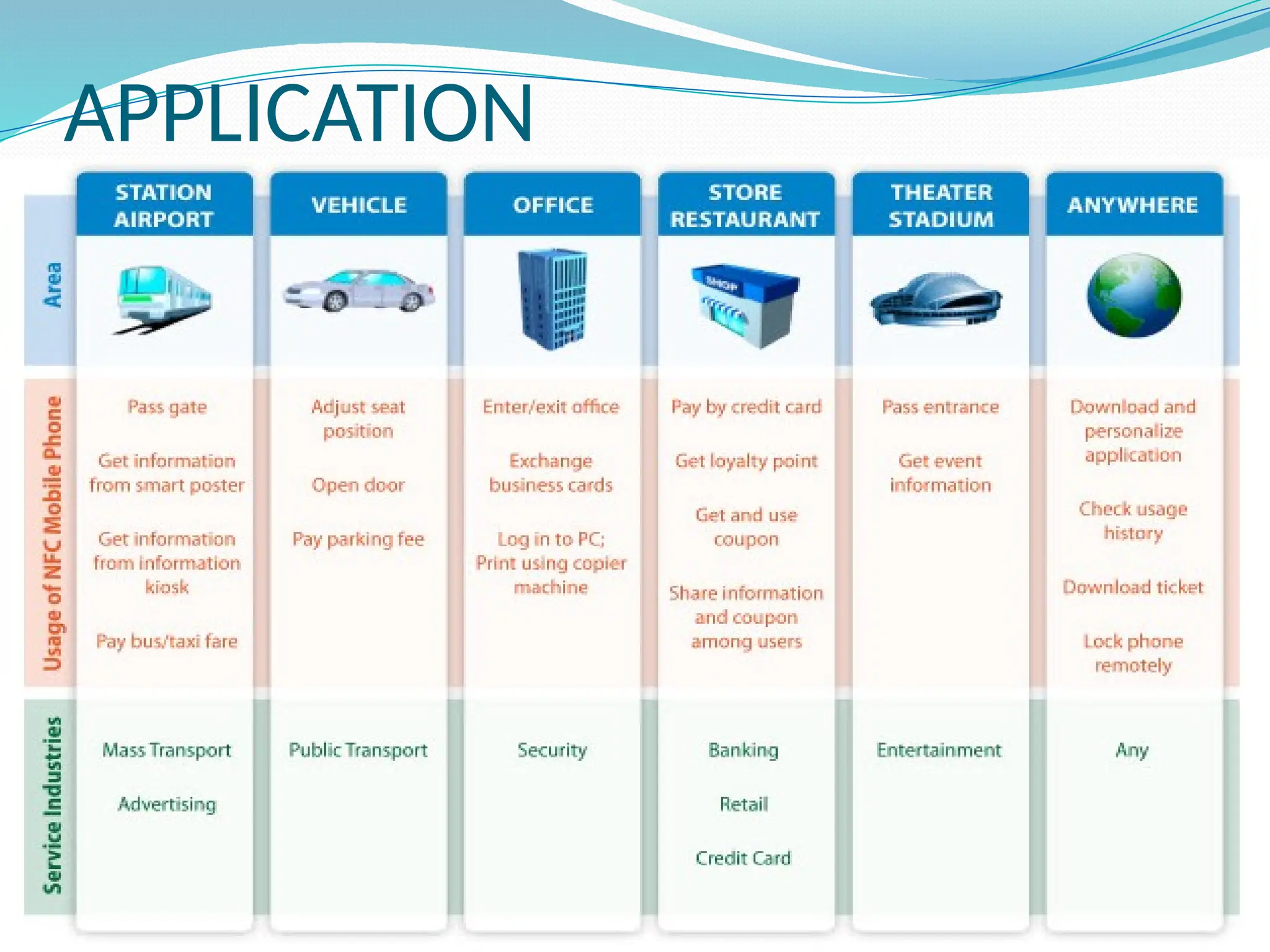
The document provides an overview of Near Field Communication (NFC), a short-range wireless communication technology primarily aimed at mobile devices. It explains the operation, features, advantages, and disadvantages of NFC, emphasizing its ability for secure two-way data exchange using inductive coupling. Applications of NFC include simplified transactions and data sharing, although it has limitations such as compatibility issues and higher device costs.